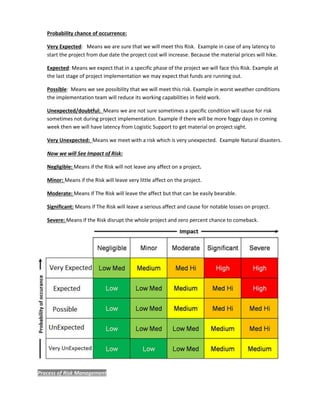
1. Risk management involves identifying risks, prioritizing them based on probability and impact, and developing strategies to address high priority risks.
2. Key steps include assigning risks to owners, monitoring risks, developing risk management plans to avoid, transfer, mitigate or accept risks, and deriving safeguards.
3. Risk identification considers technical, cost, schedule, environmental and other risks, and prioritization is based on the probability of occurrence and potential impact on the project.