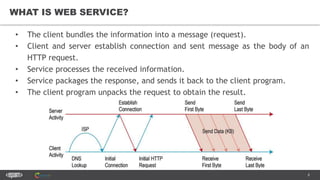
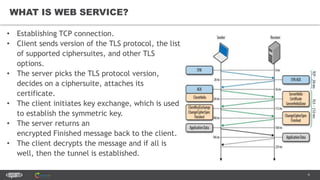
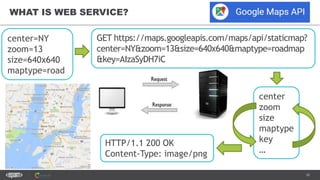
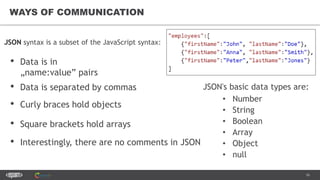
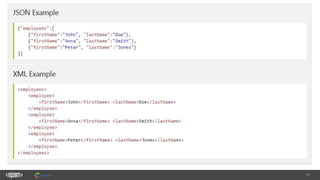
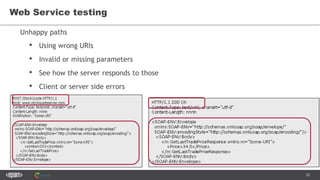
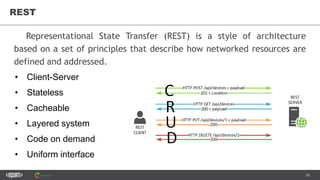
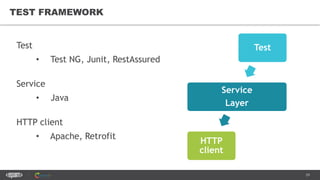
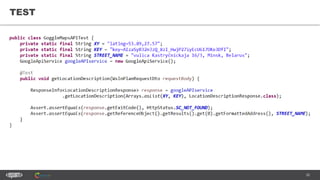
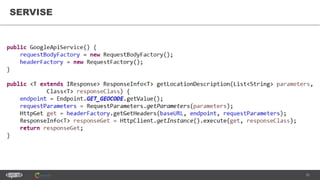
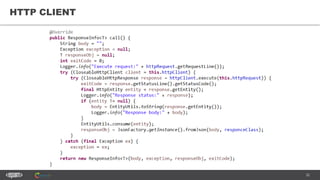
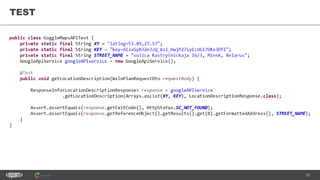
The document provides an introduction to web services and APIs, detailing their definitions, communication methods, and testing strategies. It distinguishes between SOAP and REST architectures, explaining their characteristics and structures, as well as methods for testing web services through both happy and unhappy paths. The author, Andrei Stasevich, has over five years of experience in test automation and offers insights on using various tools and frameworks for testing web services.