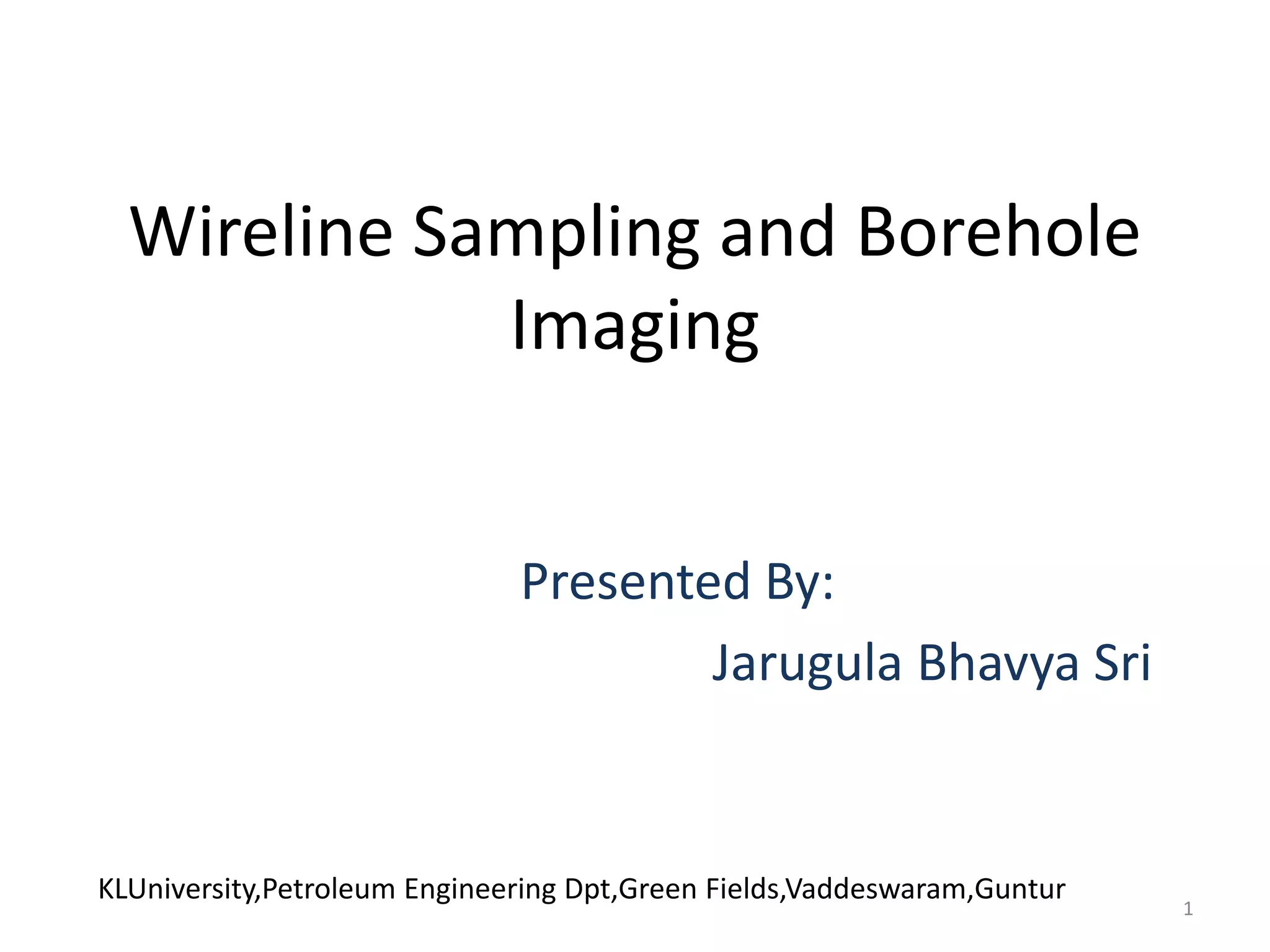
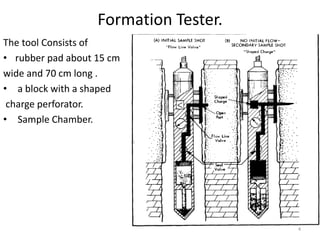
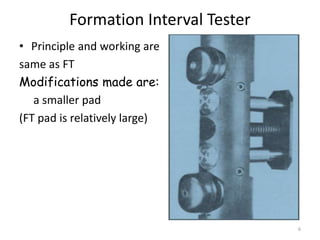
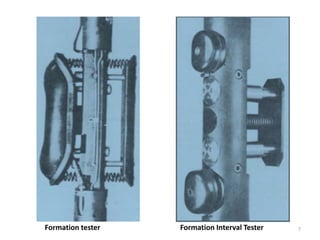
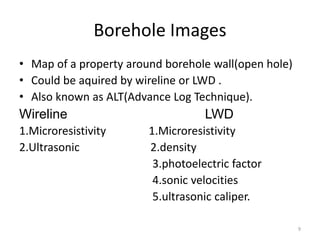
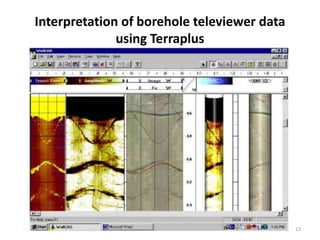
The document discusses wireline sampling and borehole imaging techniques in petroleum engineering, detailing various tools such as formation testers and borehole televiewers introduced by Schlumberger in 1937. It explains the principles, advantages, and challenges of wireline testing, including the need for precise measurements and potential issues like equipment sticking. Additionally, it covers the functionalities and applications of imaging tools for borehole analysis, focusing on their role in providing structural and lithological information.