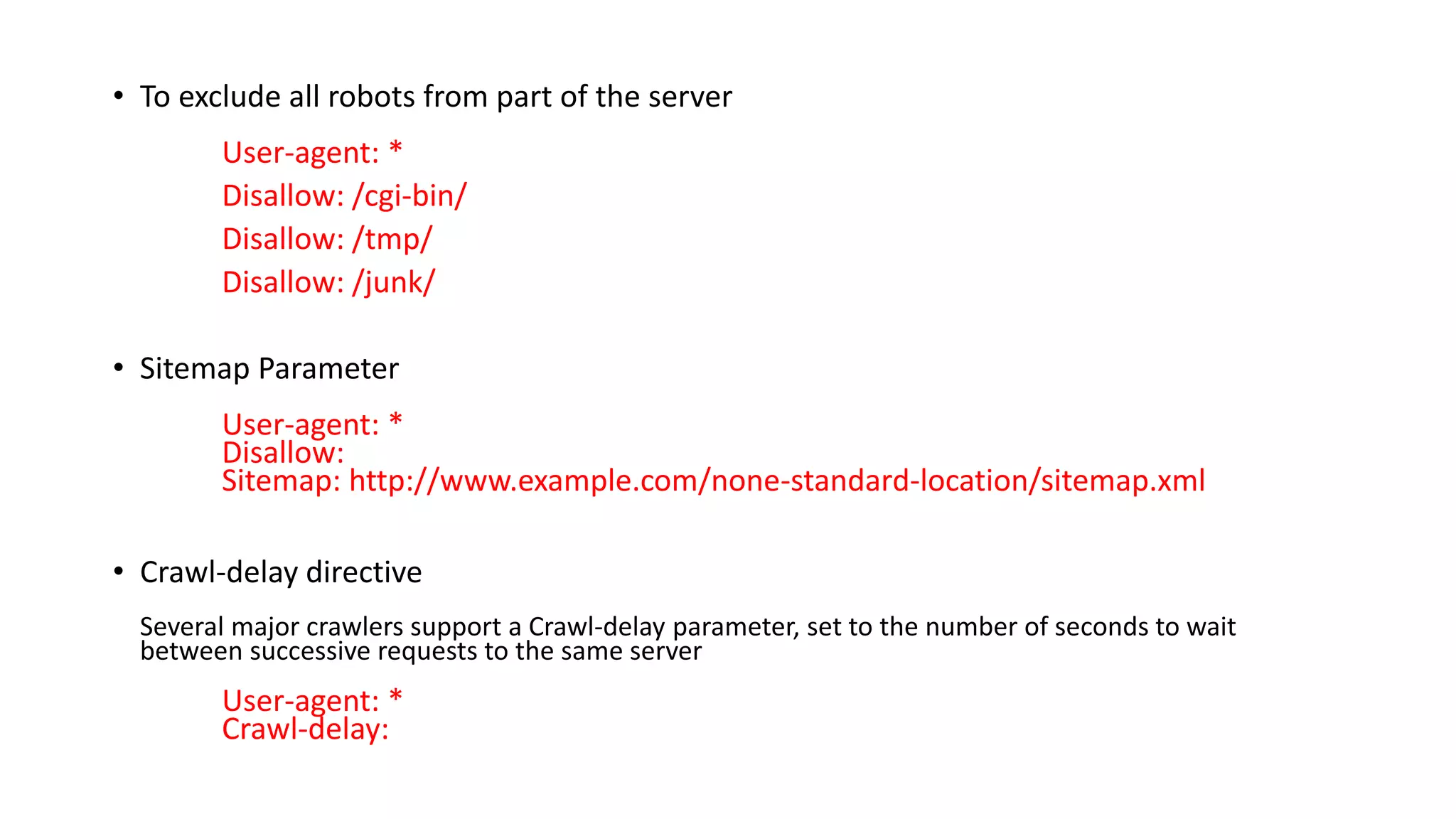
The robots.txt file is used by websites to communicate with web crawlers and robots about how to crawl and index website pages. It was proposed in 1994 as a standard for webmasters to control how search engine robots access their sites. Examples show how to block all crawlers, block specific crawlers from folders or pages, exclude parts of the site from crawling, and set crawl delays. Important rules note using meta robots tags for restricting indexing, that malicious crawlers may ignore robots.txt, and specifics of the protocol syntax.



![• Allow directive
If one wants to allow single files inside an otherwise disallowed directory, it is necessary to place
the Allow directive(s) first, followed by the Disallow.
Allow: /directory1/myfile.html
Disallow: /directory1/
• Host
Some crawlers (Yandex, Google) support a Host directive, allowing websites with multiple mirrors
to specify their preferred domain.[26]
Host: www.example.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/robots-150823064930-lva1-app6891/75/Robots-txt-6-2048.jpg)