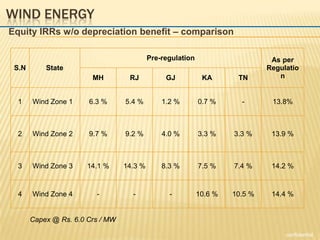
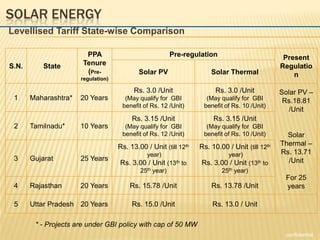
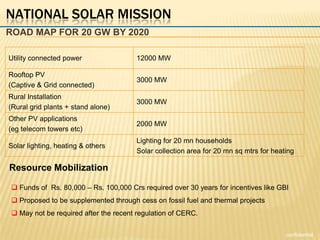
The document outlines new tariff guidelines and regulatory frameworks by the Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC) to enhance renewable energy in India, covering wind and solar energy. It details eligibility criteria, operational frameworks, and the Renewable Energy Certificate (REC) mechanism, aiming for significant solar generation capacity increases by 2020, 2030, and 2050. The National Solar Mission sets ambitious renewable energy targets while ensuring regulatory clarity and financial principles for tariff determination.