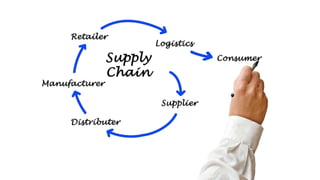
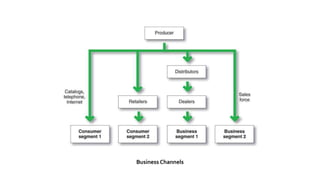
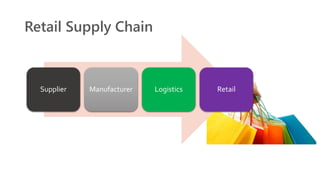
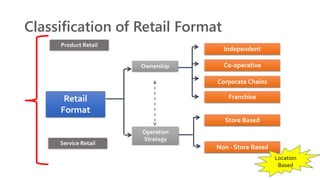
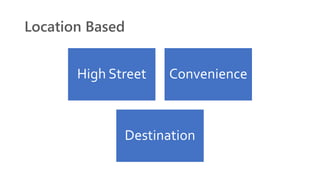
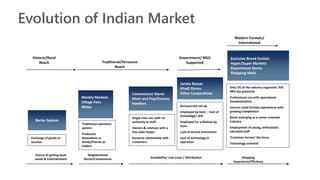
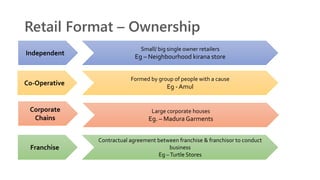
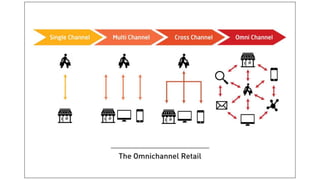
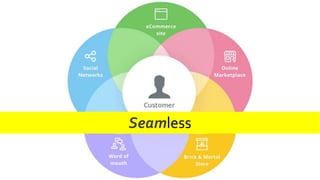
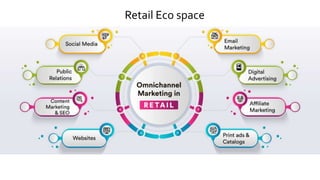
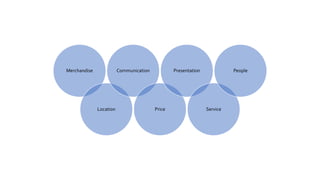
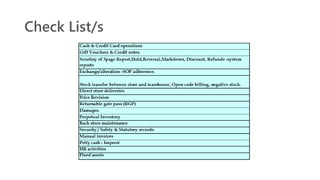
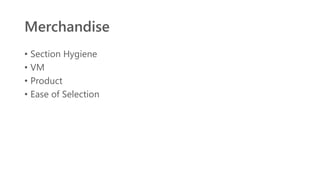
The document provides an introduction to the retail industry. It defines retailing as activities involved in selling goods or services to the final consumer for personal use. It discusses the evolution of retail from early barter systems and traditional formats like village markets to modern formats including convenience stores, supermarkets, shopping malls, and non-store formats like e-commerce. It also covers retail operations, formats based on ownership and strategy, key performance indicators for retail operations, and considerations for different customer segments.