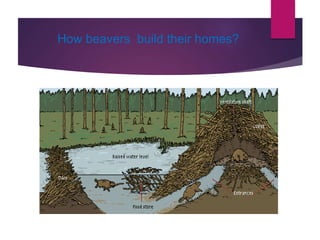
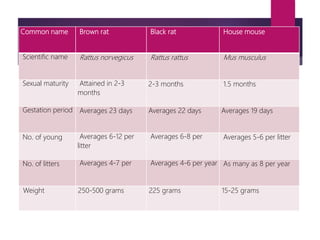
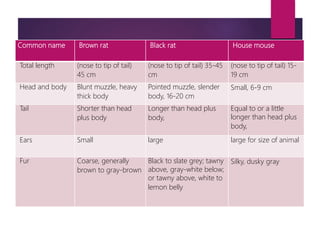
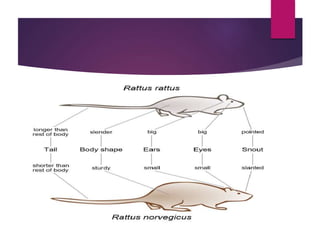
Rodents biology and classification discusses rodents including their:
1) Scientific classification within the kingdom Animalia and class Mammalia.
2) Introduction to common rodents like mice, rats, squirrels and their use of sharp incisors to cut food and defend themselves.
3) Range and success of rodents, making up over 40% of mammal species, being found worldwide except Antarctica in all habitats.