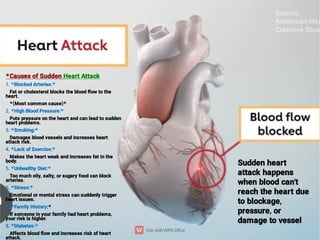
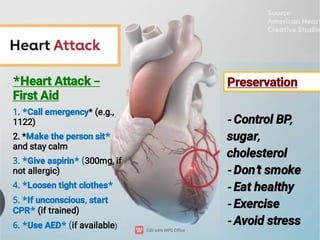
First Aid
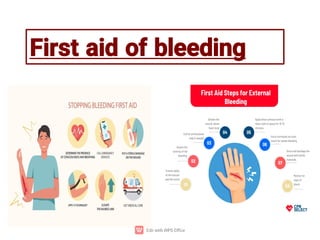
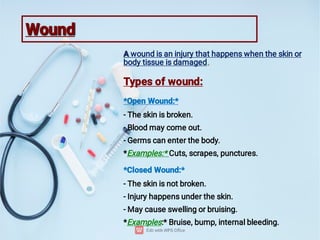
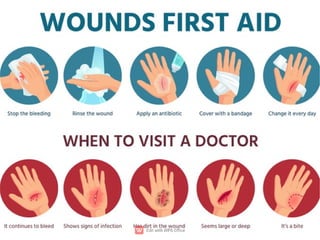
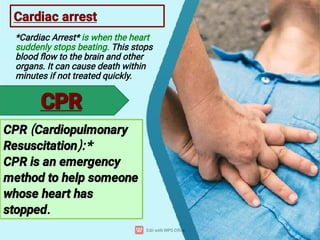
First aid is the immediate help or treatment given to a person who is injured or suddenly becomes ill before professional medical help is available. It includes simple techniques like stopping bleeding, treating burns, giving CPR, or helping someone who is choking. The main aims of first aid are to save life, prevent the condition from getting worse, and promote recovery. Knowing basic first aid can make a big difference in emergencies.