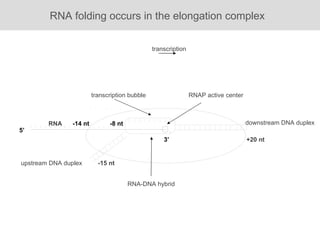
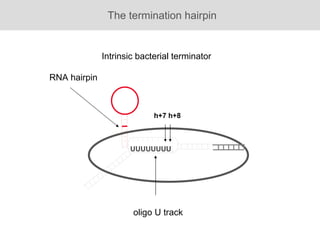
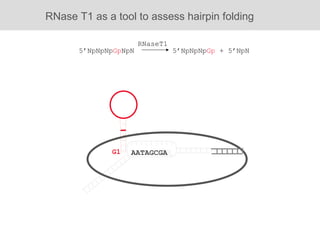
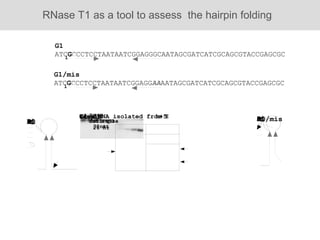
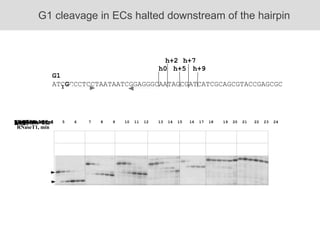
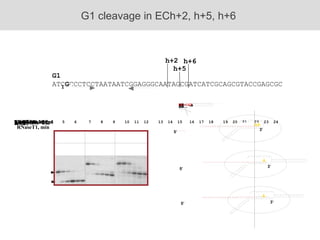
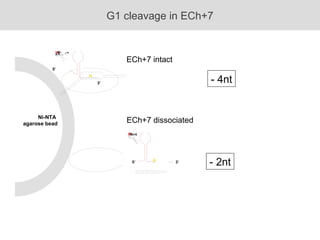
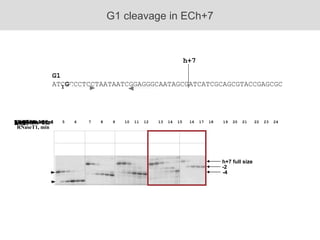
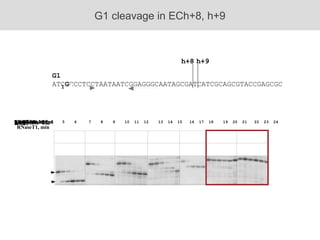
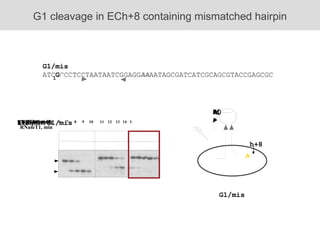
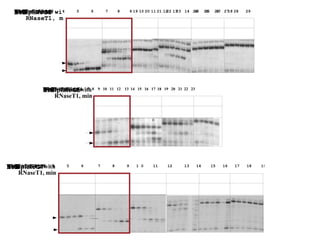
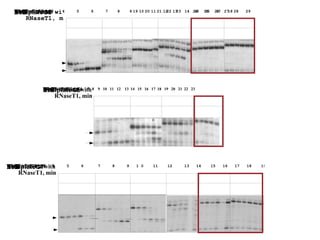
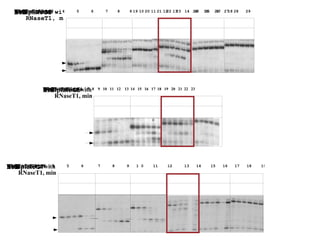
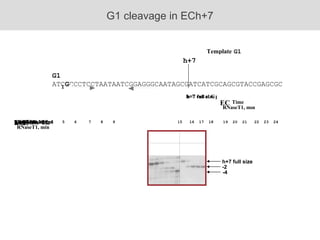
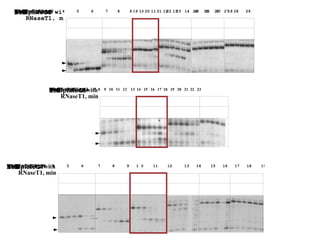
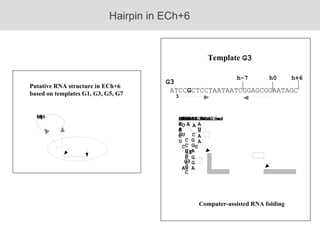
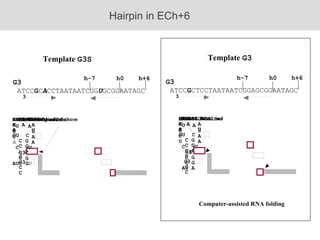
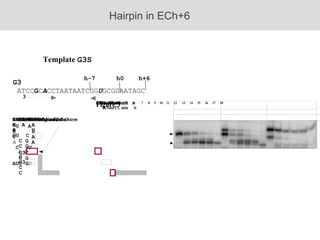
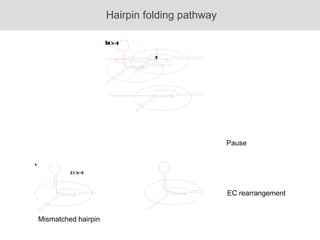
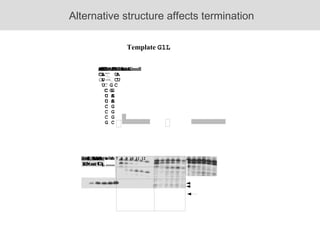
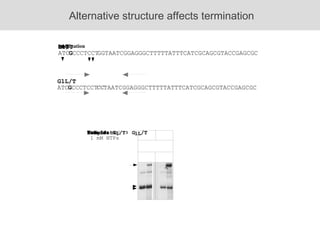
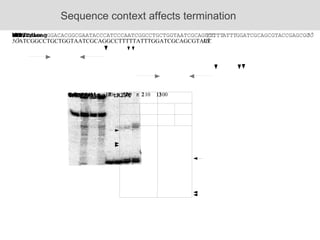
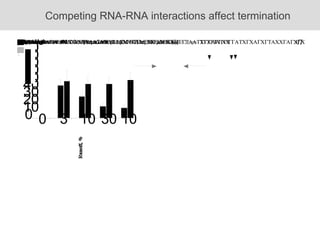
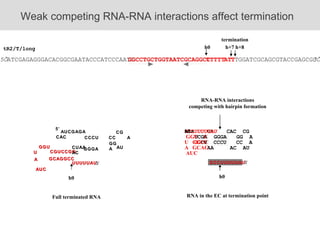
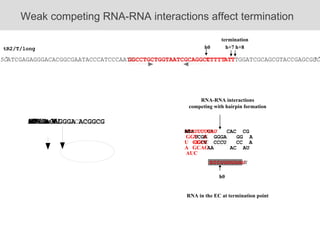
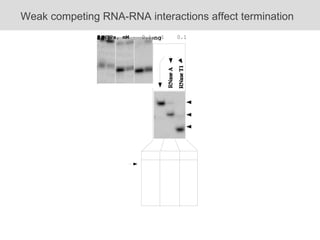
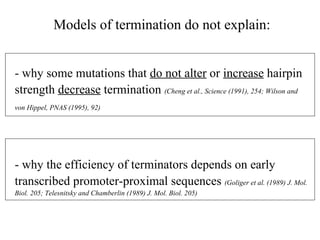
RNA folding is affected by transcription elongation. As the RNA is synthesized within the elongation complex, its ability to fold is constrained. This can affect downstream processes like intrinsic transcription termination that depend on the formation of RNA hairpin structures. Experiments using RNase T1 to probe RNA structures in elongation complexes at different positions show that the hairpin involved in intrinsic termination begins to form early but may not fully fold until after the RNA is released from the elongation complex. Competing RNA-RNA interactions or kinetic constraints of hairpin folding within the elongation complex can influence the efficiency of intrinsic termination.