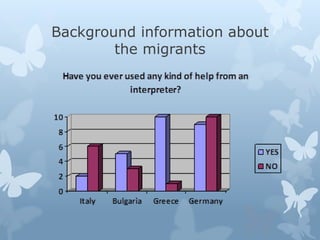
This document summarizes the findings of a needs analysis conducted in 5 countries to assess the state of language interpreting services. The analysis examined the certification process for interpreters, availability of interpreters in different areas, and training opportunities. It found that while universities offer translation and interpreting courses, none specialize in the immigration field. It also found that certification processes varied by country, and that stakeholders saw a need for more qualified interpreters and specialized training programs to address language barriers faced by migrants. The main conclusion was that interpreting requires not just linguistic skills but also strong human skills to best serve migrant communities.