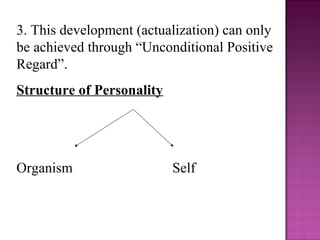
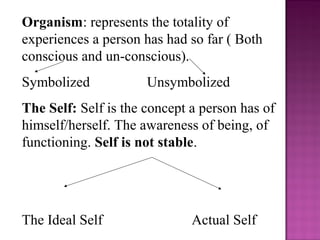
Carl Rogers was an American psychologist who developed humanistic psychology and the person-centered approach to therapy. He was born in 1902 in Illinois and had a lonely childhood. Rogers believed that all humans have an innate drive for self-actualization and that unconditional positive regard is necessary for development. He saw the self as constantly evolving based on experiences and proposed that congruence between the ideal self and actual self leads to mental health, while incongruence causes anxiety. Rogers developed non-directive client-centered therapy which focuses on reflecting feelings and letting the client guide discussion to come to their own conclusions.