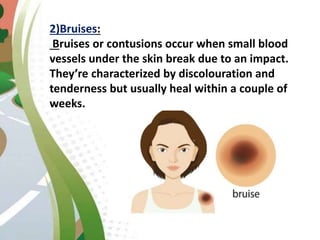
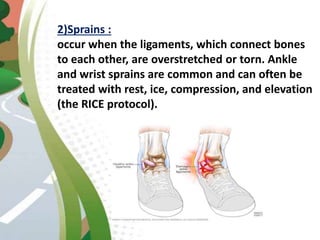
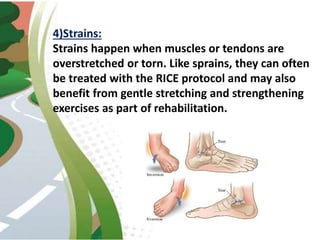
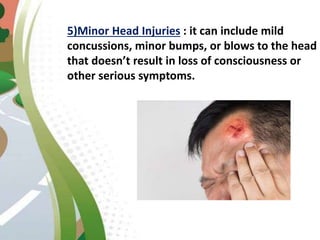
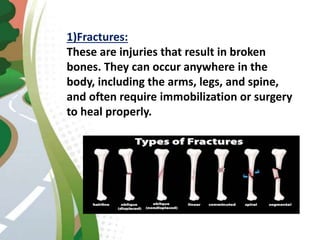
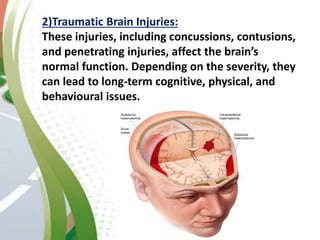
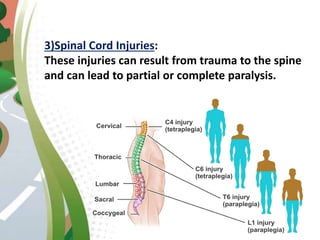
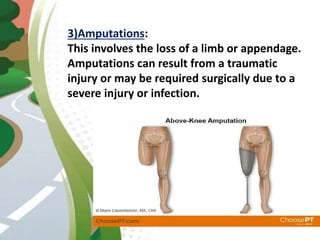
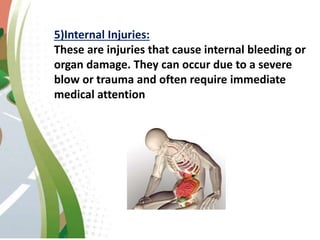
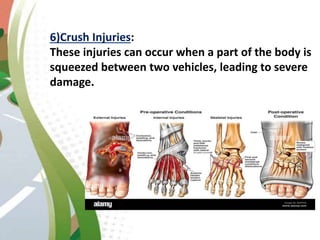
Road traffic accidents are a major public health issue, causing over 1 million deaths annually. Minor injuries include cuts, scrapes, bruises, and minor head injuries which typically heal quickly with first aid. Major injuries such as fractures, traumatic brain injuries, and amputations require immediate medical attention and may cause long-term damage. Reckless behaviors like speeding, drunk driving, and distracted driving are leading causes of accidents that can be prevented through adherence to safety protocols. Proper first aid including clearing airways, restoring breathing, and stopping bleeding can stabilize victims until emergency support arrives.