Rice Blast Diseases - An Introduction and overview
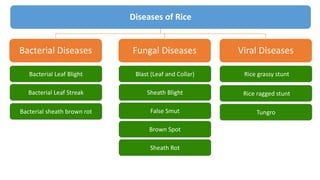
- 1. Diseases of Rice Bacterial Diseases Viral Diseases Fungal Diseases Bacterial Leaf Blight Bacterial Leaf Streak Bacterial sheath brown rot Blast (Leaf and Collar) Sheath Blight False Smut Brown Spot Sheath Rot Rice grassy stunt Rice ragged stunt Tungro
- 2. Blast • Caused by Magnaporthe oryzae (Hebert) Barr is one of the most damaging diseases of rice. • The most common symptoms in commercial rice fields induced by M. oryzae can be found on all the above ground parts of the rice plant at all growth stages. • Typically blast lesions are diamond shaped. • Initial lesions appear dark green or grey with brown borders; while, older lesions are light tan with necrotic borders. • Under favorable conditions, lesions can merge together and rapidly enlarge to several centimeters in length, eventually killing the leaf, and ultimately resulting in plant death. • Spores produced at the end of the growing season may result in collar blast and neck blast; neck blast often causes direct crop loss
- 3. Life cycle of Blast • Mycelium and conidia on diseased straw and infected seeds are the principal sources of primary infection. • The fungus can attack a number of cereal and grass hosts which could be important source of primary infection. When several crops of rice are taken in a year, the pathogen maintains a continuous disease cycle on the rice crop itself. • Under favorable conditions, the conidia can produce symptoms within 4–5 days of infection. • Conidia are produced on the lesions 6–7 days after infection and disseminated by wind. • A typical leaf blast lesion produces 2000–6000 conidia each day for about 14 days. The rate of sporulation increases with increase in relative humidity, while release and flight of spores increase with enhancement in dew period and wind speed, respectively. (Laha et al., 2017)
- 4. Distribution and economic losses by Rice blast • Average losses in the range of 10–30 % although regional epidemics can be more devastating (Dean et al. 2012) resulting in grain yield loss up to 100 %. • Severe yield losses due to blast have been reported in different African countries ranging from 36 to 63 % in Burkina Faso, 35–50 % in Nigeria, 20–30 %in Benin, 64 % in Togo, up to 80 % in Sierra Leone and Cote d’Ivoire and up to 100 % in Ghana and Gambia (Sere et al. 2013). Worldwide distribution of rice blast disease. Red dots show the countries or regions where blast disease has been reported. (Wang et al., 2014) (Laha et al., 2017)
- 5. Genetic map of blast resistance genes on different rice chromosomes 0 5 10 15 20 25 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 No. of R genes Chromosomes Major R genes mapped Minor R genes mapped R gene cloned Chromosome position in Centimorgan ; The underlined words indicate either SSR or RFLP markers (Wang et al., 2014)
- 6. List of cloned blast resistance genes (Ning et al., 2020)
- 7. • Blast R genes are predicted to play important roles in the frontier of rice defense responses. • During interactions between rice and blast pathogens, products of the R gene can specifically recognize the corresponding elicitors of M. oryzae. Since the Pia gene, identified in 1967 by Kiyosawa as the first blast R gene from the japonica variety Aichi Asahi, 99 blast R genes have been identified; in which 45% were found in japonica cultivars, 51% in indica cultivars, and the rest 4% in wild rice species. • Most deployed R genes have often been identified in Asian cultivated rice, specially rice cultivars from Japan and China, with the exception of Pi9, Pi54rh, Pi40(t), and Pirf2-1(t), which were domesticated from O. minuta, O. rhizomatis, O. australiensis, and O. rufipogon, respectively. All R genes have been mapped on all rice chromosomes except for chromosome 3 • Among them, three major R gene clusters have been well characterized: the Piz locus on Chromosome 6, the Pik locus on Chromosome 11, and the Pita locus on Chromosome 12. Resistance genes and resistance genes clusters for blast resistance
- 8. Rice innate immunity signaling pathways triggered by M. oryzae (Meng et al., 2019)
- 9. A, Breeding strategies for improving blast resistance in the previous studies. B, Breeding strategies that have been used. C, Novel breeding strategies that can be utilized in further research. Molecular breeding strategies using rice blast resistance genes (Ning et al., 2020)
