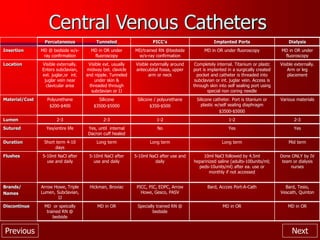
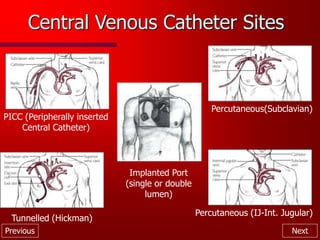
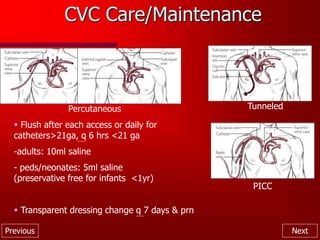
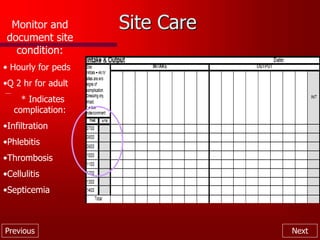
This document provides an overview of intravenous therapy, including vein anatomy, purposes of IV therapy, types of peripheral and central venous access devices, and guidelines for starting and maintaining IVs. It discusses topics like flushing protocols, dressing changes, complications to monitor for like infiltration and phlebitis, and troubleshooting issues with IV devices. The overall aim is to enhance nurses' knowledge of caring for patients receiving intravenous therapy.




![Previous Next
Flushing Peripheral IV’s
Use prefilled saline and heparin flush syringes located in PYXIS
Heparin flush concentrations available:
-100u/ml (5ml in a 10ml syringe)
-10u/ml (2ml in a 3ml syringe)
Flushing intervals and amounts
- Peds: q 6hrs.
<22ga 1ml 0.9%NS followed by 1ml heparinized
(10units/ml) saline
- Adults: q 8hrs
w/1ml. 0.9%NS [3ml heparinized saline for OB]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/revisedwebivtherapy-221121134228-4722bc02/85/Revised_web_IV_therapy-ppt-13-320.jpg)