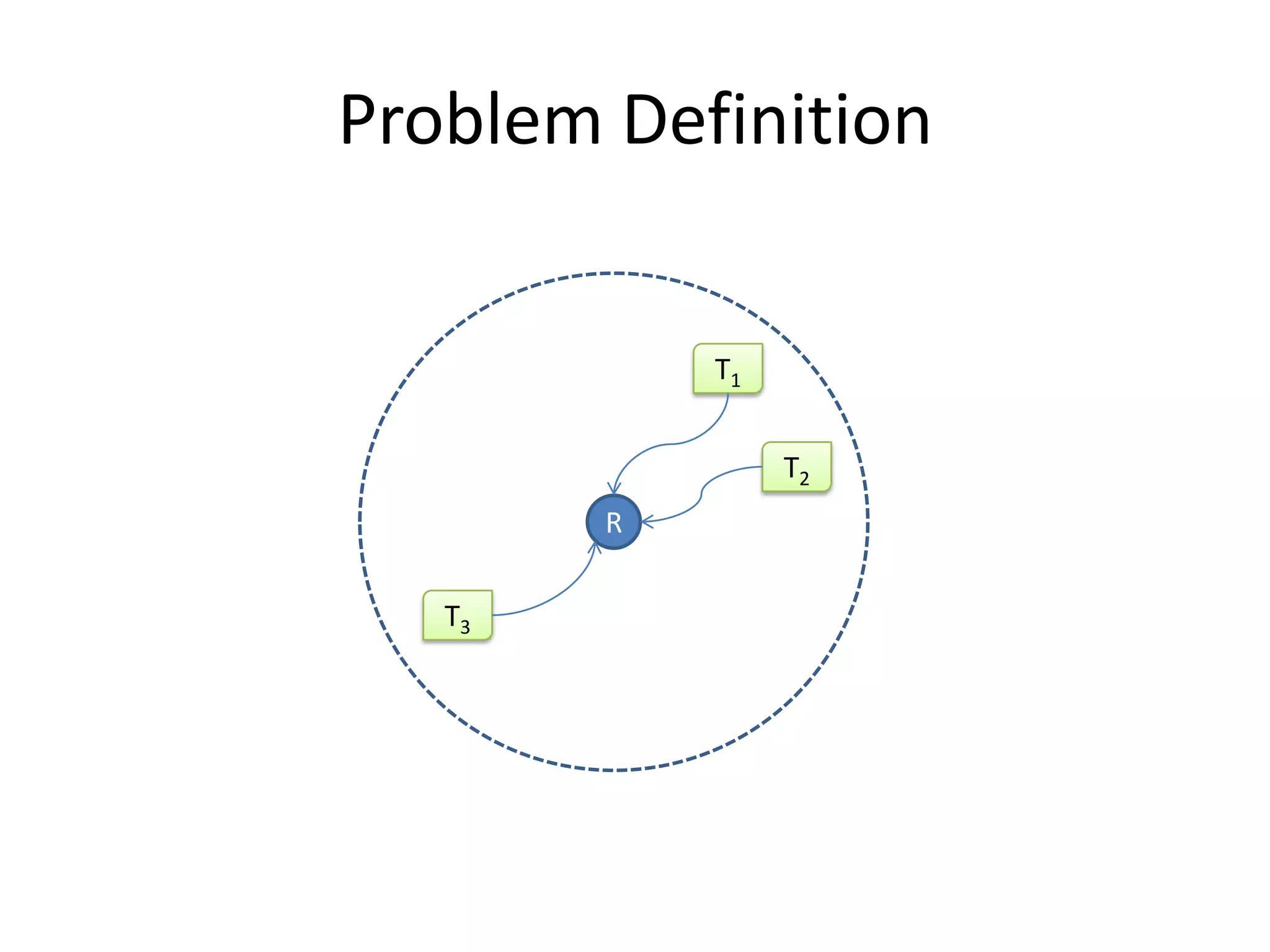
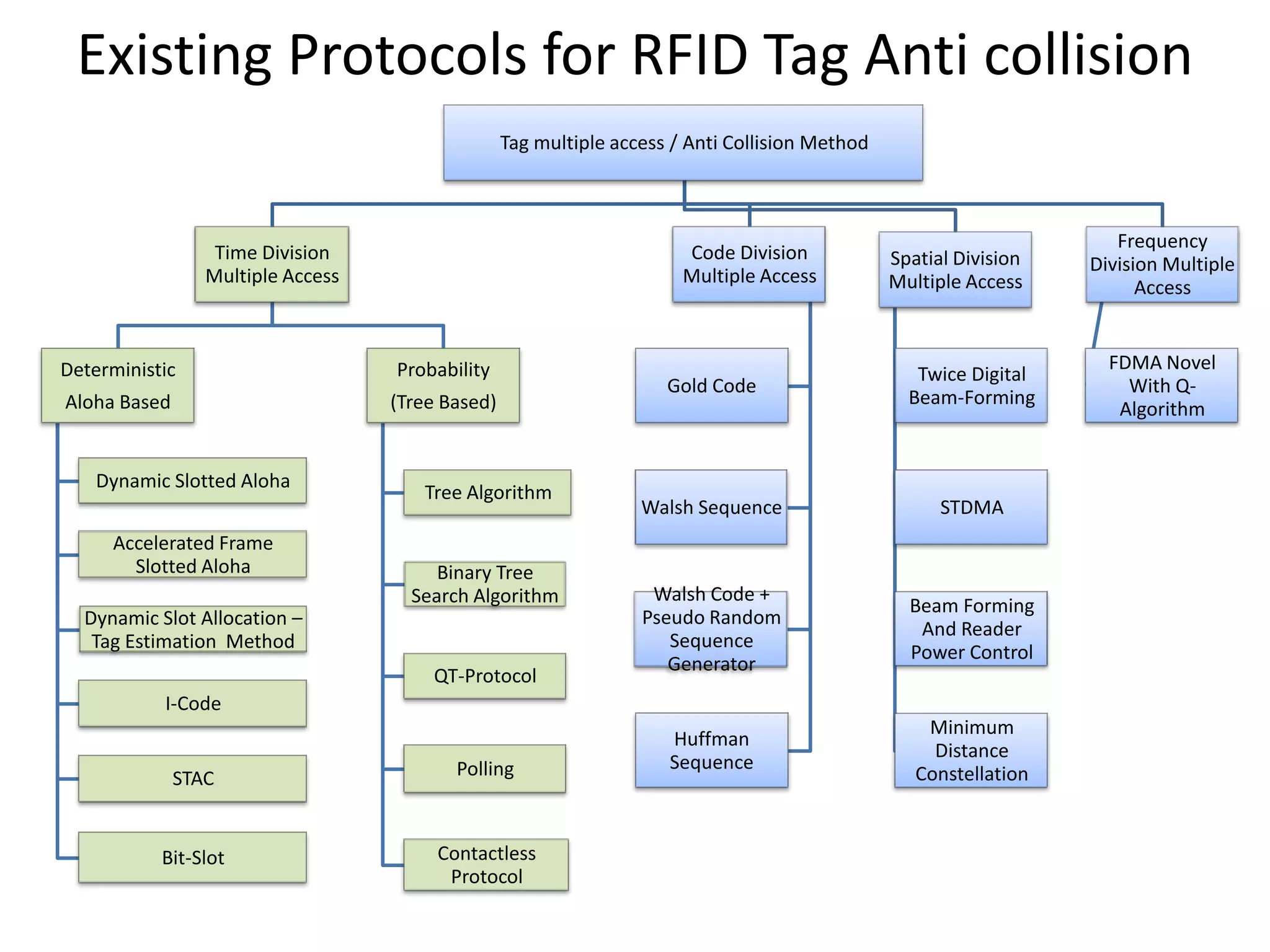
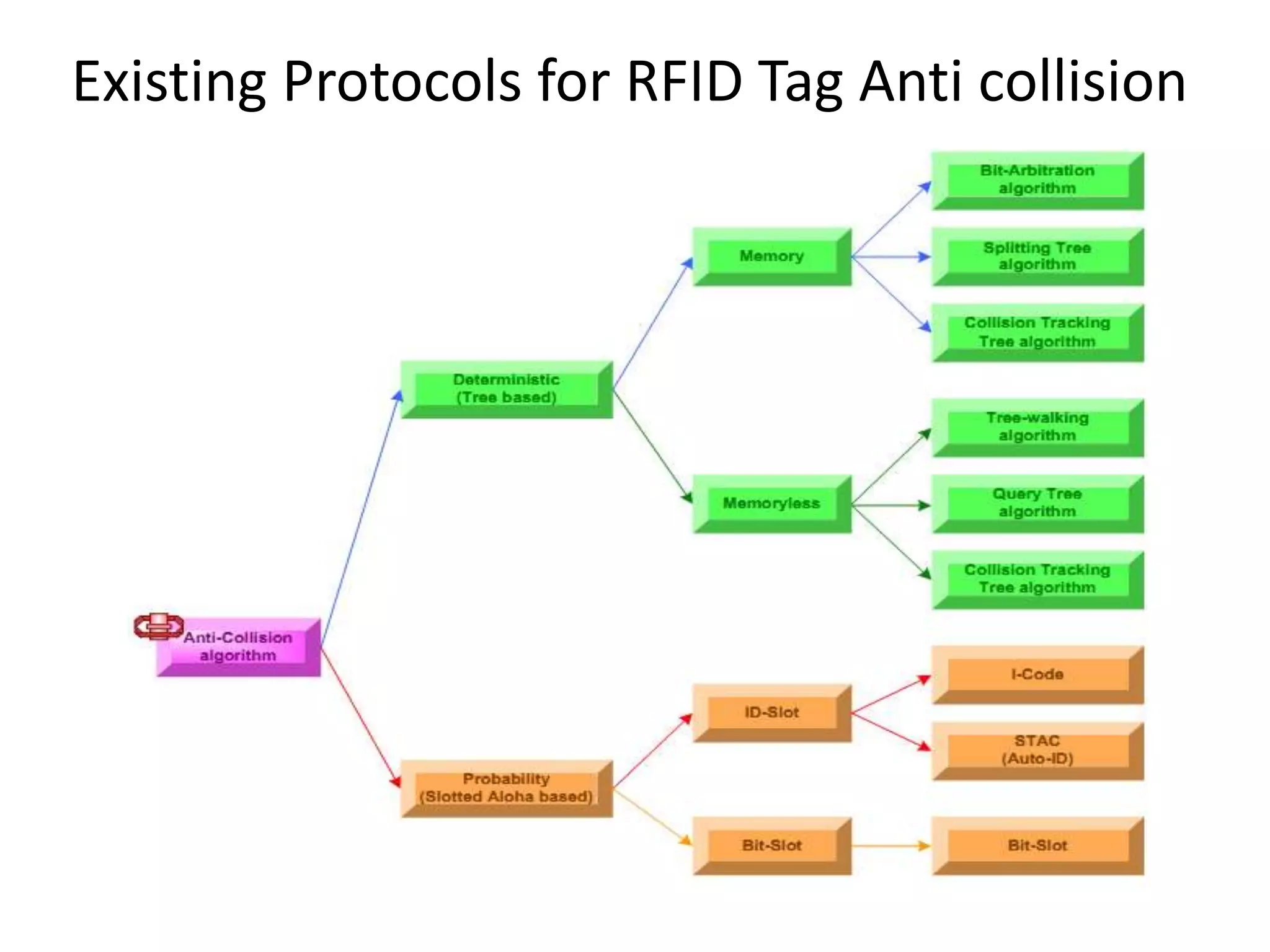
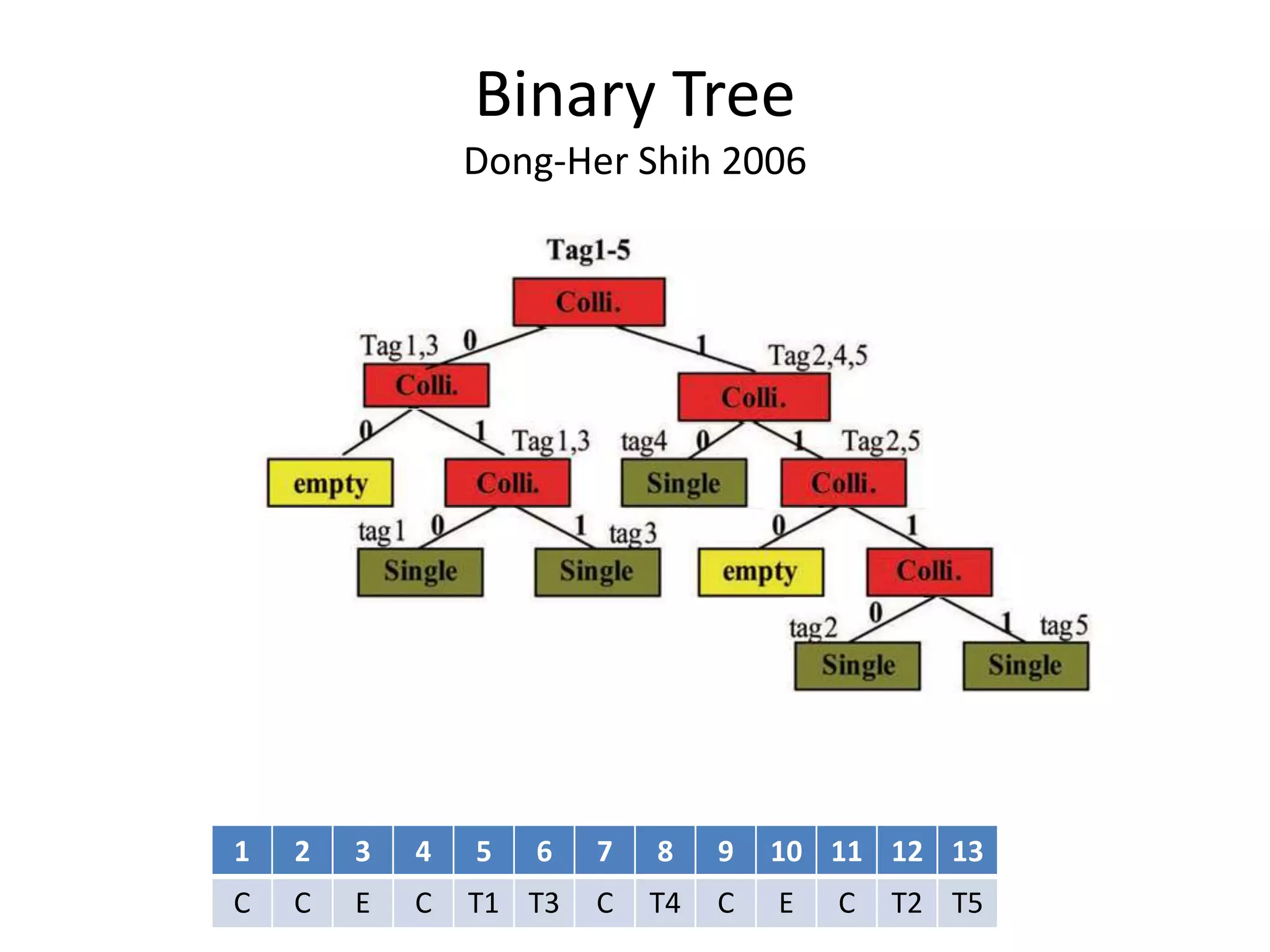
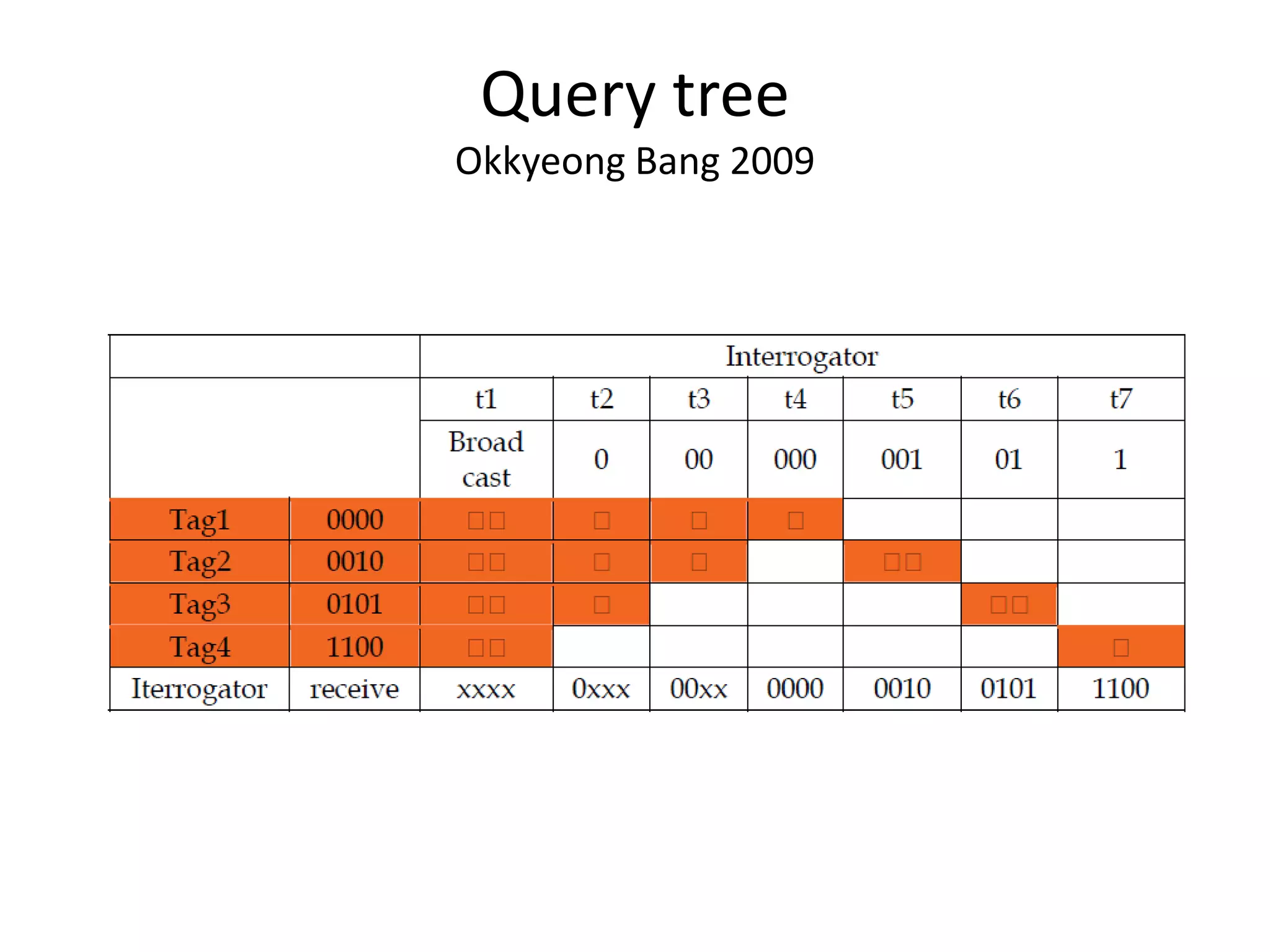
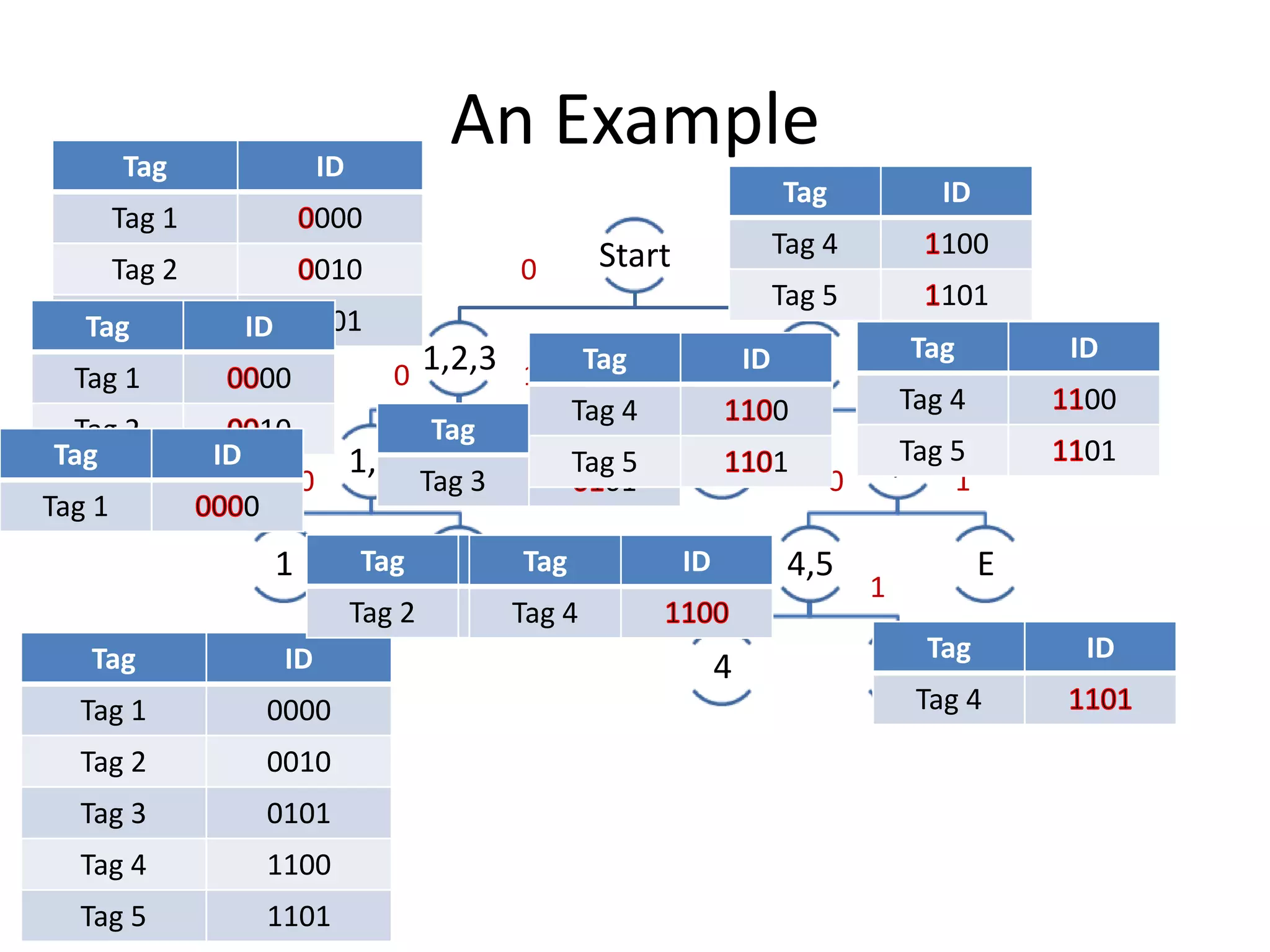
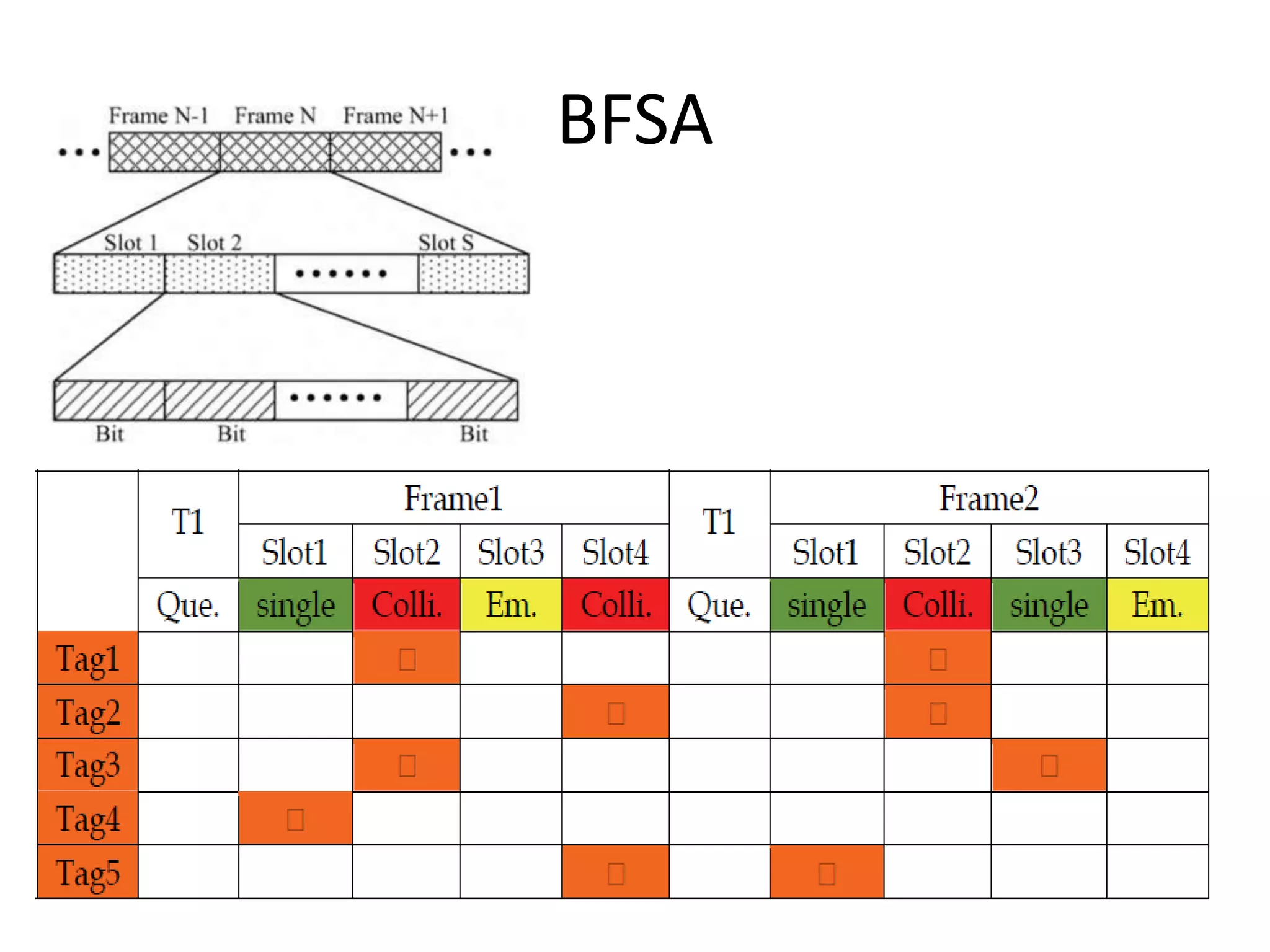
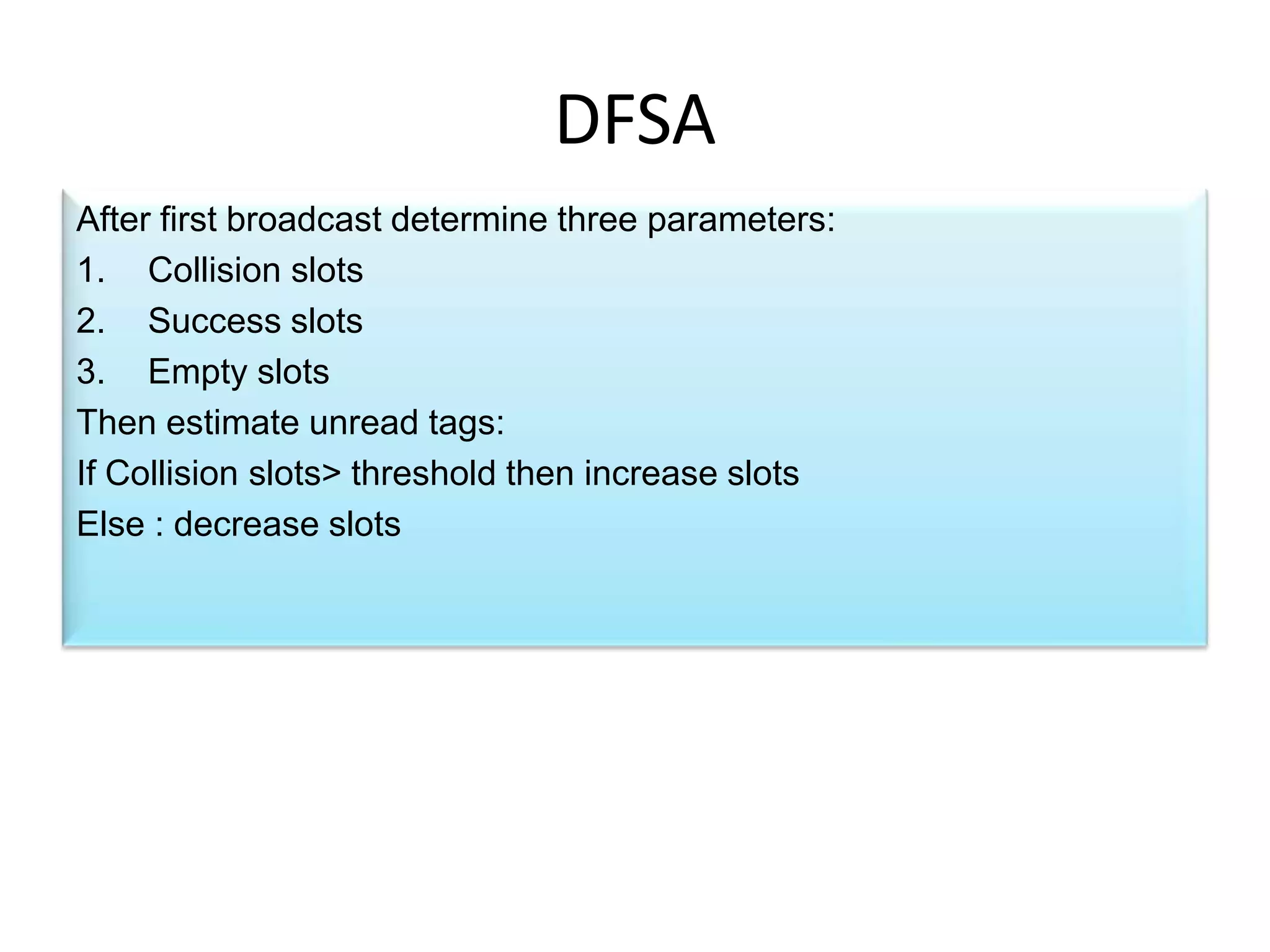
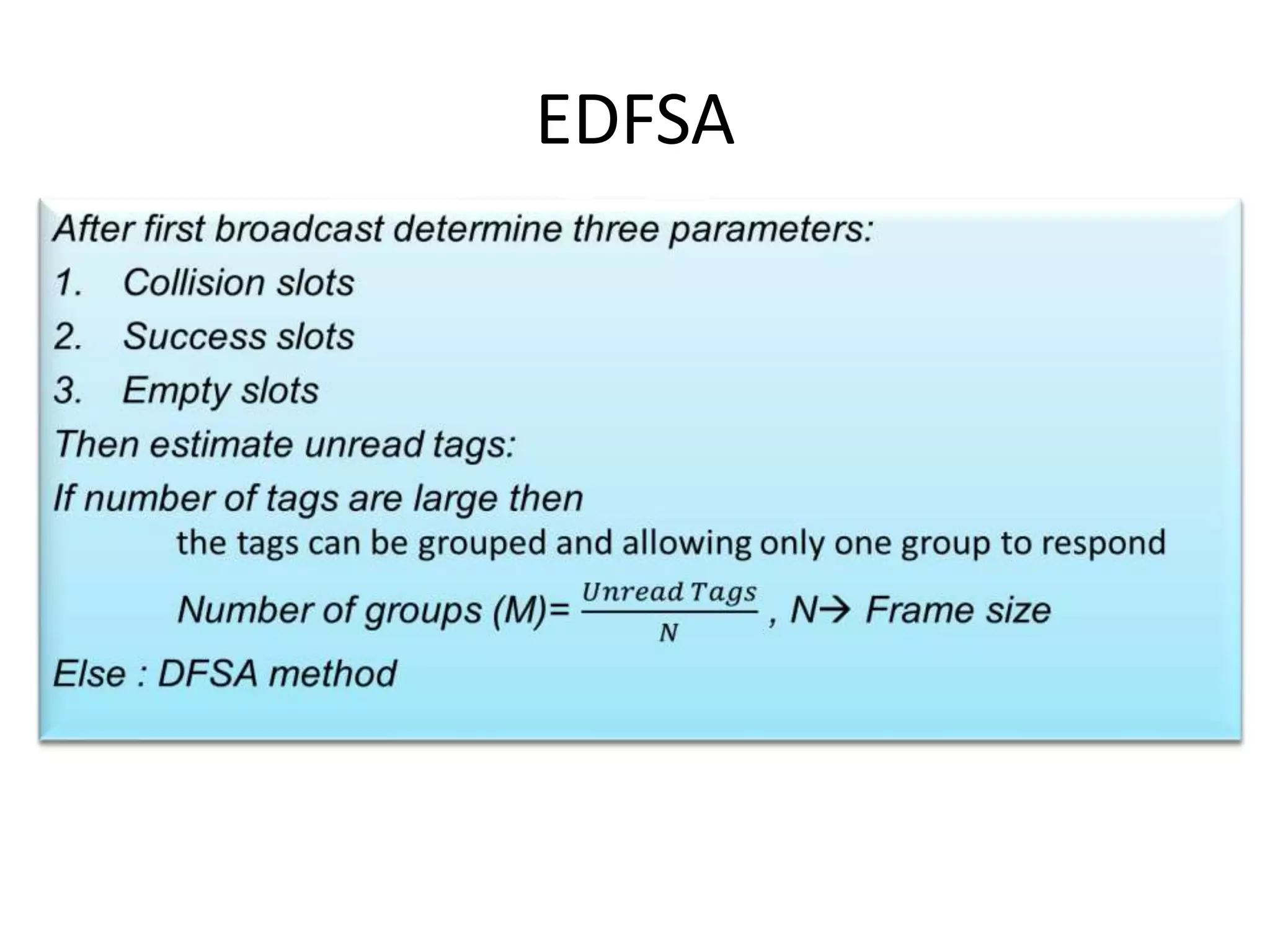
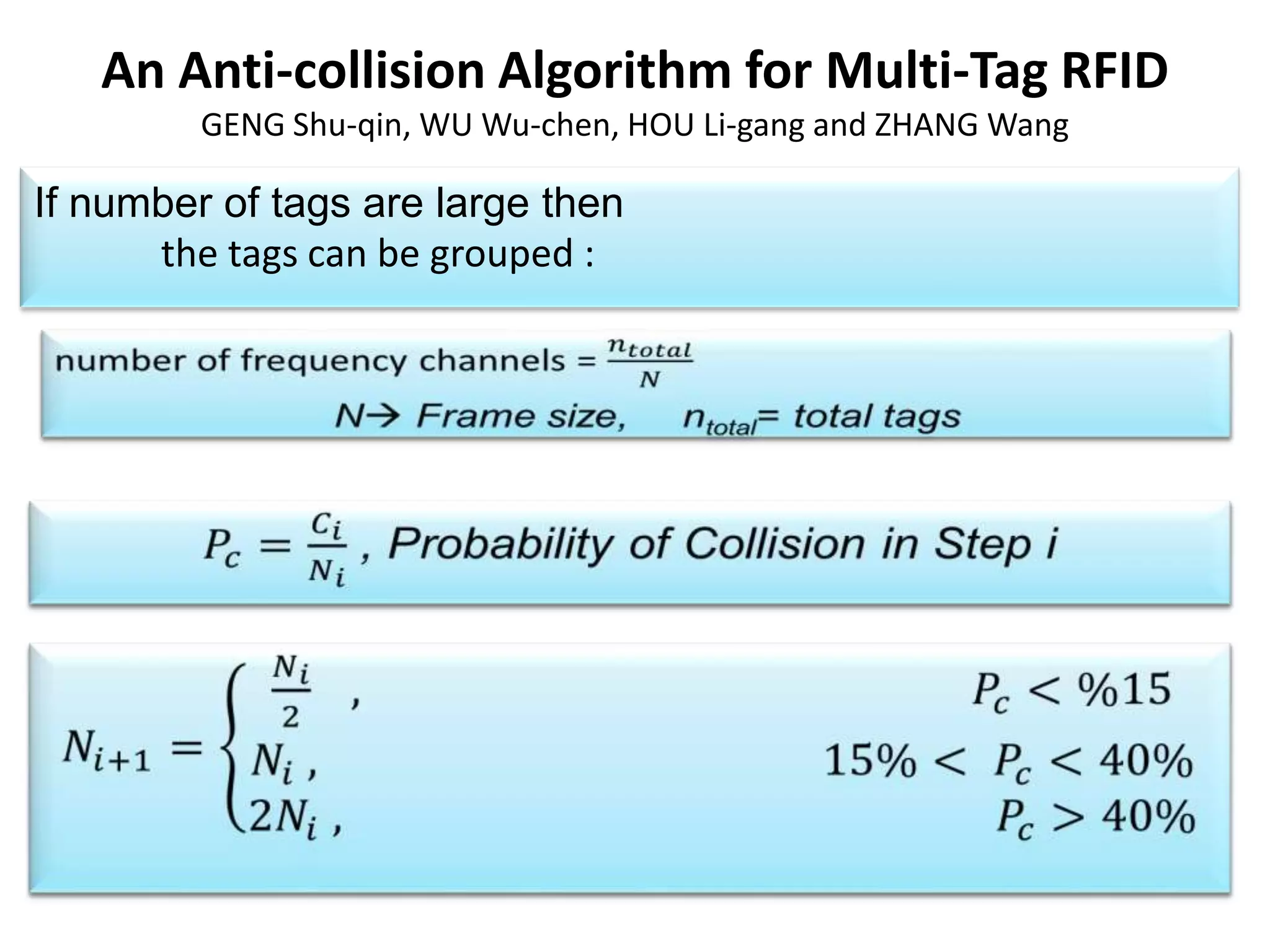
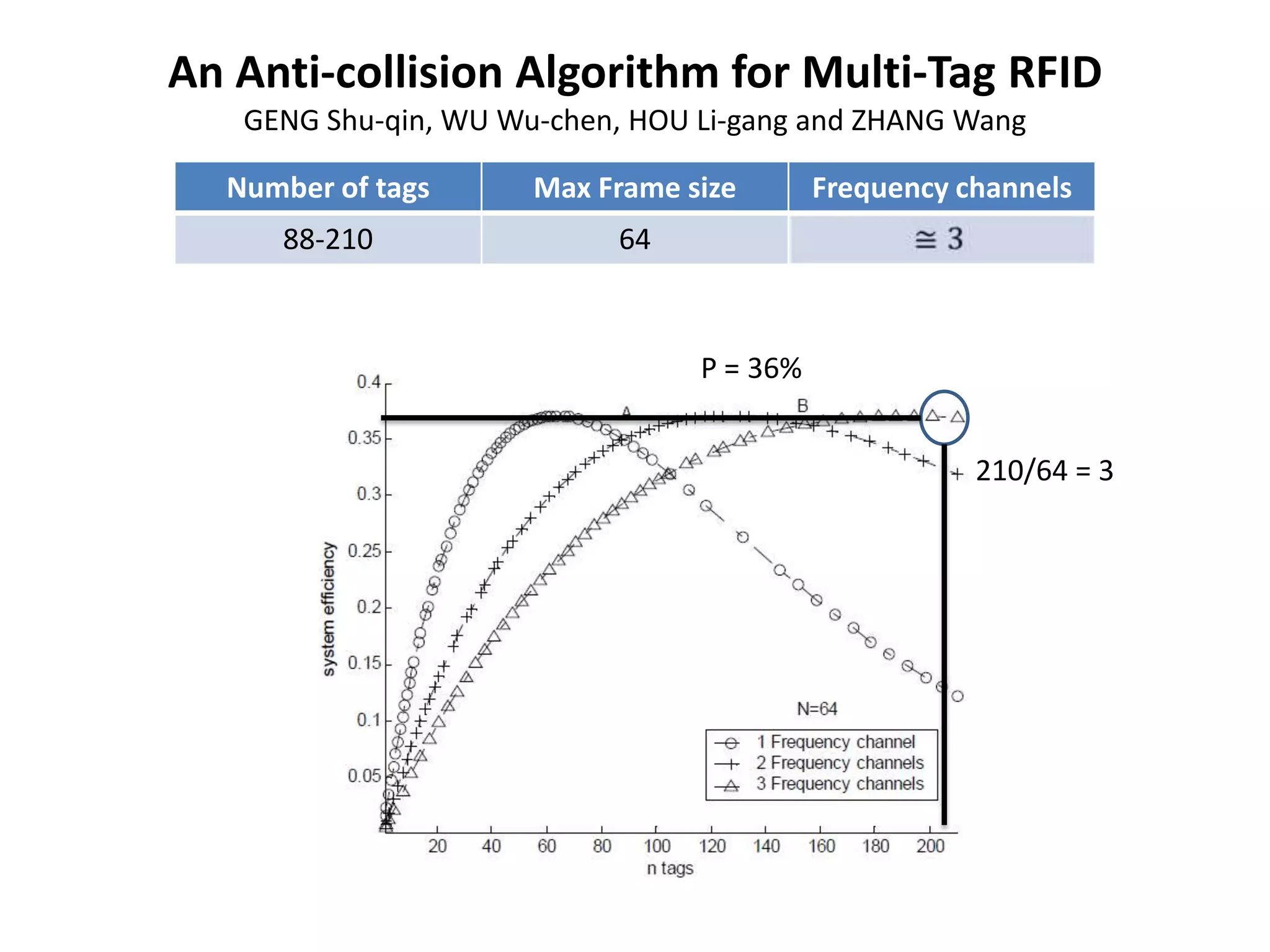
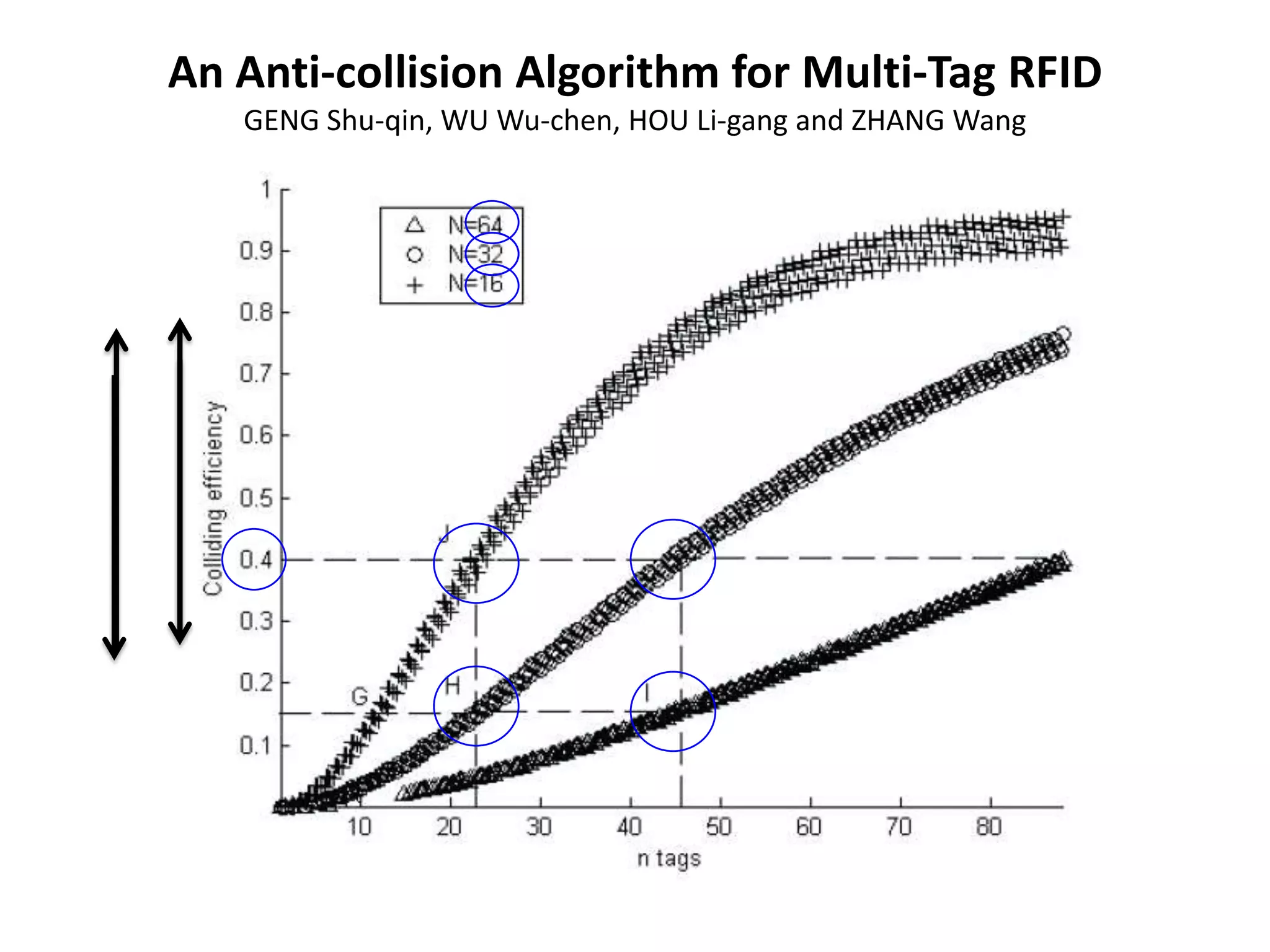
A tree-based anti-collision protocol is proposed for RFID tag identification. The protocol uses a binary tree structure where tags respond in assigned slots determined by their IDs. In each time slot, the reader broadcasts a query and any responding tags transmit their IDs. If a collision occurs, the reader divides the tags into two groups for the next slot based on their IDs. This process continues until all tags are identified without collision. The protocol reduces the identification time compared to Aloha-based methods.







![A Novel Anti-collision Protocol in Adaptive Framed Slotted Aloha about RFIDTags
Deng Zhongting, Wu Haifeng* , Liu Jing, Tan Yuan
Algorithm 1. ADFA Reader Operation
1 Start
2 % Initialize L and RSC % L is frame length.
3 if RSC=NULL
4 L=N % N is set by user (frame size)
5 else
6 L=RSC (frame size = readable s n)
---------7 end if
8 RSC=0
------------9 do {
10 SC=0 % initialize SC
11 Transmit the command starting a frame
-----------------12 do {
13 Transmit the command starting a slot
14 Receive tag response and detect a
collision
15 if tag collision
16 f=collision
17 Transmit f
18 else if no tag response
19 f=idle
20 Transmit f
21 else only a tag response
22 Receive ID from tag and store it
23 RSC=RSC+1
24 f=successful
SC = Slot Counter
RSC = Readable slot number
frame length in a read cycle is set to
the RSC’s value in the last cycle
25 Transmit f with RSC
26 end if
27 SC=SC+1
28 }while SC<L ( end do line 12)
29 [E, S, C]=performCountSlot(L)
30 % Counts empty, successful and collision slots in
31 % a frame with L
32 L=2C
33 }while C>0 ( end do line 9)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rfid-20tag-20anti-collision-20protocols-140309144556-phpapp02/75/RFID-tag-anti-collision-protocols-20-2048.jpg)

