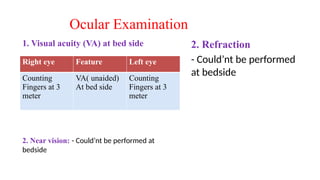
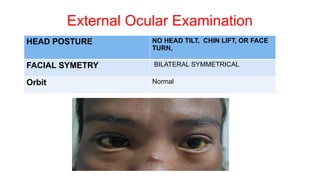
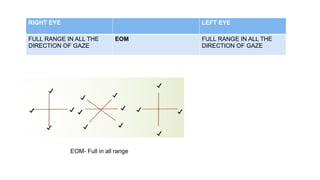
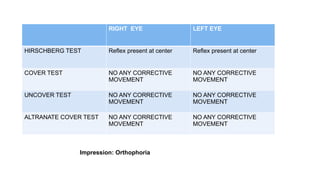
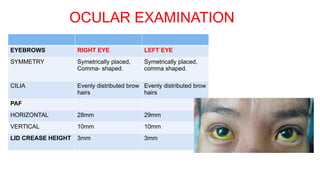
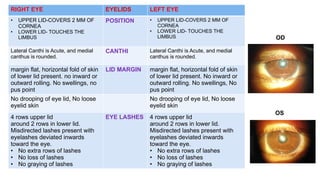
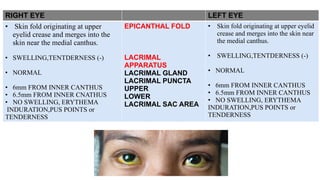
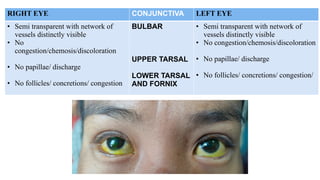
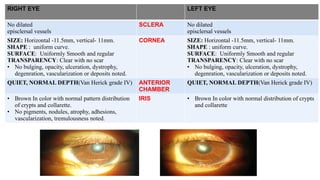
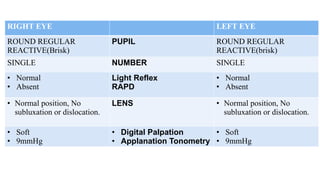
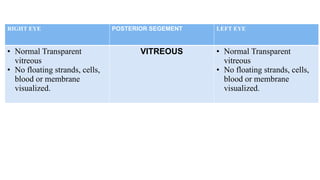
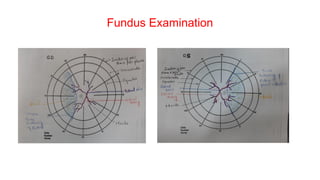
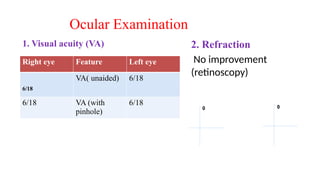
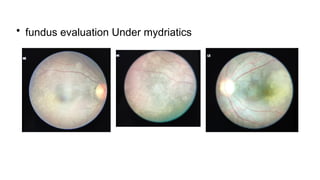
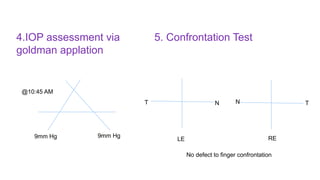
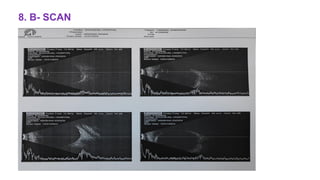
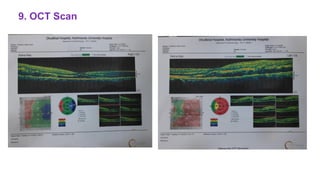
The document presents a case of a 30-year-old female diagnosed with exudative retinal detachment (ERD) associated with severe pre-eclampsia, showing acute onset of blurred vision and curtain-like visual disturbances following emergency cesarean delivery. ERD, although rare in pre-eclampsia cases, is linked to choroidal ischemia and can lead to significant visual impairment if untreated; however, with proper management focusing on blood pressure control and timely delivery, the visual prognosis can be favorable. The case emphasizes the importance of multidisciplinary care between obstetricians and ophthalmologists for optimal maternal and fetal outcomes.