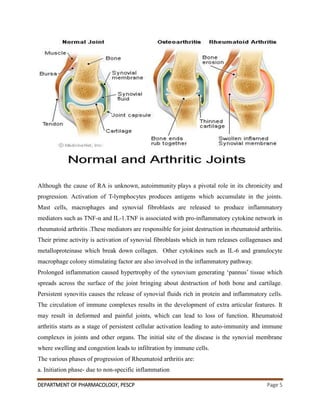
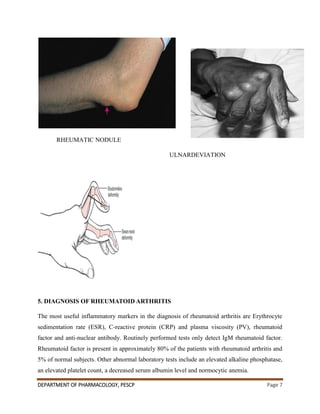
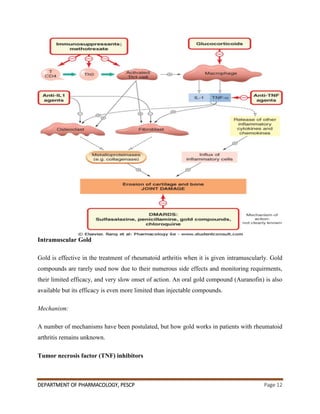
This document summarizes the pathophysiological mechanisms of rheumatoid arthritis and the mechanisms of action of drugs used to treat it. It discusses how autoimmunity and inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-1 contribute to joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. It also describes the clinical manifestations of the disease and diagnostic tests. The treatment section covers non-drug approaches like physiotherapy and commonly used drugs like NSAIDs, DMARDs, and corticosteroids. NSAIDs work by inhibiting cyclooxygenase enzymes to reduce inflammation, while corticosteroids inhibit inflammatory cytokines.