Rheumatoid arthritis 2019
- 1. RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS ADELU ADESEWA RHODA PHARM D IV YEAR B16102 1
- 2. CONTENTS 1. DEFINITIONS 2. EPIDEMIOLOGY 3. ETIOLOGY 4. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY 5. CLINICAL PRESENTATION 6. DIAGNOSIS 7. TREATMENT a. NON PHARMACOLOGICAL TREATMENT b. PHARMACOLOGICAL TREATMENT 2
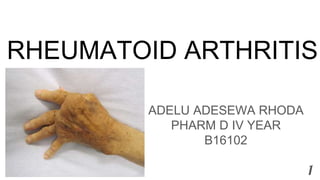
- 3. DEFINITION ❖ Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease caused by chronic inflammation of unknown etiology maked by symmetric, peripheral polyarthritis which results in joint damage & physical disability. It is a progressive disease of synovial lining of peripheral joints characterized by symmetrical inflammation leading to potentially deforming polyarthritis. It is the most common systemic inflammatory disease characterized by symmetrical joint involvement. Extra Articular involvement, including rheumatoid nodules, vasculitis, eye inflammation, neurologic dysfunction, cardiopulmonary disease, lymphadenopathy, and splenomegaly, can be manifestations of the disease. 3
- 4. 4 ❖ Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disorder that may affect many tissues and organs—skin, blood vessels, heart, lungs, and muscles—but principally attacks the joints, producing a nonsuppurative proliferative and inflammatory synovitis that often progresses to destruction of the articular cartilage and ankylosis of the joints. ❖ Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic and usually progressive inflammatory disorder of unknown etiology characterized by polyarticular symmetrical joint involvement and systemic manifestations. ❖ Rheumatoid arthritis is a long-term, progressive, and disabling autoimmune disease. It causes inflammation, swelling, and pain in and around the joints and other body organs. ❖ Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that can cause joint pain and damage throughout your body
- 5. 5
- 6. 6
- 7. EPIDEMIOLOGY The Rheumatoid Arthritis Support Network estimate that RA affects up to 1 percent of the world's population and over 1.3 million people in America. Affects all age groups. RA affects about 24.5 million people as of 2015.This is between 0.5 and 1% of adults in the developed world with 5 and 50 per 100,000 people newly developing the condition each year.Onset is most frequent during middle age and women are affected 2.5 times as frequently as men. In 2013, it resulted in 38,000 deaths up from 28,000 deaths in 1990. Data suggests that a genetic predisposition an exposition to unknown environmental factor may be necessary for expression of the disease. The MHC molecules located on the T lymphocytes appears to have an important role in most patients with RA, in majority of patients with RA have HLA DR4, HLA DRI, or both found in MHC region. 7
- 8. ETIOLOGY The cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown.. It is believed that the tendency to develop rheumatoid arthritis may be genetically inherited (hereditary). It is suspected that certain infections or factors in the environment might trigger the immune system to attack the body's own tissues; resulting in inflammation in various organs of the body such as the lungs or eyes. Environmental factors also seem to play some role in causing rheumatoid arthritis. For example, scientists have reported that smoking tobacco increases the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. The cause of RA is not fully understood but appears to be multifactorial. It is considered an autoimmune disease in which the body loses its ability to distinguish between synovial and foreign tissue. 8
- 9. 9 Other factors involved in RA are as follows: 1. Environmental influences, such as infections or trauma, are thought to trigger the development of RA. 2. Genetic markers, such as human leukocyte antigen DR4 (HLA-DR4), have been associated with triggering the inflammatory process in RA. Such markers, however, are not considered diagnostic because 30% of people with HLA-DR4 never develop RA. 3. Antigen-dependent activation of T lymphocytes leads to proliferation of the synovial lining, activation of proinflammatory cells from the bone marrow, cytokine and protease secretion, and autoantibody production. 4. Anti Citrullinated proteins and peptides are high specific for RA. 5. Tumor necrosis factor & (TNF-&), IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, and growth factors propagate the inflammatory process, and agents found to alter these cytokines show promise in reducing pain and deformity.
- 10. 10 6. Inflamed synovium is a hallmark of the pathophysiology of RA. Synovium proliferates abnormally, growing into the joint space and into the bone, forming a pannus. The pannus migrates to the articular cartilage and into the subchondral bone leading to destruction of cartilage, bone, tendons, and blood vessels.
- 11. PREDISPOSING FACTORS Genetic and environmental factors play a part. ➔ Gender. Women before the menopause are affected three times more often than men. After the menopause the frequency of onset is similar between the sexes, suggesting an etiological role for sex hormones. The use of the oral contraceptive pill has shown no effect on RA overall, as previously thought, but it may delay the onset of disease. ➔ Familial. The disease is familial with an increased incidence in first degree relatives and a high concordance amongst monozygotic twins (up to 15%) and dizygotic twins (3.5%). In occasional families it affects several generations. 11
- 12. 12 Genetic factors are estimated to account for up to 60% of disease susceptibility. There is a strong association between susceptibility to RA and certain HLA haplotypes. HLA-DR4, which occurs in 50–75% of patients, correlates with a poor prognosis, as does HLA-DRB1. Individuals with HLA- DRB1 combined with a positive rheumatoid factor are 13 times greater risk for developing bone erosions in early disease
- 13. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY ● Unknown antigen stimulates CD4+T lymphocytes. ● Active CD4+ T lymphocytes; a. stimulates macrophages to release IL1 and TNF. b. Release RANKL which stimulates osteoclasts leading to bone destruction. ● IL-1 and TNF stimulates synovial cells leading to: a.Synovial cell proliferation and formation of pannaus. b.Production of prostaglandins (pain sensation) and matrix metalloproteinases that cause cartilage destruction. 13
- 14. 14
- 15. 15
- 16. * Sequence of events : 1. Proliferation of synovial membrane cells with inflammatory cell infiltrate 2. Destruction of joints 3. Disability
- 17. 17
- 18. CLINICAL PRESENTATION Articular manifestations: ➢ Symmetric peripheral polyarthritis ➢ Morning Stiffness >1 hour Extra-articular manifestations: ● Symmetric peripheral polyarthritis: ❖ 3 or more Joints for >6 weeks ❖ Small Joints ➢ Hands & feets ➢ Peripheral to Proximal ❖ Leads to deformity & destruction of Joints. 18
- 19. 19 ● Morning stiffness: ❖ Morning or after Prolonged Inactivity. ❖ Bilateral ❖ > 1 hour. ❖ Better with movement ❖ Pain with movement of joint ● Physical Examination: ❖ Decreased grip strength ❖ Carpal tunnel syndrome(condition characterized by pain and numbing or tingling sensations in the hand and caused by compression of a nerve in the carpal tunnel at the wrist. ❖ Ulnar deviation
- 20. * Extra-articular manifestations: ● Myalgia ● Fatigue ● low-grade fever ● weight loss ● depression ● Anemia ● Rheumatoid nodules ● Pleuropericarditis ● Neuropathy ● Scleritis ● Splenomegaly ● Vasculitis
- 21. 21 ● Rheumatoid Nodules ❖ Extensor surfaces especially elbows Very Specific ❖ Only occur in ~30% ❖ Late in Disease
- 22. DIAGNOSIS The American Rheumatism Association(ARA) criteria for classification of RA. 1. Morning stiffness 2. Arthritis of 3 or more joints 3. Arthritis of hand joints 4. Symmetric arthritis - bilateral involvement 5. Rheumatoid nodules 6. Subcutaneous Nodules over bony area 7. Serum rheumatoid factor 8. Radiographic changes: posterior, anterior hand, wrist 9. X-RAYS, which includes erosions and bony decalcification. 22
- 23. 23
- 24. 2 ● LABORATORY ABNORMALITIES Laboratory abnormalities that may be seen includes; 1. Normocytic 2. Normochromic anaemia 3. Leucopenia 4. Elevated CSR 5. Positive Rheumatoid factor (60-70% patient) 6. Positive antinuclear antibodies (ANA) 25% patient
- 25. TREATMENT ● TREATMENT OBJECTIVES The goals in the management of RA are: 1. To prevent or control joint damage. 2. To prevent loss of function. 3. To decrease pain. 4. To maintain the patient’s quality of life. 5. To avoid or minimize adverse effects of treatment. 6. Preservation of muscle and joint function. 7. Return to a desirable and productive life. 25
- 26. 26 Non pharmacological Treatment ➔ Diet ➔ Exercise ➔ Acupuncture ➔ Herbal Medicines ➔ Massage ➔ Stress Reduction Techniques – prayer, meditation, hypnosis, yoga ➔ Nutrition:The most commonly observed vitamin and mineral deficiencies in patients with RA are; ◆ Folic acid ◆ Vitamin C ◆ Vitamin D ◆ Vitamin B6, B12 ◆ Vitamin E ◆ Calcium ◆ Magnesium ◆ Zinc
- 27. 27 ➔ Exercise Being overweight strains joints and leads to further inflammation Exercise 4 times a week for 30 minutes ◆ Walking ◆ Light jogging ◆ Water aerobics ◆ Cycling ◆ Yoga ◆ Tai chi ◆ stretching
- 28. 28 PHARMACOLOGICAL TREATMENT There are four types of medications used to treat RA: 1. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) 2. Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs(DMARDS). 3. Corticosteroids 4. Biologic Response Modifiers (“Biologics”)
- 29. 29 GENERAL USE DOSE SIDE EFFECTS 300mg,400mg, 600mg or 800mg.<3200m g/day 2 IBUPROFEN 500-1000 mg/day <1500mg 3 NAPROXEN 50 mg PO q8-12hr <100 mg 4 DICLOFENA C 25-50 mg PO/PR q8- 12hr <200mg 5 INDOMETHA CIN Nausea •Vomiting •Diarrhea •Constipation •Dizziness •Drowsiness •Edema •Kidney failure •Liver failure •Prolonged bleeding •Ulcers Anti- inflammator y: Used in the managemen t of inflammator y conditions •Antipyretic: used to control fever •Analgesic: Control mild to moderate pain 2.1-7.3g/day in divided doses 1 ASPIRIN Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) EXAMPLES
- 31. 31 Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) 1. Methotrexate 2. Sulfasalazine 3. Hydroxychloroquine 4. Leflunomide 5. Gold 6. Azathioprine Action of DMARDS ● Control symptoms ● No immediate analgesic effects ● Can delay progression of the disease (prevent/slow joint and cartilage damage and destruction) ● Effects generally not seen until a few weeks to months
- 32. 32 Methotrexate ● most commonly used drug ● fast acting (4-6 weeks) ● po, SQ - weekly ● 7.5 mg PO as a single weekly dose, OR 2.5 mg PO q12hr for 3 sequential doses per week. Sulfasalazine ● 1 g bid - tid upto 2g & 3g daily in divided doses ● CBC, LFTs ● onset months (1-2 months)
- 33. 33 Hydroxychloroquine ● mild non-erosive disease ● combinations ● 200 mg bid upto 400 mg in 2 divided doses ● eye exams ● Onset 6-12 weeks IM Gold ● 10mg IM 1st week, 25mg IM the 2nd week, then, ● 25-50 mg IM q weekly then monthly injections ● CBC, UA before each injection ● slow onset (3-6 months)
- 34. 34 Oral Gold ● less effective ● slow acting (4-6 months) ● daily ● CBC, UA ● 6 mg PO qDay or divided BID; may increase to 9 mg /day divided TID ● after 3 months, discontinue drug.
- 35. 35 Biologic Response Modifiers(“Biologics”) 1. Etanercept 2. Infliximab 3. Anakinra 4. Adalimumab ACTION OF BIOLOGICS ● Etanercept and infliximab target tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-) ● Anakinra targets interleukin-1 receptor Etanercept ● Twice a week subcutaneous injection ● SC 25 mg twice weekly/ 50 mg once weekly ● Very Expensive
- 36. 36 Infliximab ● 3-10 mg/kgs as IV infusion every 8 weeks ● Very expensive Anakira ● 100 mg SC injection daily ● Very expensive
- 37. REFERENCE 1. Anjali Rarichan. Rheumatoid arthritis. Slideshare;2016:https://www.slideshare.net/angeline777/rheumatoid-arthritis-ppt-by-ann 2. Halle Gill. Rheumatoid Arthritis Systemic chronic inflammatory disease. Slideplayer;2015:https://slideplayer.com/slide/2501082/ 3. Brenda Parish.Rheumatoid arthritis. Slideplayer;2015:https://slideplayer.com/slide/6256455/ 4. Healthline Editorial Team.Everything You Want to Know About Rheumatoid Arthritis. Healthline;2019:https://www.healthline.com/health/rheumatoid-arthritis 5. Yvette Brazier.What is rheumatoid arthritis? MedicalNewsToday;2018:https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323361.php 6. Allan Gibofsky, MD, JD, FACP, FCLM. Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Synopsis. AJMC;2014:Allan Gibofsky 7. Grace College of Pharmacy.Rheumatoid arthritis. Slideshare;2015:https://www.slideshare.net/aishuanju/rheumatoid-arthritis-44955735 8. Wikipedia contributors.Rheumatoid Arthritis. Wikipedia;2019:https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Rheumatoid_arthritis&oldid=9133655 56 9. Vishalakshi. Rheumatoid Arthritis.CCPER;2019.My Pharm D III Year PT II Note 37
- 38. 38
Editor's Notes
- X-RAYS PICTURES OF RA.