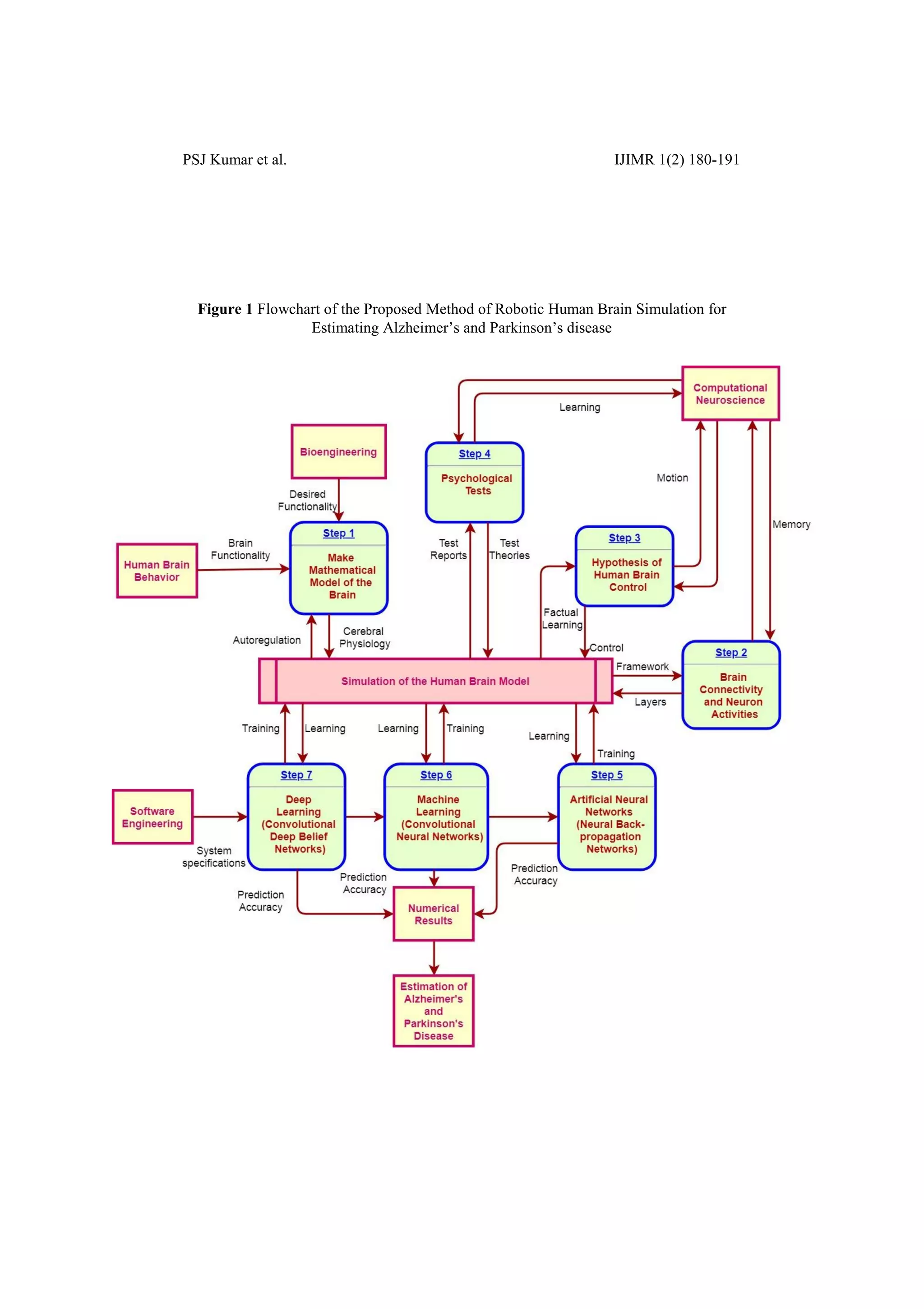
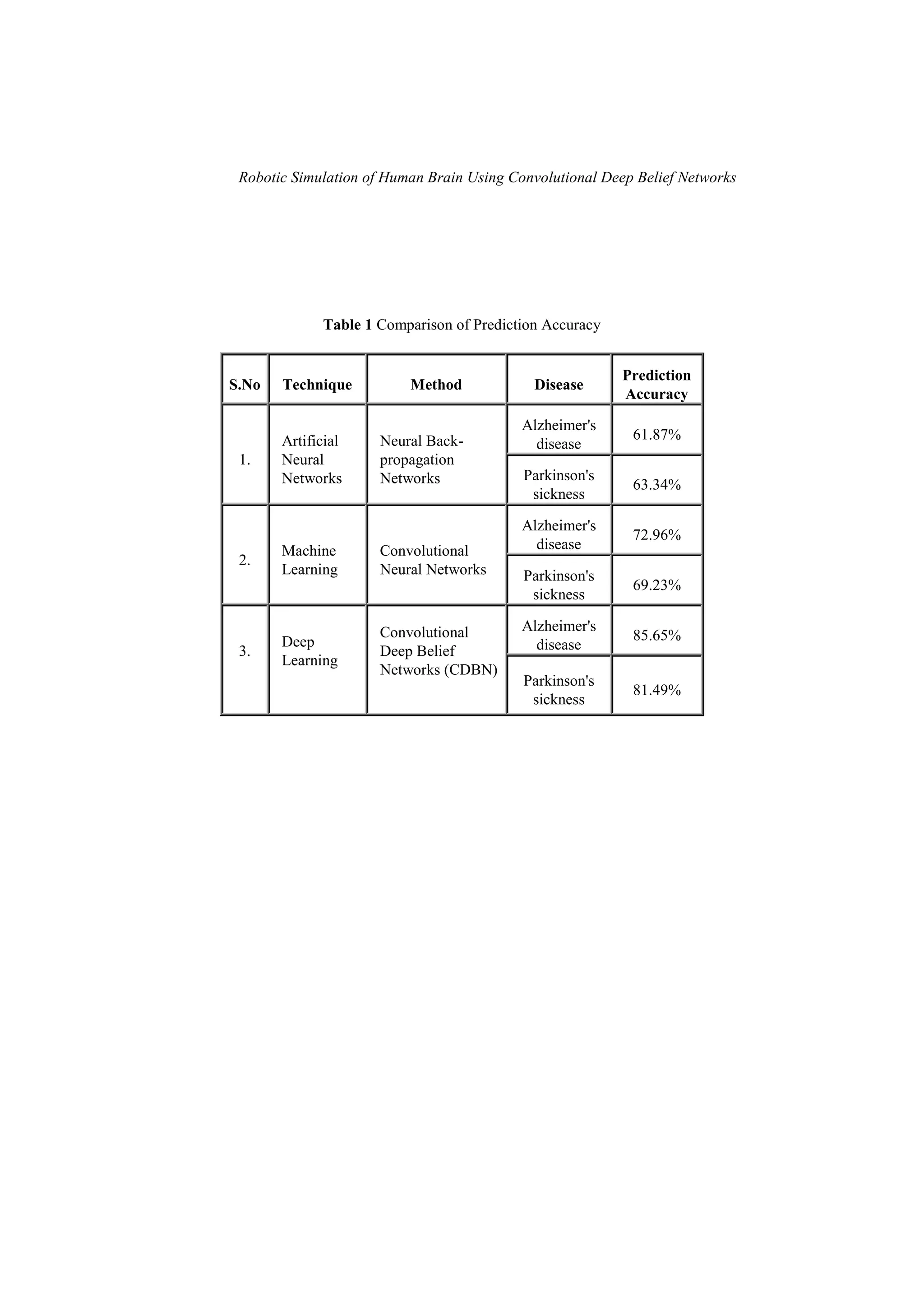
1. The document discusses using convolutional deep belief networks to simulate the human brain and identify brain diseases. It compares the predictive accuracy of artificial neural networks, machine learning, and deep learning for diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, finding that convolutional deep belief networks performed best.
2. It provides background on computational neuroscience and outlines models of neurons, neural systems, and brain function at different scales that are used to test theories about the brain.
3. The summary briefly describes key parts of the human brain like the cerebral cortex, cerebellum, thalamus, hypothalamus, and hippocampus and their functions in areas like motor control, memory, learning, emotion, and decision making.