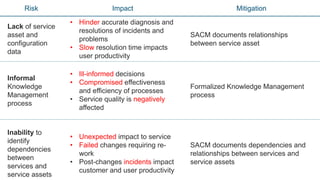
The document discusses several risks that can occur without proper IT service management processes and the impacts of those risks. For each risk, it provides a brief description of the impact and proposes a mitigation process to address the risk, such as implementing a service portfolio management process to address the risk of ill-informed decisions without a formal service portfolio.