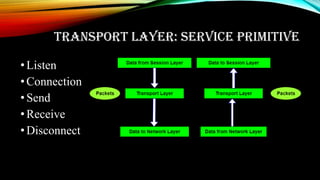
The document discusses the seven-layer OSI reference model. It describes each layer including the physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation, and application layers. The physical layer deals with physical connections and converting data to bits. The data link layer converts bits to frames and provides tools for establishing connections. The network layer converts frames to packets and provides routing between networks. The transport layer reliably transmits packets and provides different classes of service. The session layer transmits data at time intervals and manages dialogs and tokens. The presentation layer translates data formats and performs encryption/compression. The application layer produces data and provides network services like file transfer and mail.