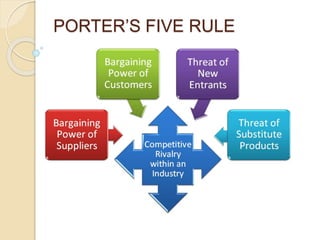
India, with a 7517 km coastline, is the fifth largest producer of wind energy, primarily in states like Tamil Nadu and Gujarat. The wind energy sector is attractive due to short construction periods and low operational costs, but faces competition from other renewable sources and requires substantial investment. Regulatory support and technological advancements further enhance the industry's potential while promoting green energy solutions and job creation.