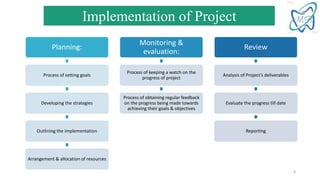
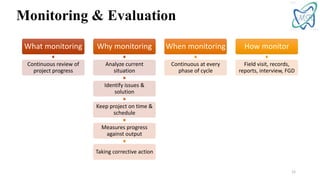
The document provides an overview of the Logical Framework Approach (LFA) for project management. It discusses how the LFA establishes a framework to clearly connect all components of a project, including the goal, objectives, activities, results, and indicators. This leads to achievement of expected outcomes through a tight relationship between the different components. The LFA helps ensure all aspects of a proposal are logically aligned and interconnected.