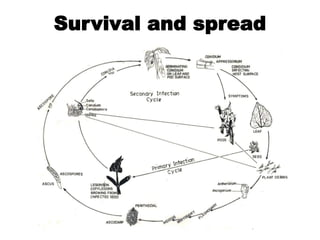
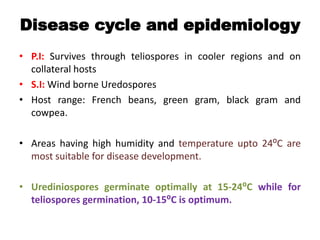
This document summarizes three common diseases that affect beans: anthracnose, rust, and yellow mosaic. Anthracnose causes sunken black spots on leaves, stems, and pods and can kill seedlings. It is caused by the fungus Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. Rust appears as small reddish-brown pustules on the lower leaf surface and is caused by the fungus Uromyces fabae. Yellow mosaic causes yellow mottling and stunting in beans and is transmitted by the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Management of these diseases involves crop rotation, resistant varieties, and fungicide or insecticide applications to control the pathogens and vectors.