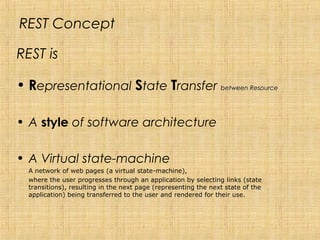
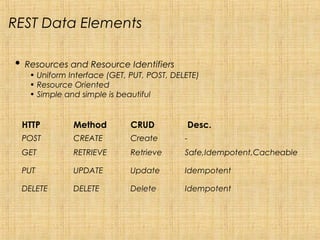
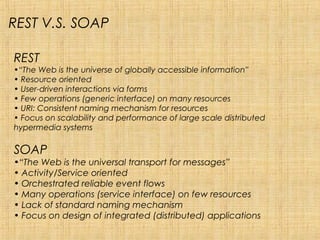
REST is a style of software architecture for distributed hypermedia systems such as the World Wide Web. It uses a stateless, client-server, cacheable communications protocol and standard interface to access and manipulate representations of web resources. The key aspects of REST include using a uniform interface, separating concerns through resources and representations, and hypermedia as the engine of application state. REST contrasts with SOAP which is message-oriented and focuses on integrated applications rather than interacting with resources. While REST and SOA share some principles like loose coupling and statelessness, REST emphasizes resources and representations over messages and operations.