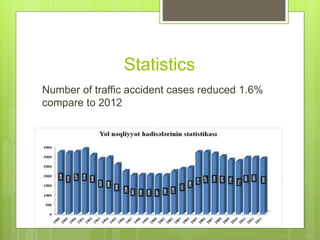
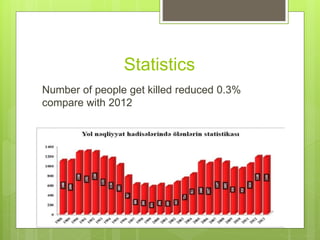
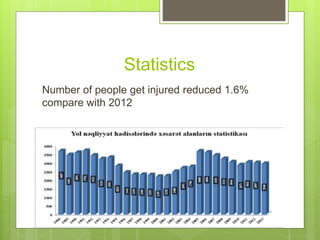
In 2013, Azerbaijan reported 2,846 traffic accidents resulting in 1,164 fatalities and 2,948 injuries, with a decrease in accidents, deaths, and injuries compared to 2012. Major causes of these accidents include driver rule violations, speeding, and distracted driving, with pedestrian involvement accounting for a significant portion of incidents. Preventive measures emphasize avoiding distractions, adhering to speed limits, and maintaining vehicle safety to enhance road safety.