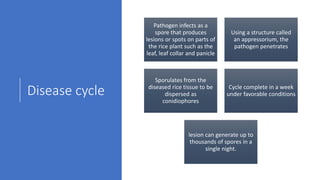
Rice blast, caused by the fungus Magnaporthe oryzae, infects rice plants worldwide and can destroy enough rice to feed over 60 million people. It causes lesions on leaves, collars, and panicles. High humidity and temperatures between 77-82°F favor the disease. Biocontrol methods include the fungi Aspergillus niger and Trichoderma harzianum and bacteria like Streptomyces, which can inhibit the growth of M. oryzae. Management strategies involve using certified seed, crop rotation, resistant varieties, and maintaining proper flooding and nutrition levels for rice.