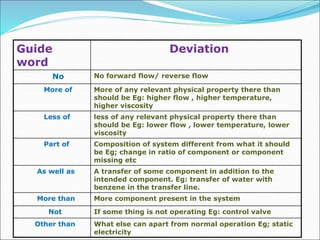
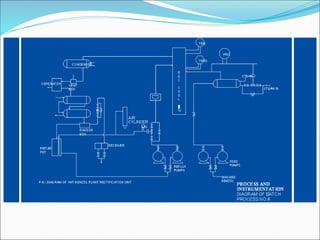
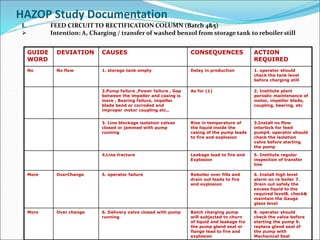
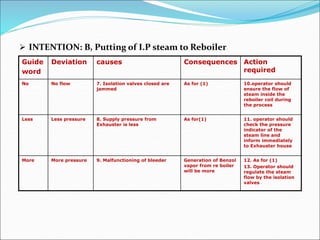
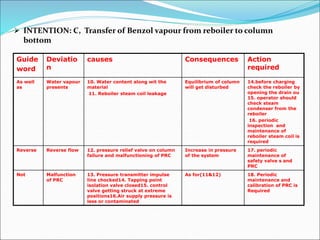
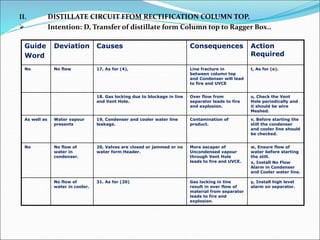
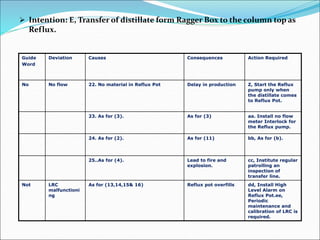
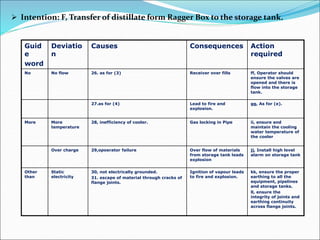
The Hazard and Operability (HAZOP) analysis technique is used to identify safety hazards and operability problems in a process plant that could compromise productivity or lead to undesirable consequences. A multi-disciplinary team uses a systematic approach and guide words like "no," "more," and "less" to examine how deviations from the design intent could occur. The team conducted a HAZOP study on a 1 MT benzol plant, identifying deviations and their causes and consequences for processes like transferring benzol to a reboiler. Key findings included pump seal leaks, improper equipment earthing, unscreened vents, and needed instrument maintenance. Recommendations focused on replacing seals, improving grounding, adding vent screens, and