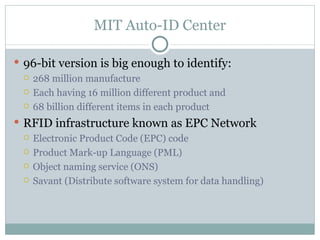
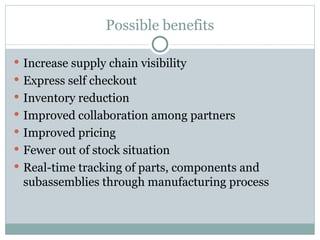
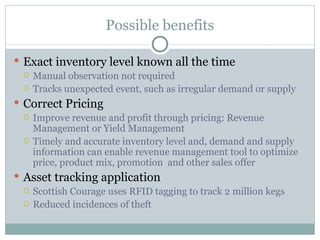
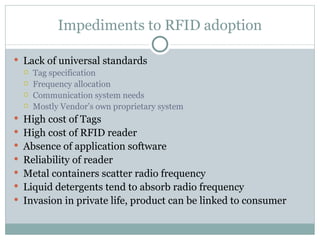
RFID technology uses tags and readers to transmit data without direct line of sight and can help increase supply chain visibility. The Auto-ID Center was established in 1999 to develop low-cost RFID standards and included several university labs. It later split into the Auto-ID Center for research and EPCglobal to develop and administer the EPC Network RFID infrastructure. While RFID adoption faces challenges like cost and lack of standards, it provides benefits like inventory tracking, asset management, and reducing theft.