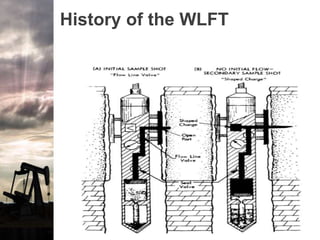
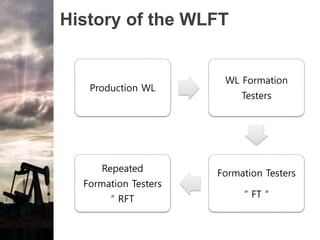
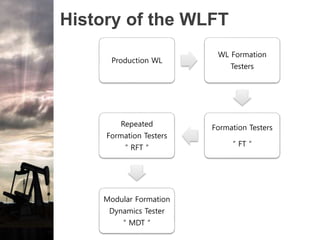
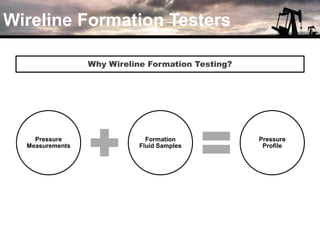
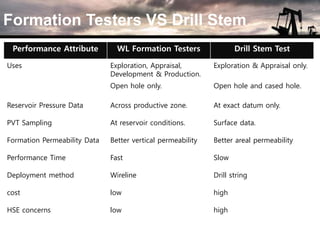
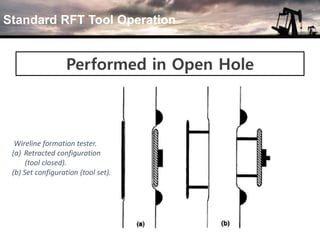
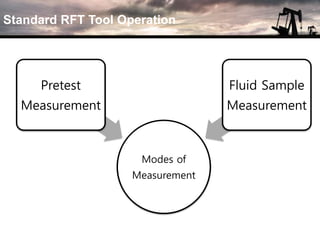
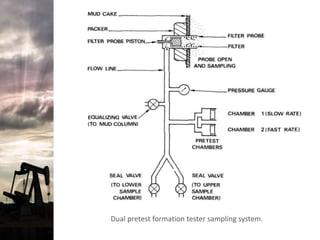
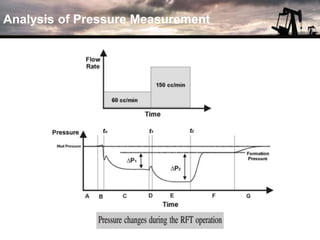
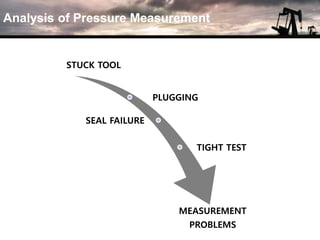
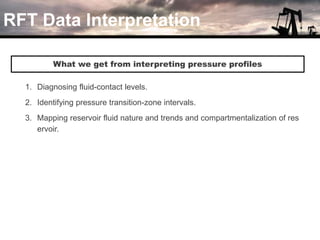
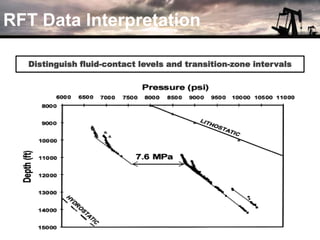
The document discusses the history and operation of wireline formation testers (WFT) and their roles in exploration, appraisal, and production of reservoirs. It examines various testing methods, including repeated formation testing (RFT) and modular formation dynamics testing (MDT), alongside the interpretation of pressure profiles to assess reservoir characteristics such as fluid contact levels and permeability. Additionally, it addresses the advantages and limitations of wireline formation testing compared to drill stem testing.