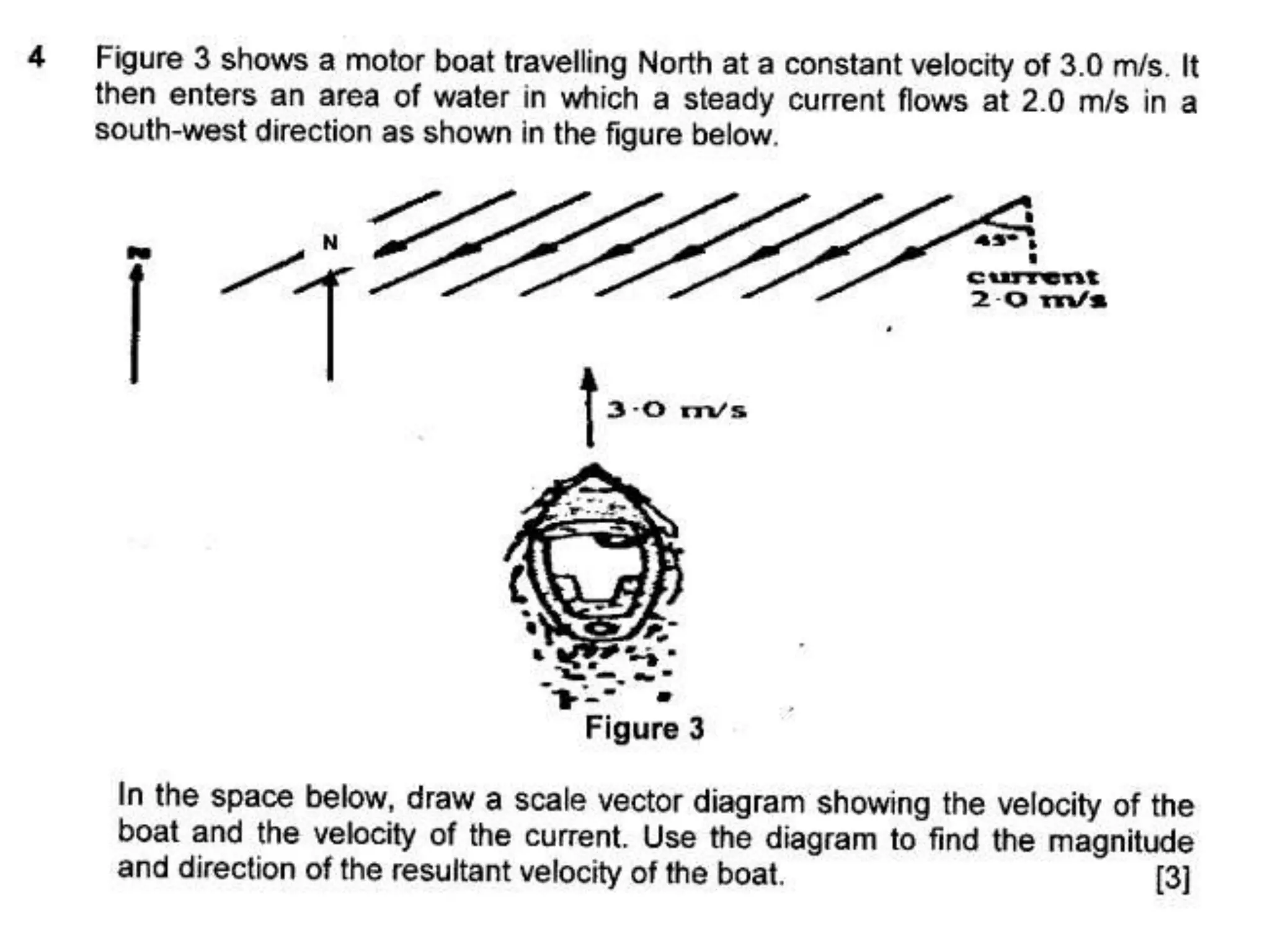
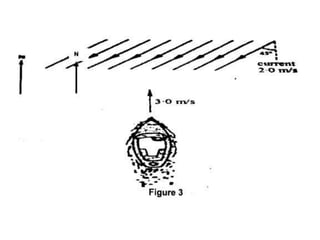
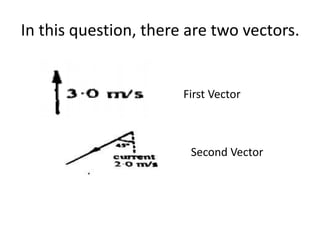
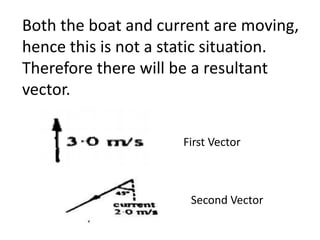
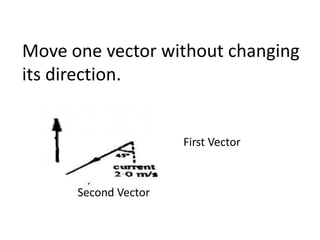
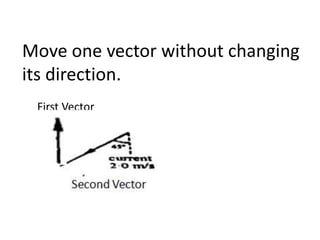
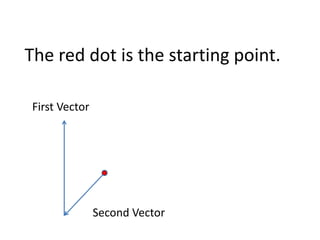
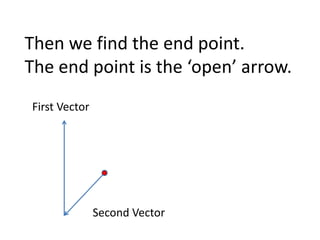
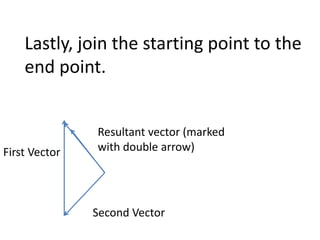
This document discusses how to find the resultant vector of two vectors using the tip-to-tail method. It explains that because the boat and current are both moving, their relationship can be represented by two vectors. It then demonstrates using the tip-to-tail method by showing how to move one vector without changing its direction, identify the starting and end points on a scaled diagram, and join the points to determine the resultant vector.