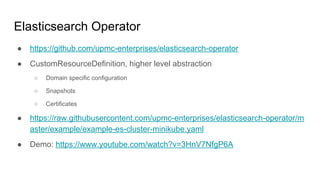
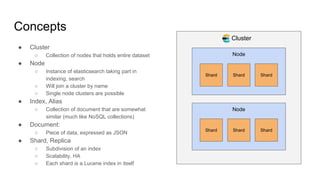
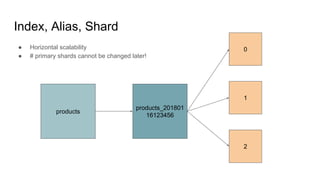
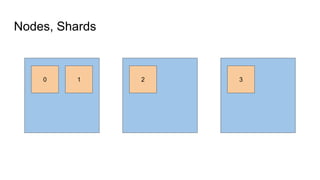
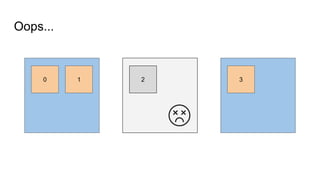
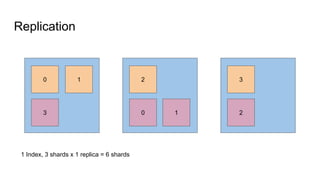
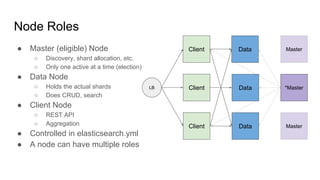
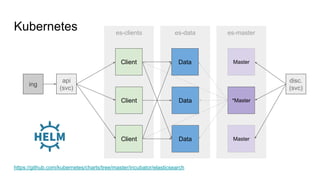
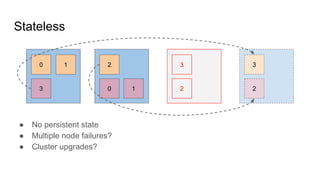
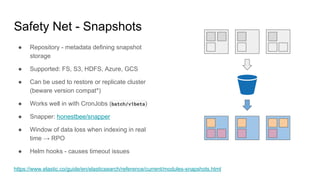
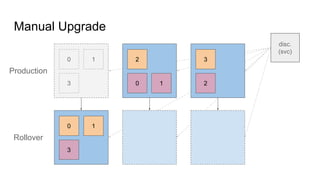
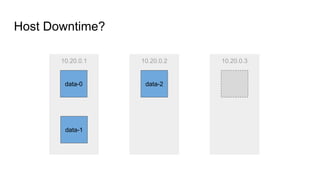
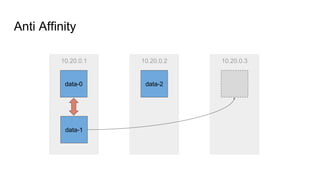
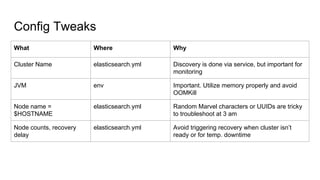
The document provides a comprehensive overview of deploying and managing Elasticsearch on Kubernetes, detailing key concepts such as nodes, clusters, shards, and indexing. It discusses the architecture, configuration, and role of different node types, addressing operational considerations like resource limits, monitoring, and troubleshooting. Additionally, it highlights the importance of proper data management and safety measures, such as snapshots, during cluster upgrades and failures.

![Elasticsearch [is] a distributed, multitenant-capable full-text search engine with
an HTTP web interface and schema-free JSON documents [based on Lucene]
(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elasticsearch)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elasticsearchonkube-180117045248/85/Elasticsearch-on-Kubernetes-2-320.jpg)






![apiVersion: apps/v1beta1
kind: StatefulSet
# ...
spec:
serviceName: {{ template
"elasticsearch.data-service" . }}
# ...
podManagementPolicy: Parallel # quicker
updateStrategy:
type: RollingUpdate # default: onDelete
template:
# Pod spec, like deployment
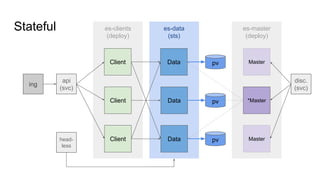
Statefulset vs. Deployment
# ...
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: "es-staging-pvc"
labels:
# ...
spec:
accessModes: [ReadWriteOnce]
storageClassName: ”gp2”
resources:
requests:
storage: ”35Gi”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elasticsearchonkube-180117045248/85/Elasticsearch-on-Kubernetes-20-320.jpg)


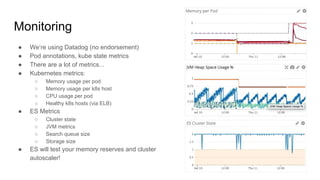

![Example: JVM heap usage
curl $ES_URL/_nodes/<node_name> | jq '.nodes[].jvm.mem'
{
"heap_init_in_bytes": 1073741824, # 1 GB
"heap_max_in_bytes": 1038876672, # ~1 GB
"non_heap_init_in_bytes": 2555904,
"non_heap_max_in_bytes": 0,
"direct_max_in_bytes": 1038876672
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elasticsearchonkube-180117045248/85/Elasticsearch-on-Kubernetes-29-320.jpg)