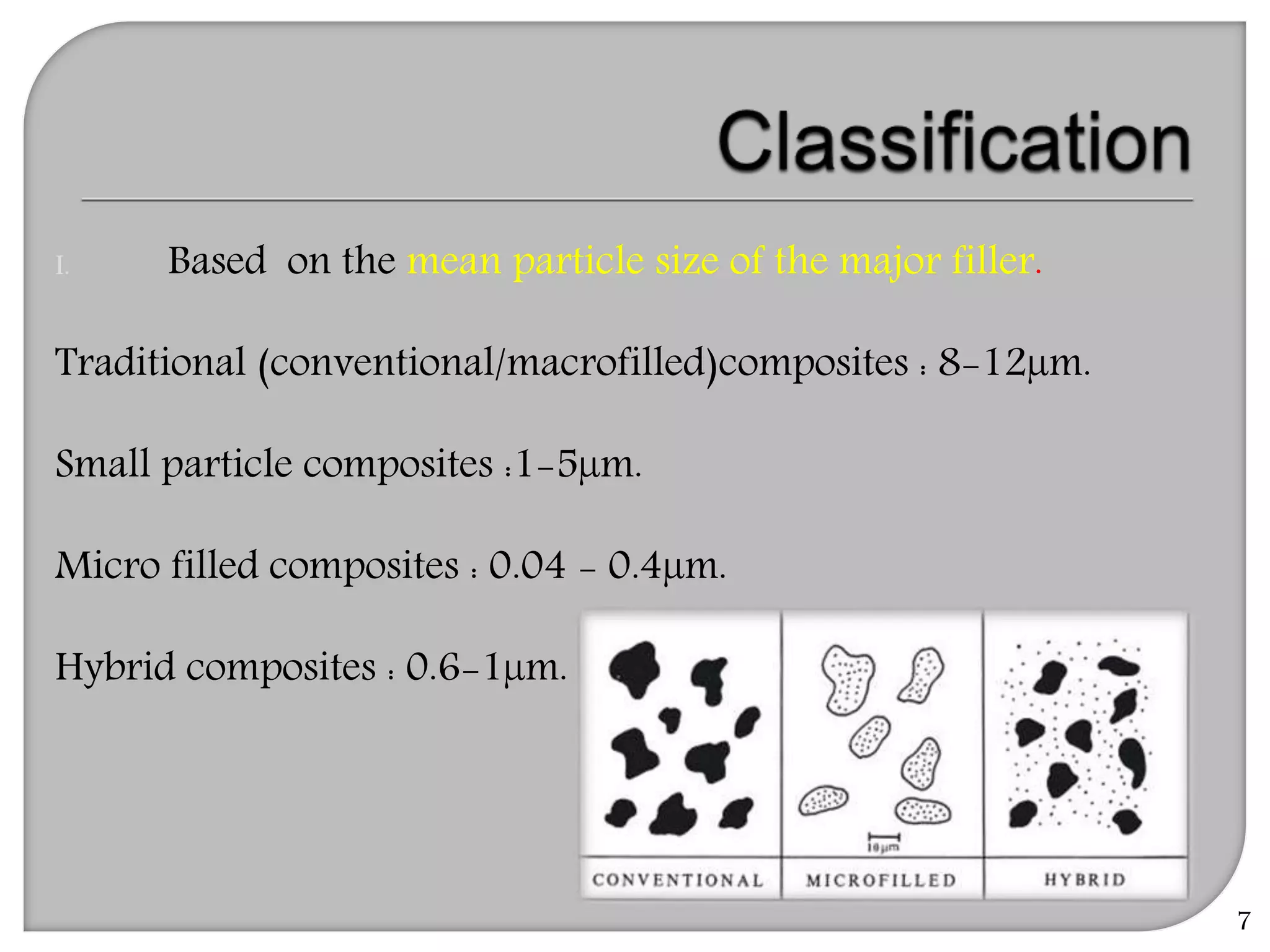
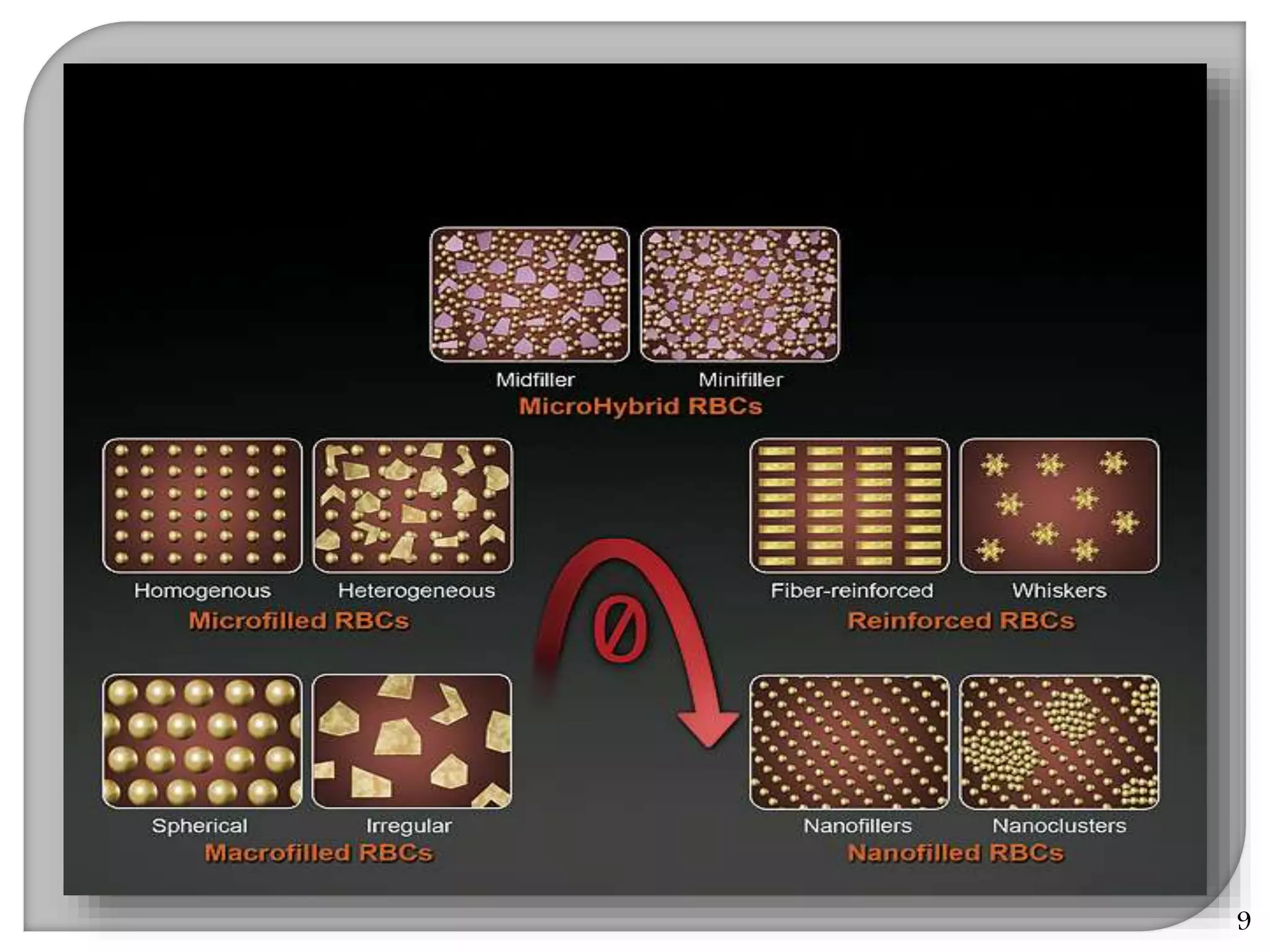
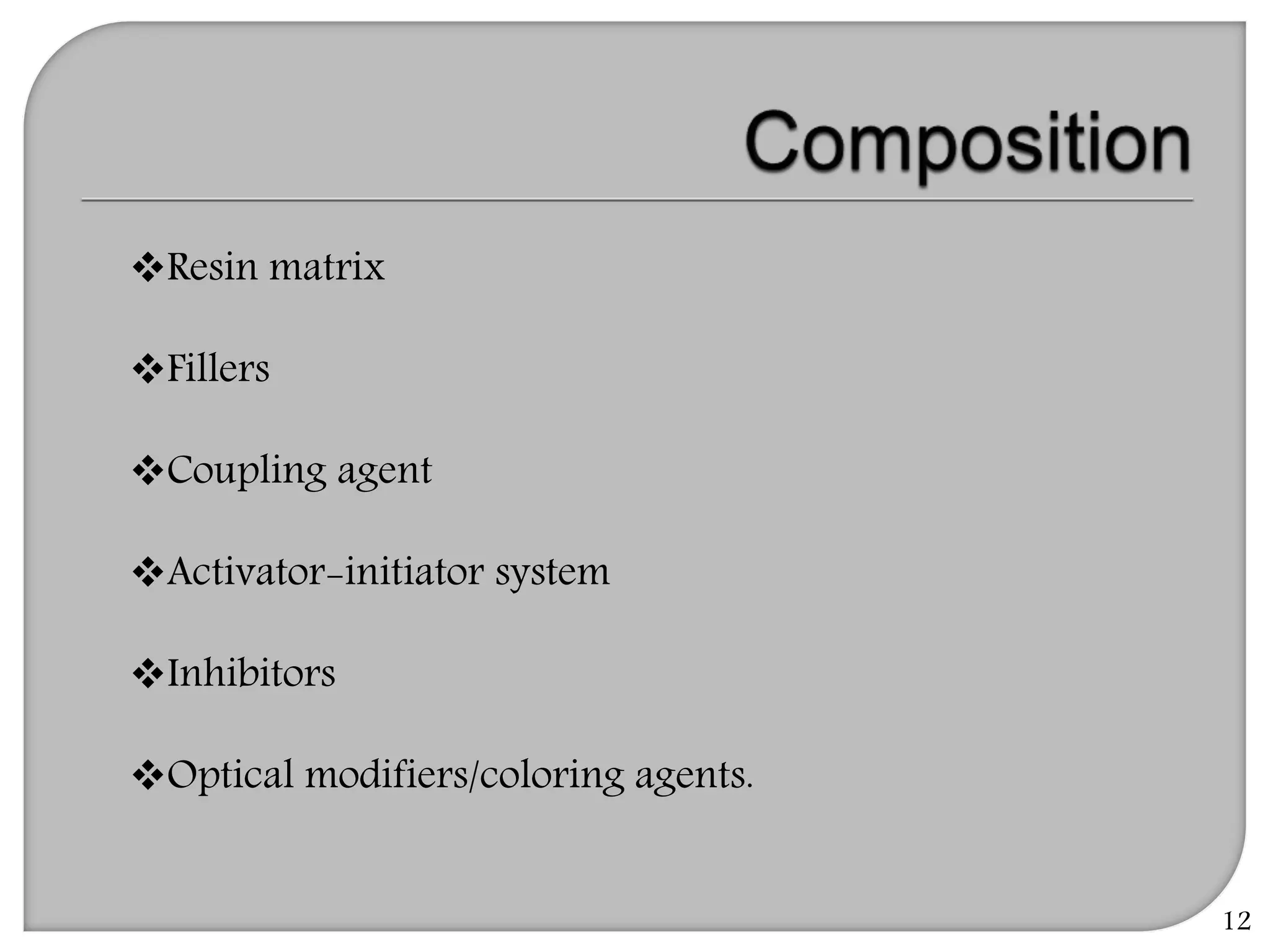
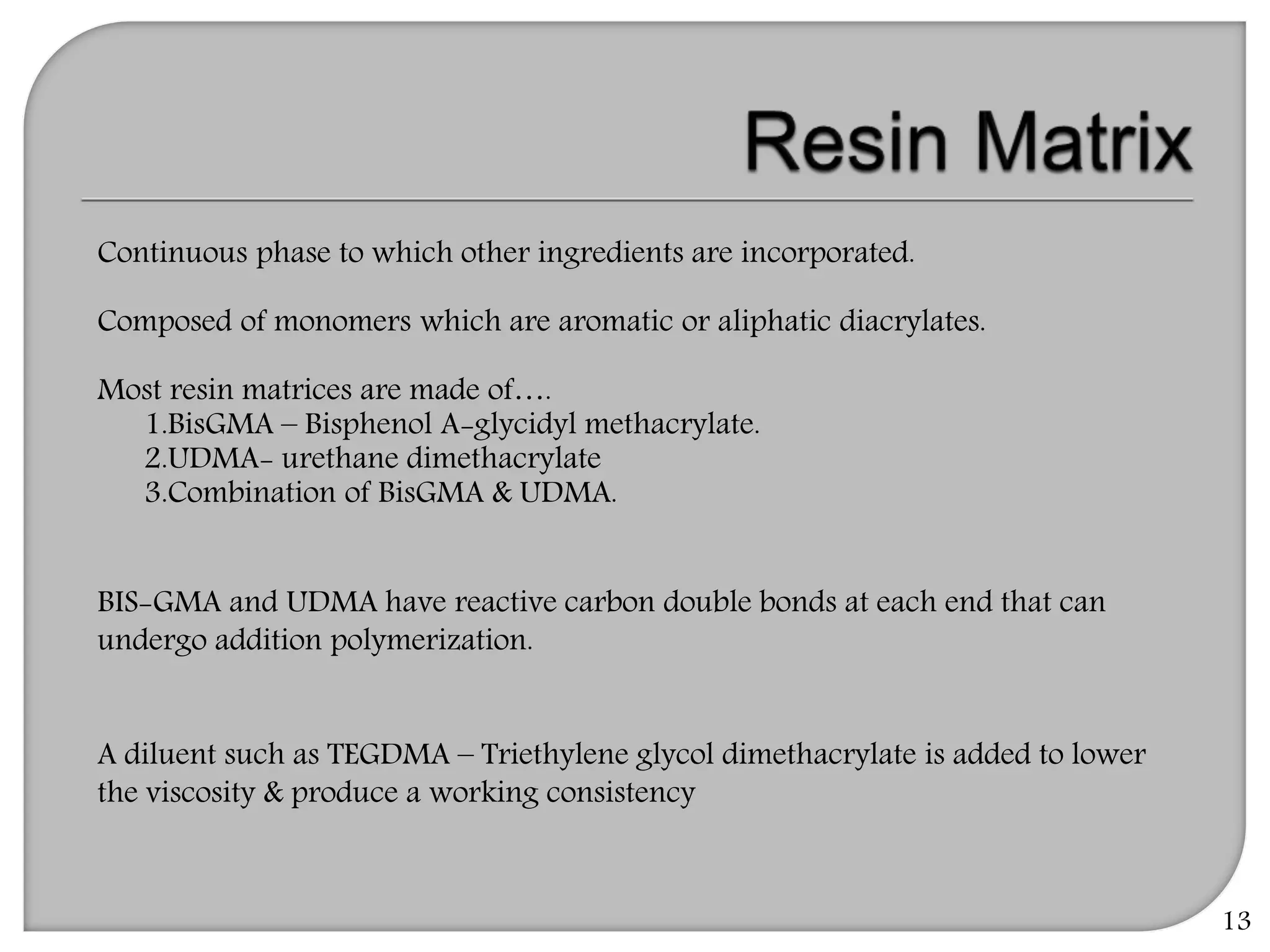
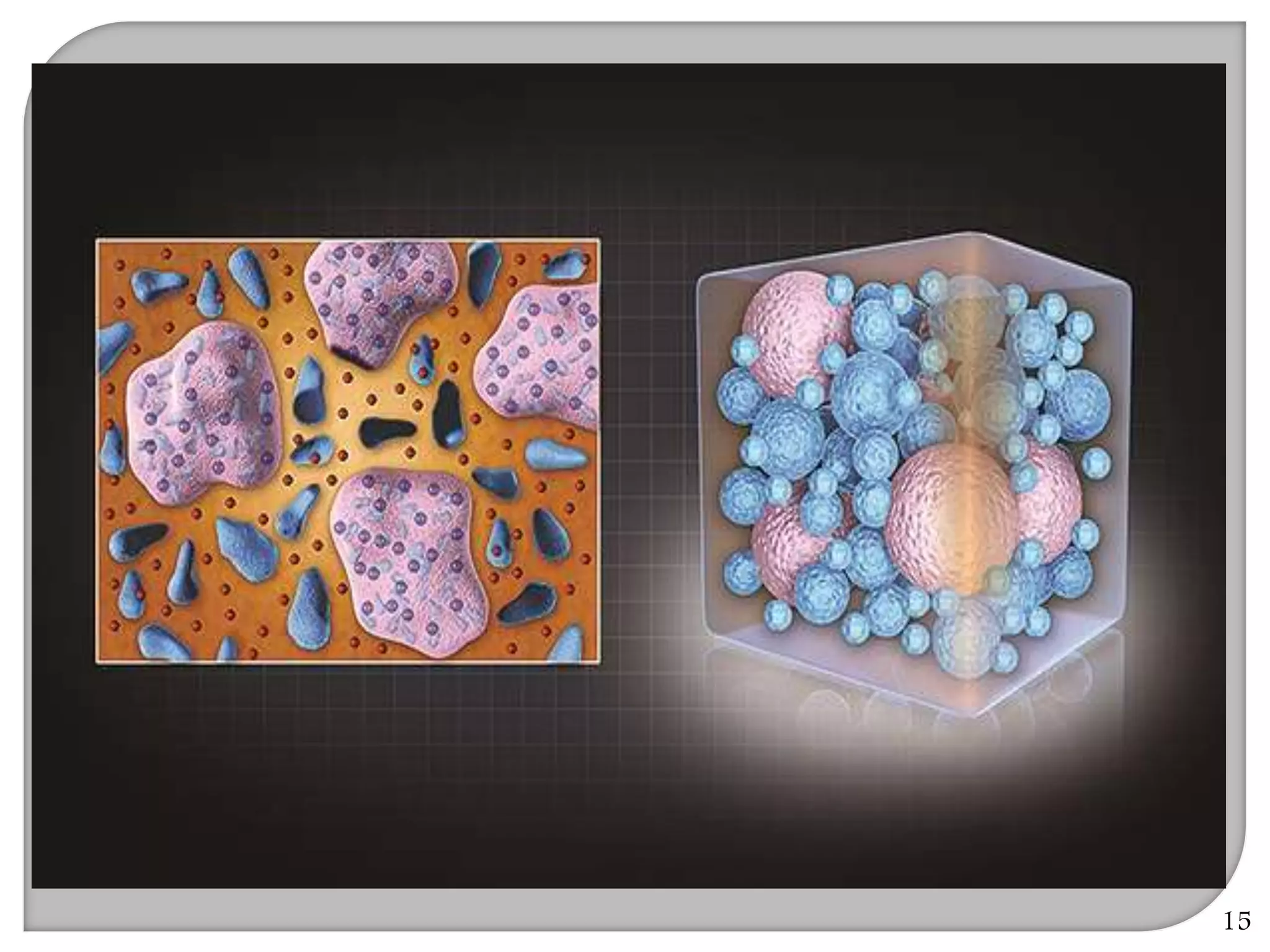
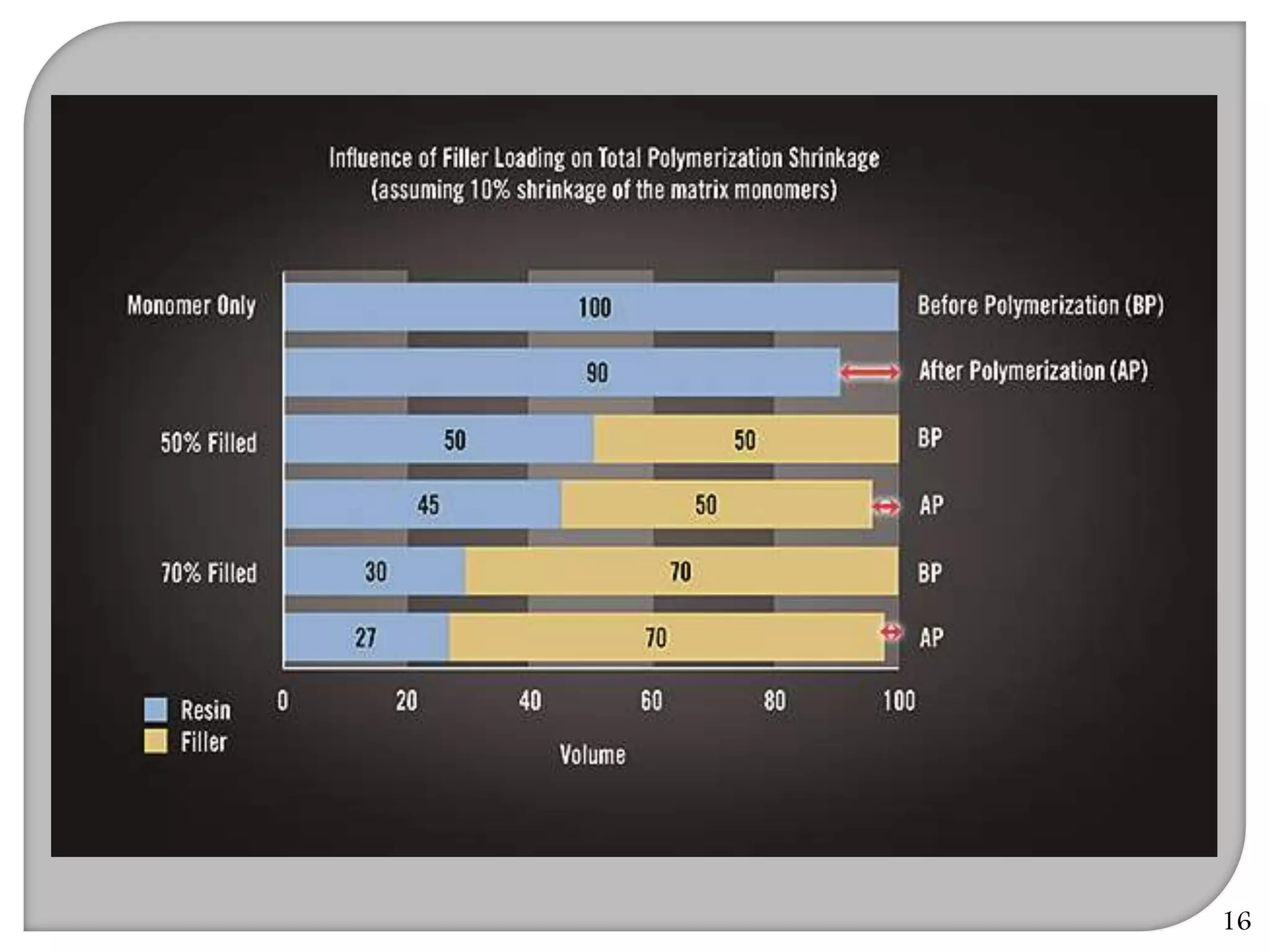
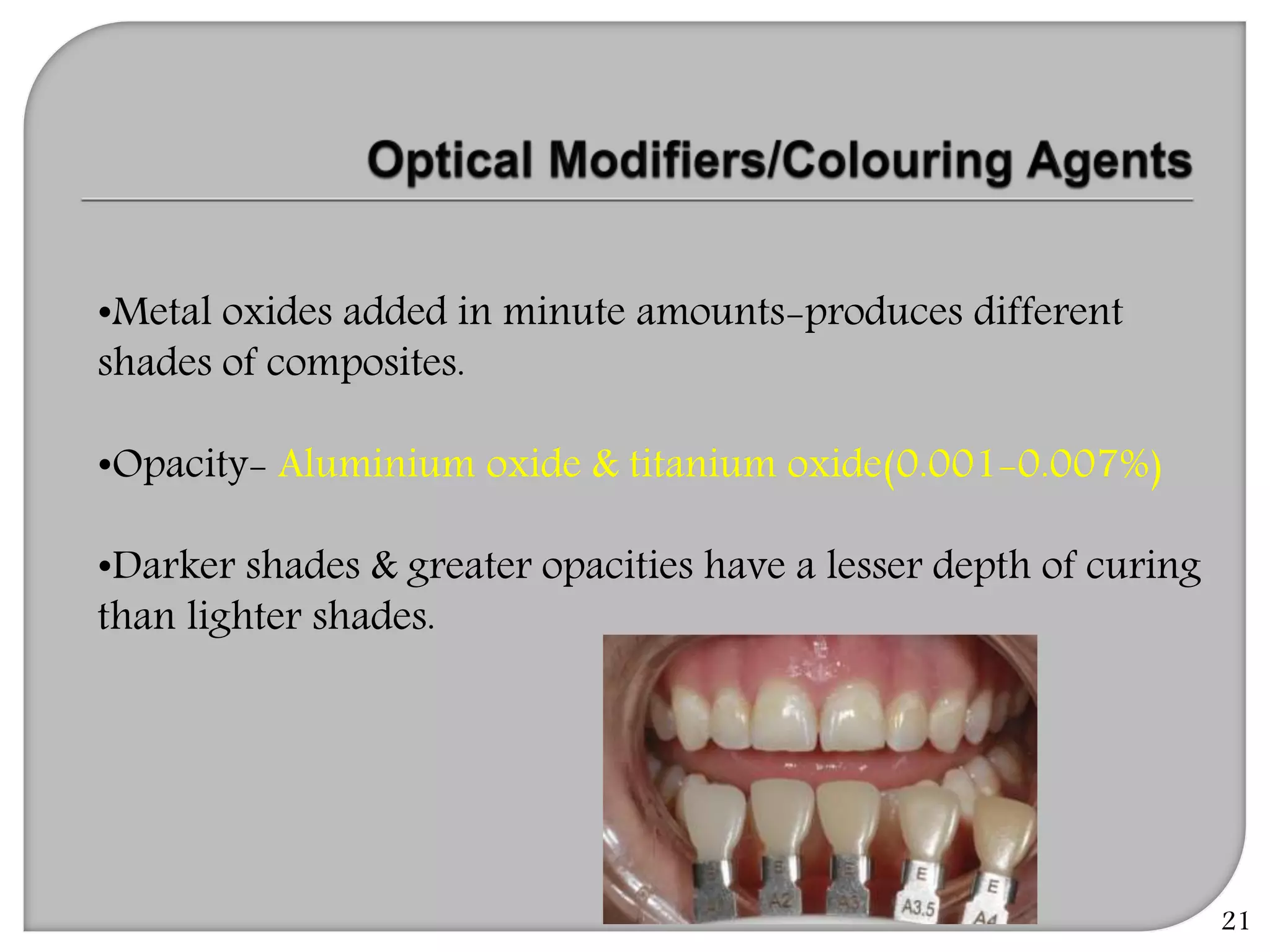
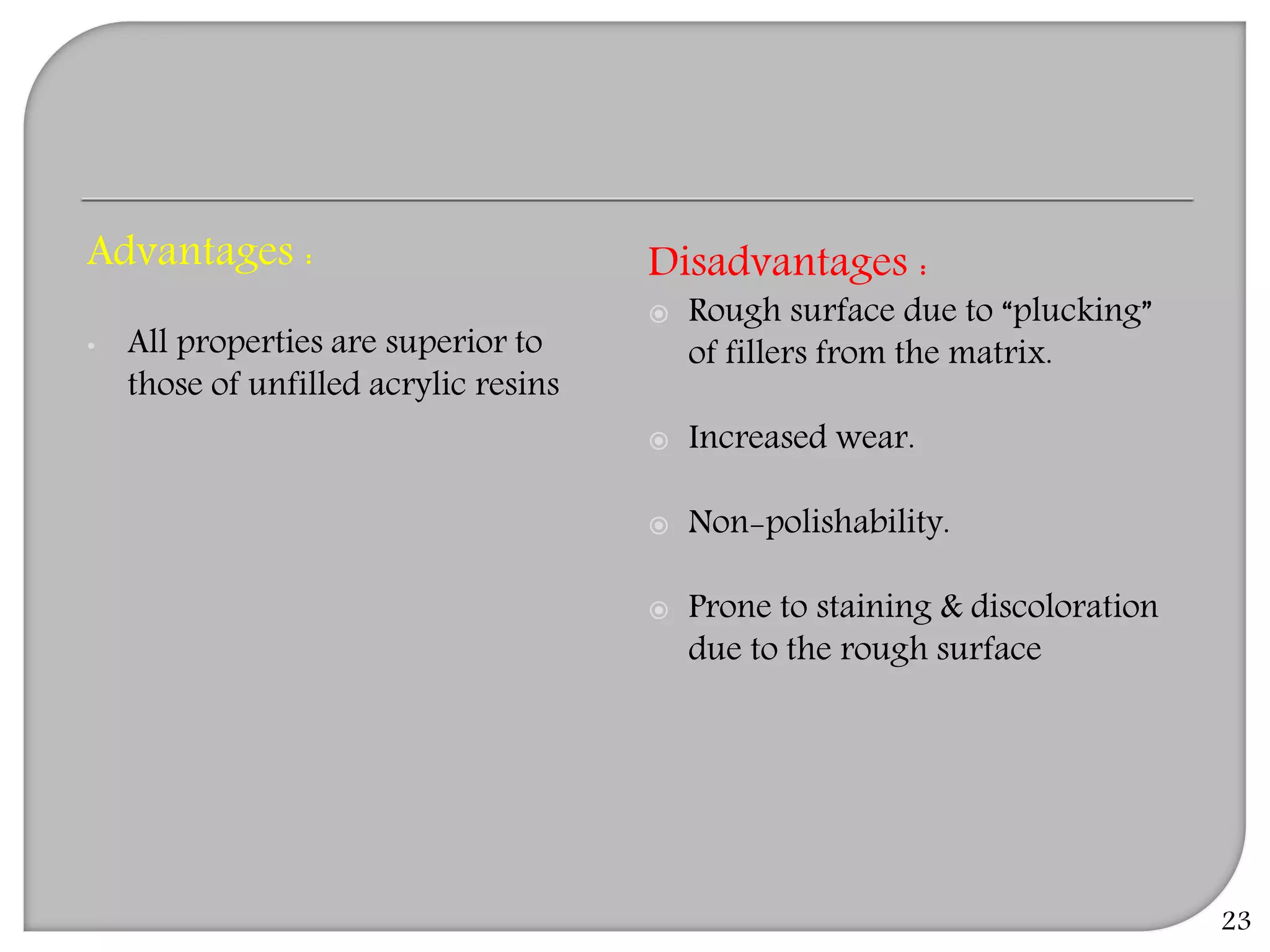
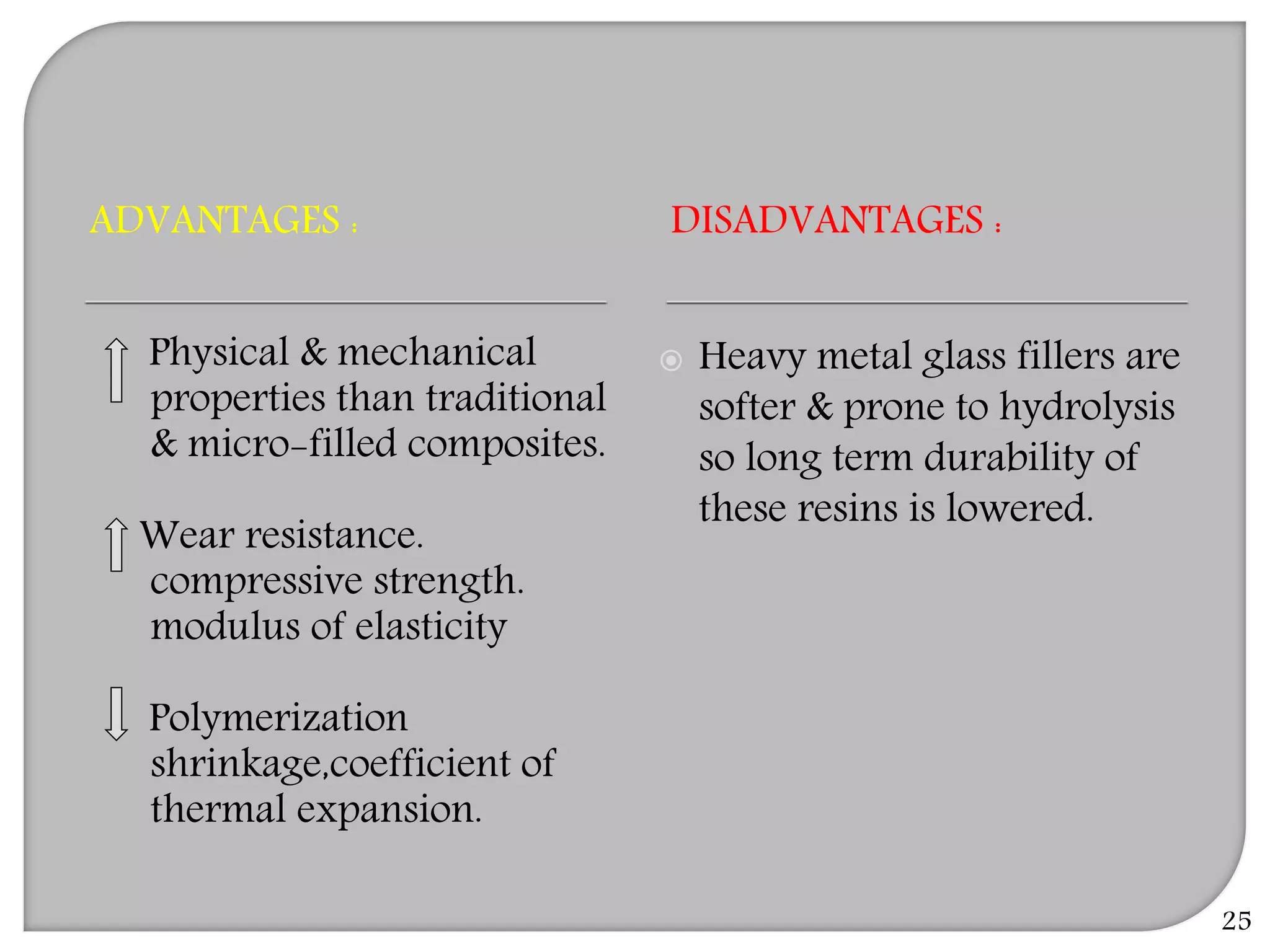
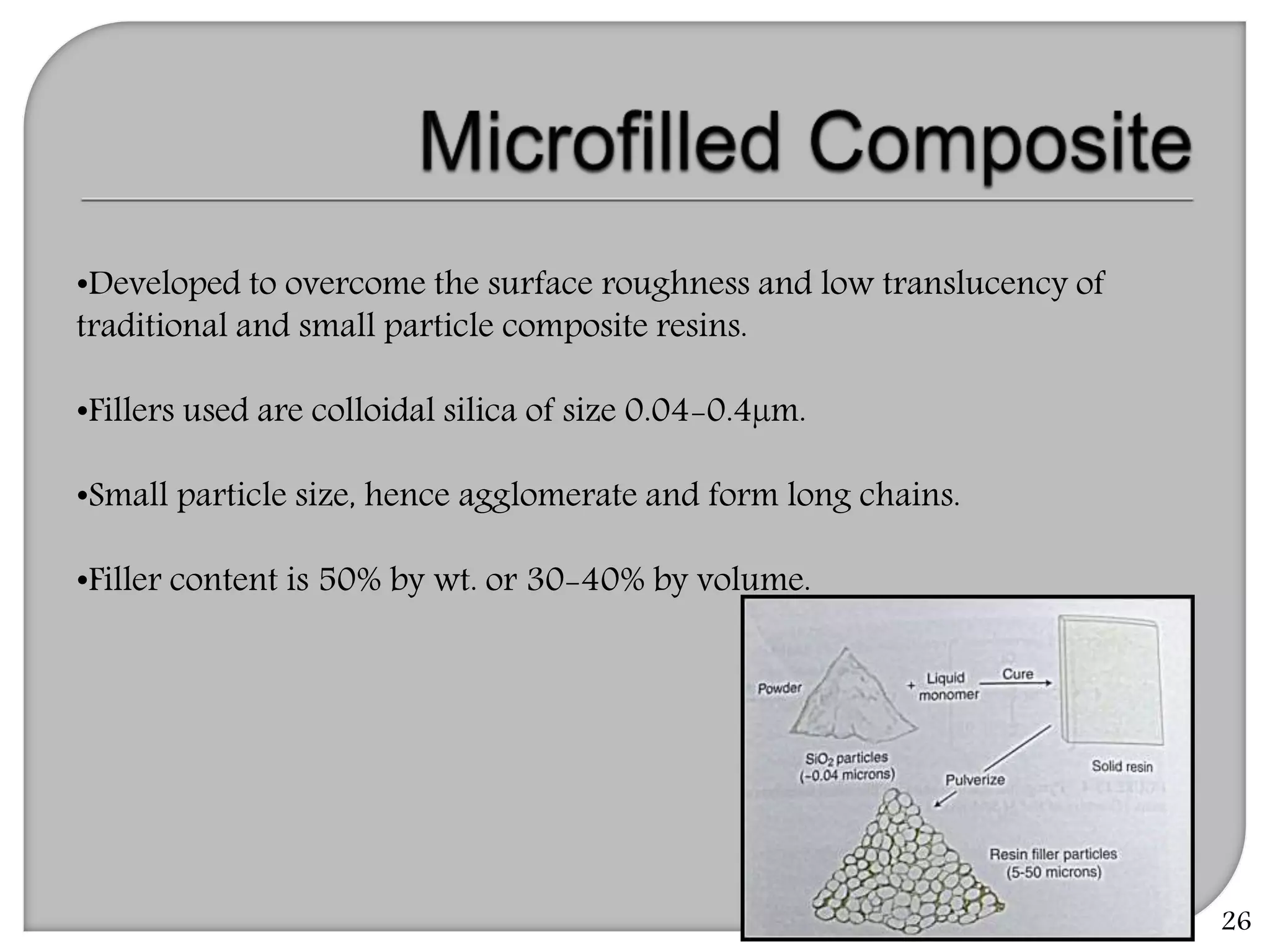
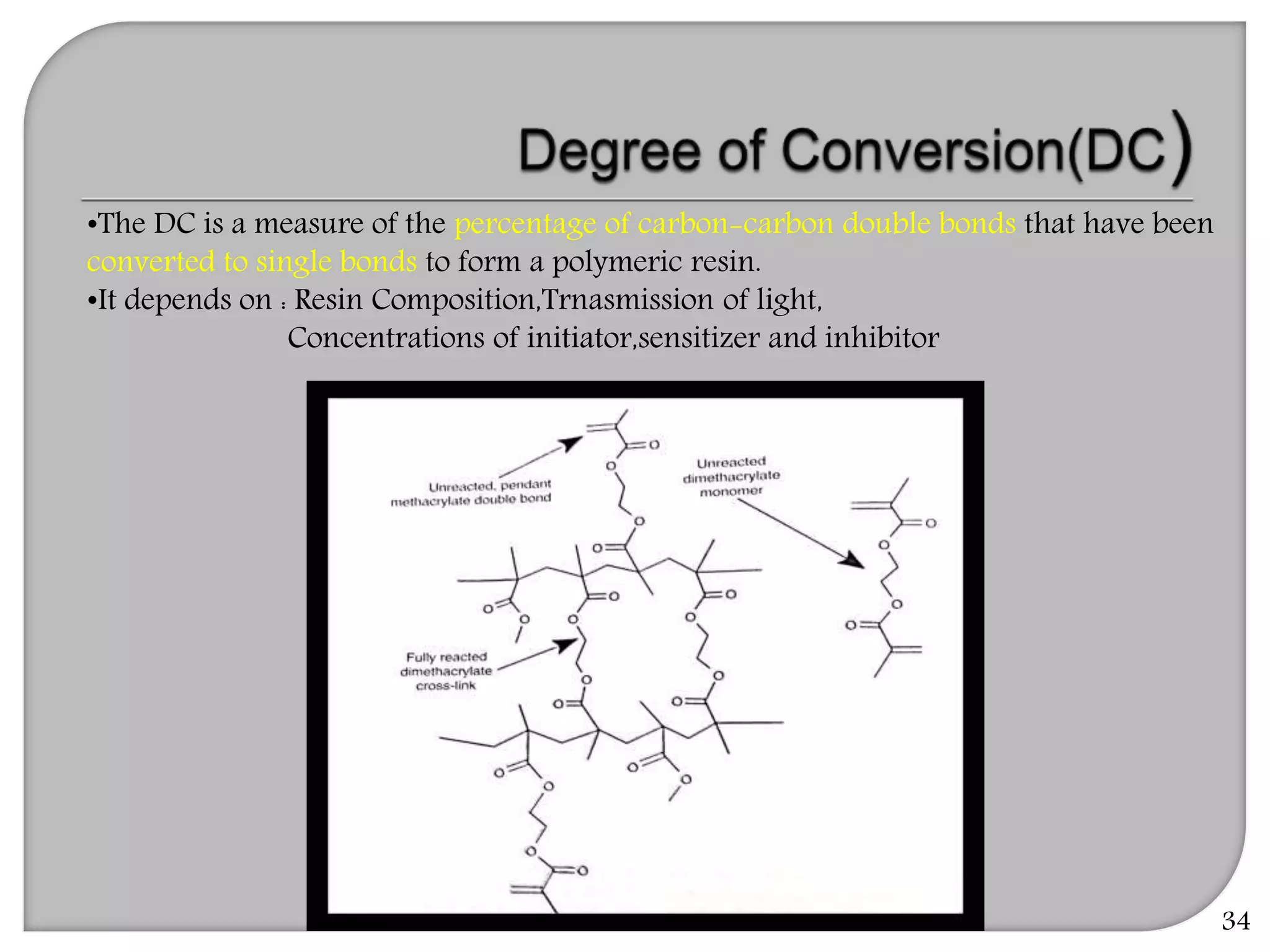
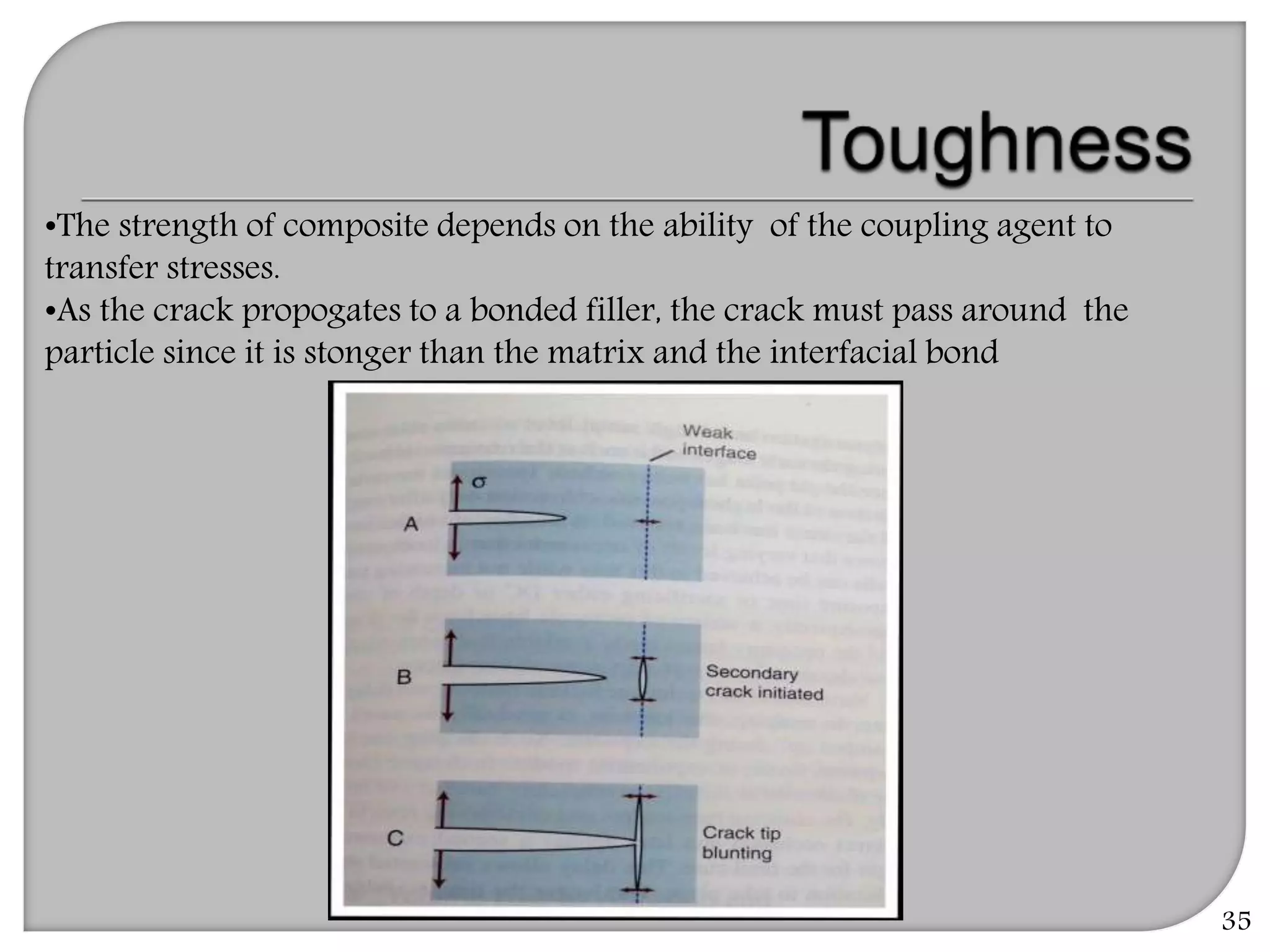
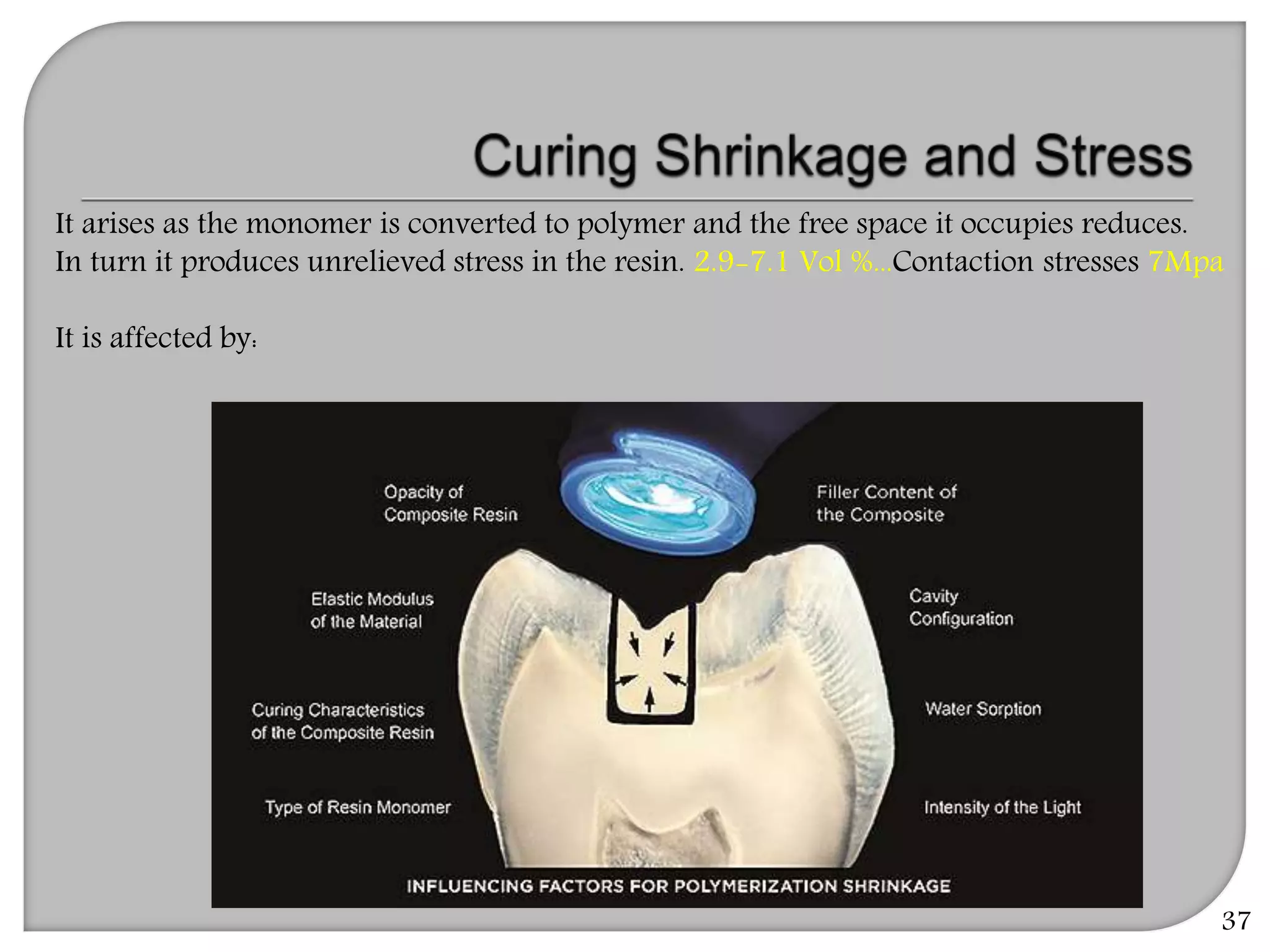
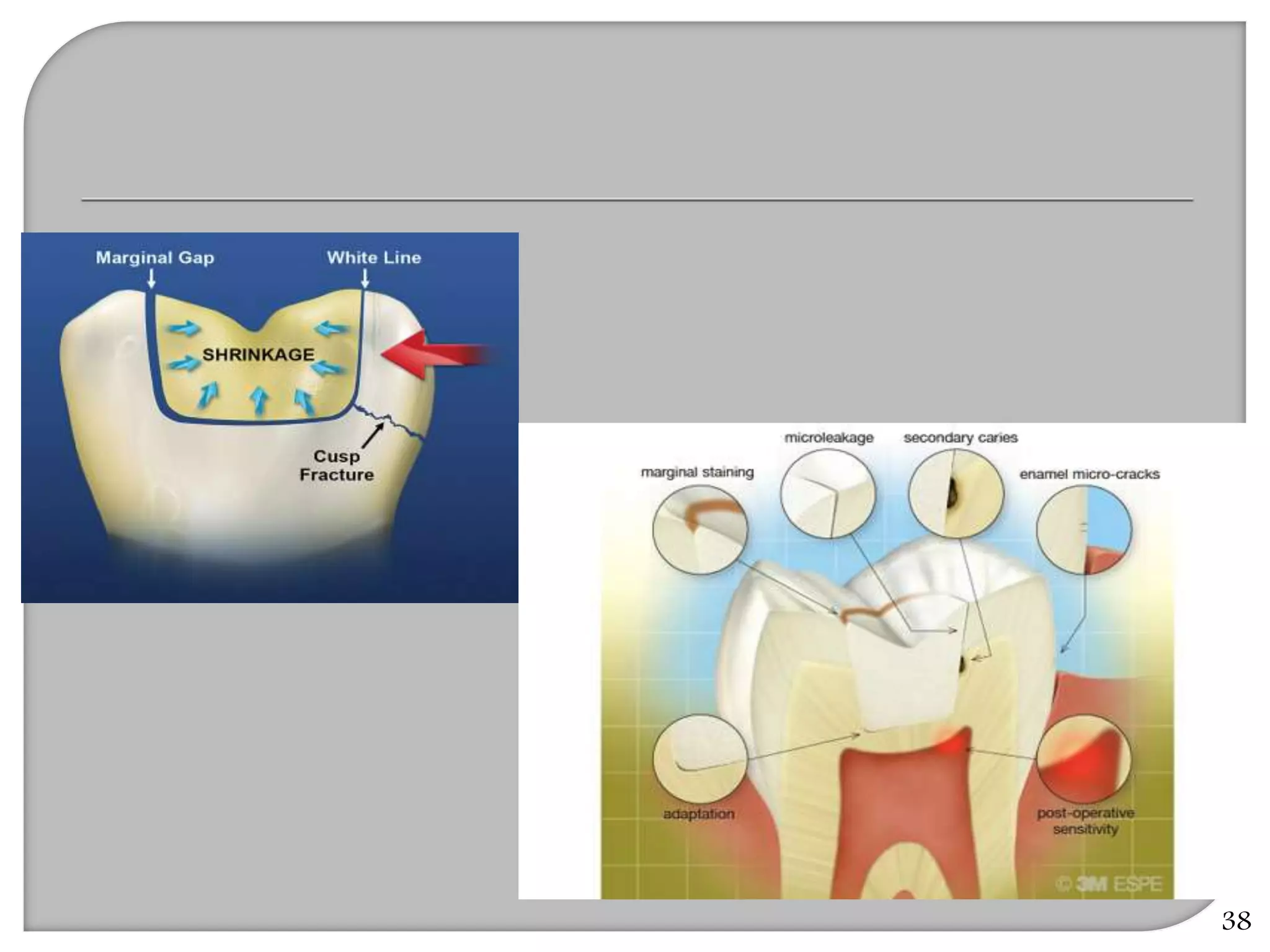
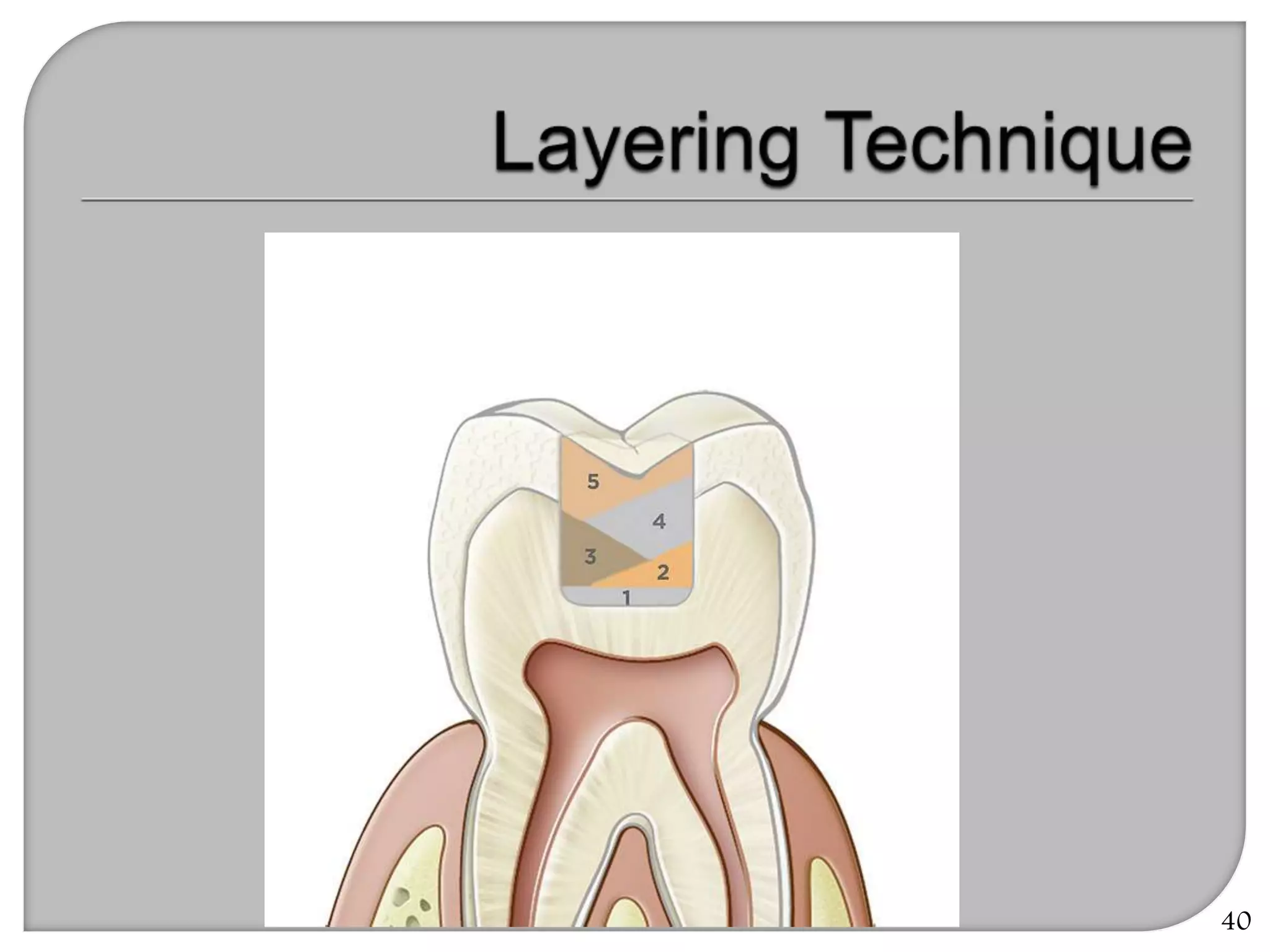
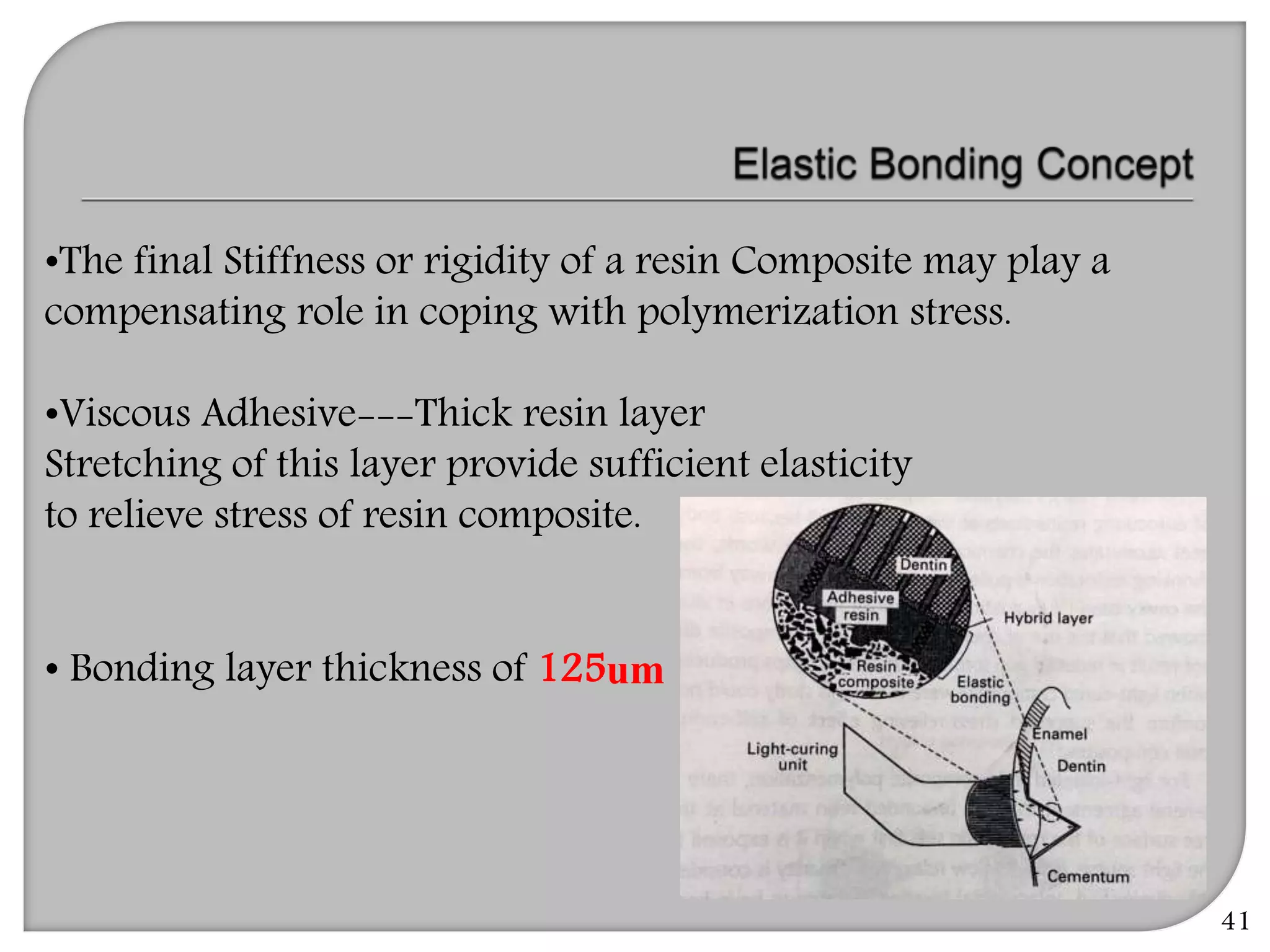
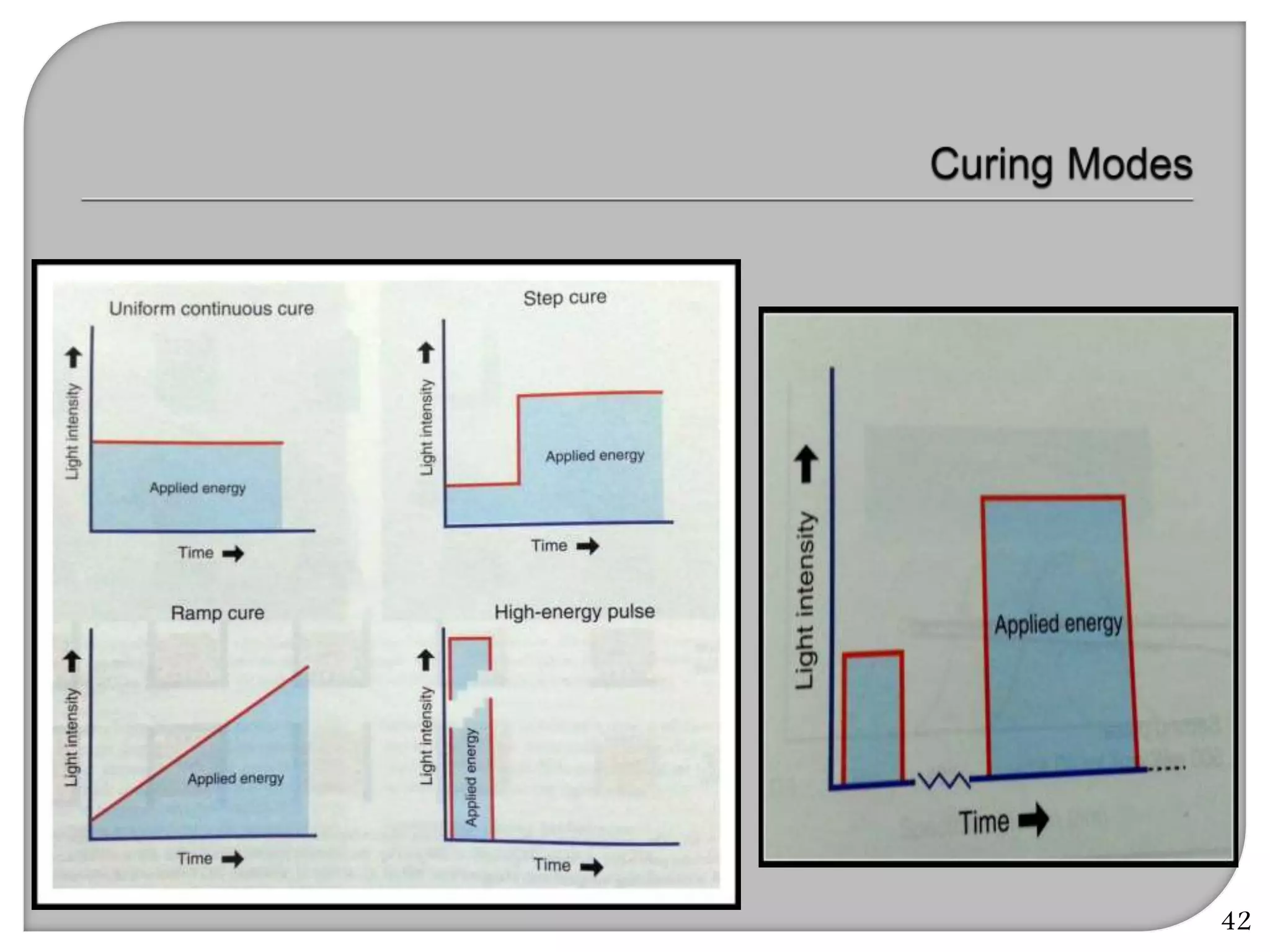
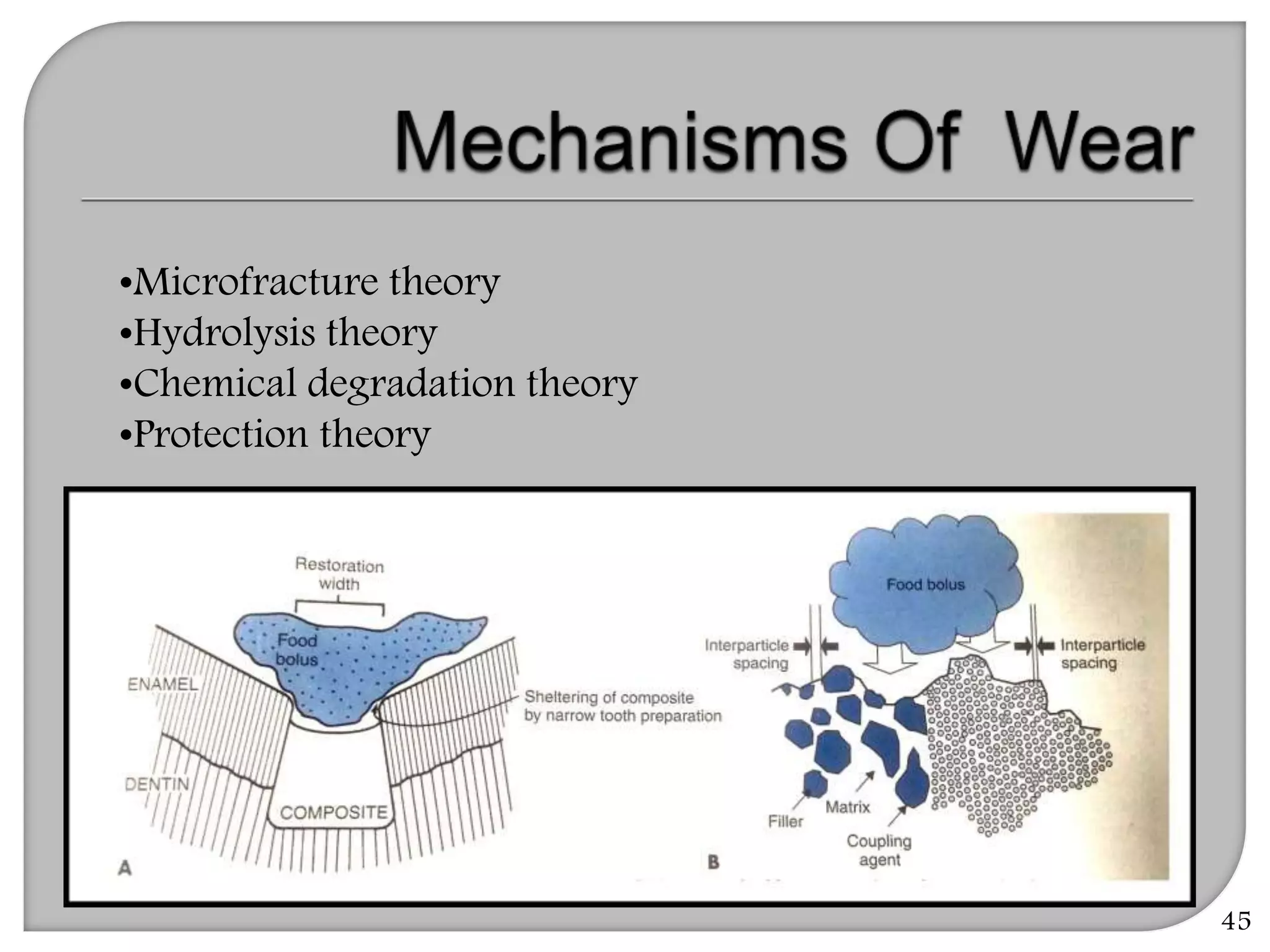
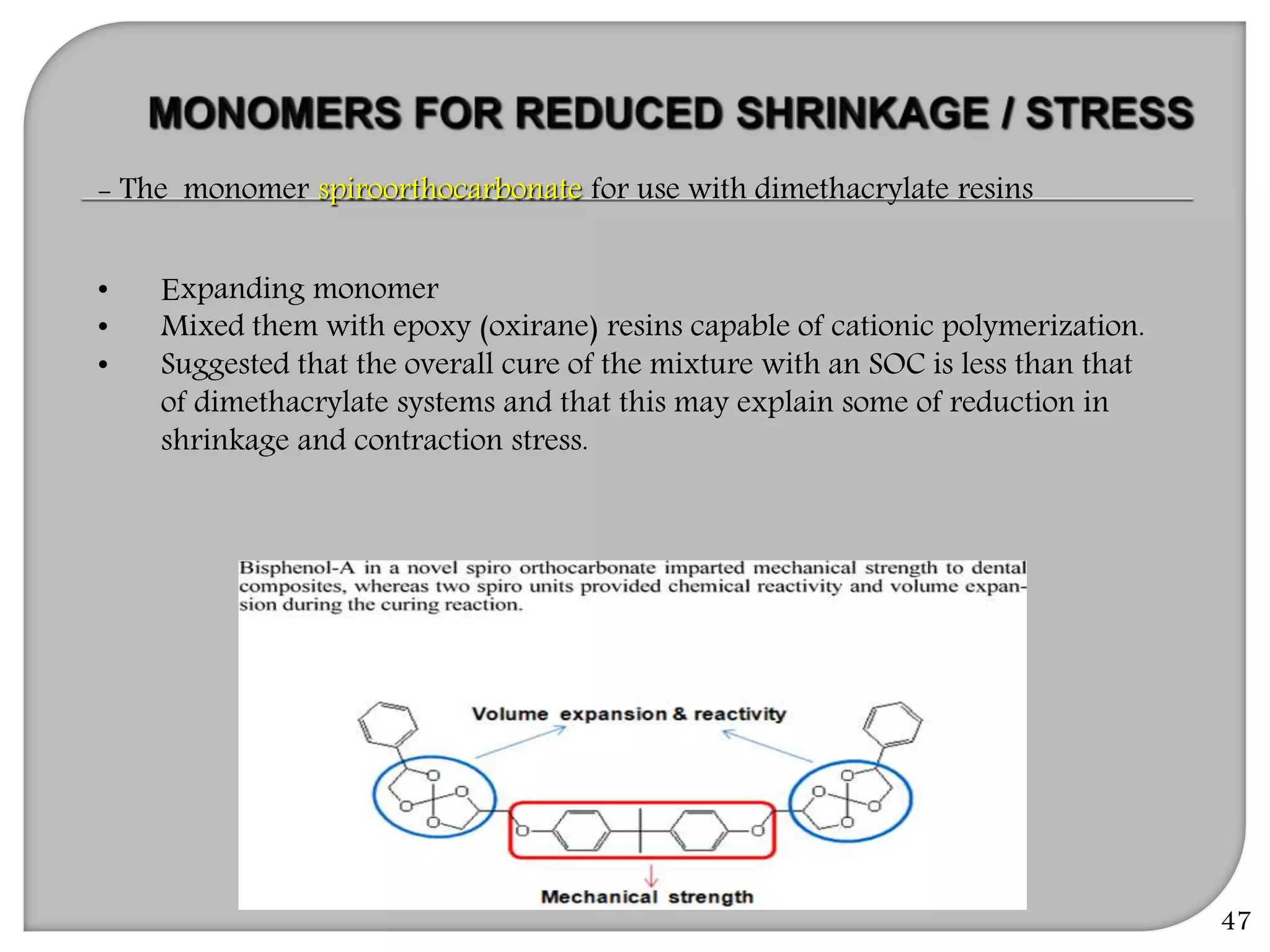
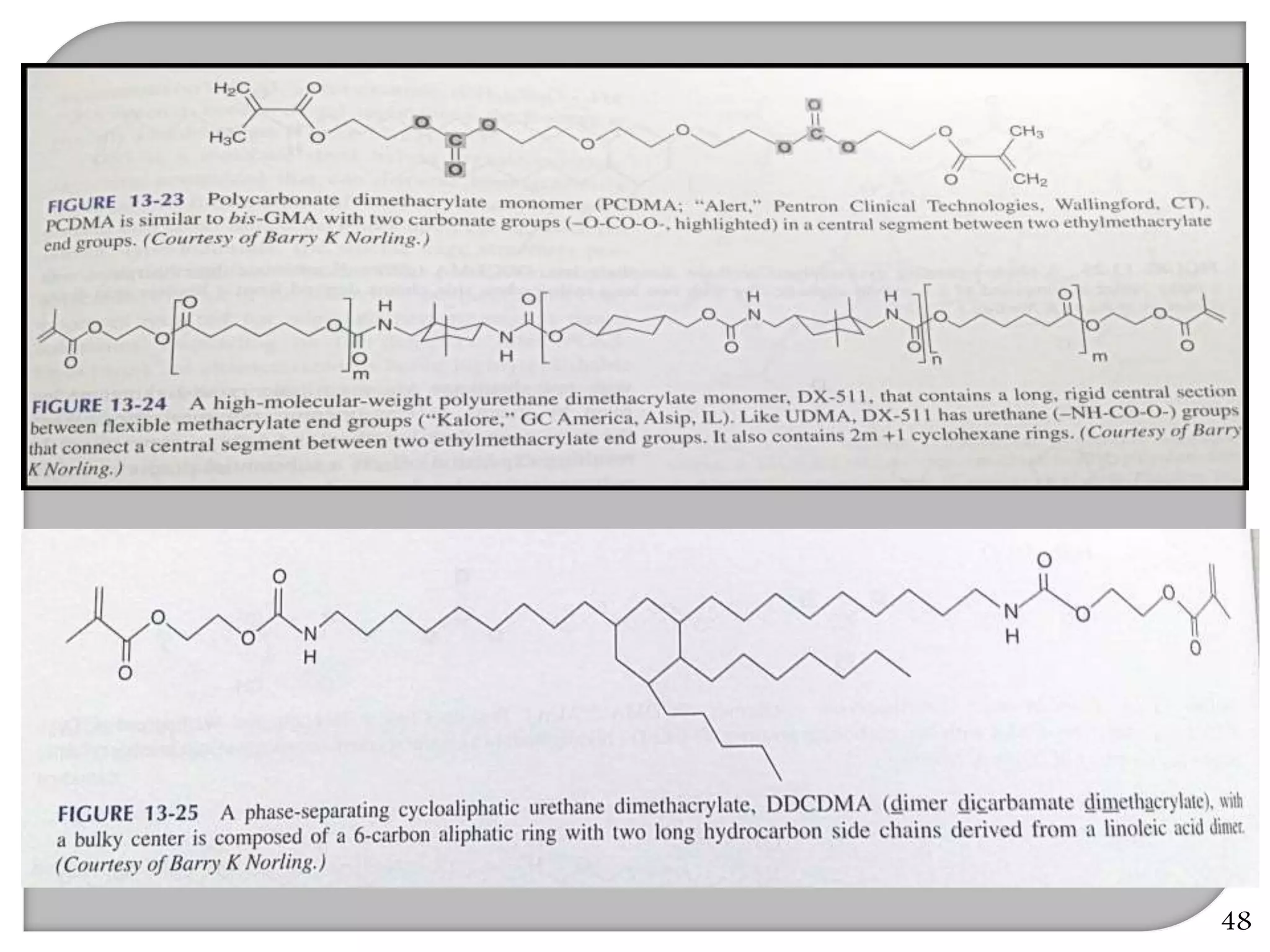
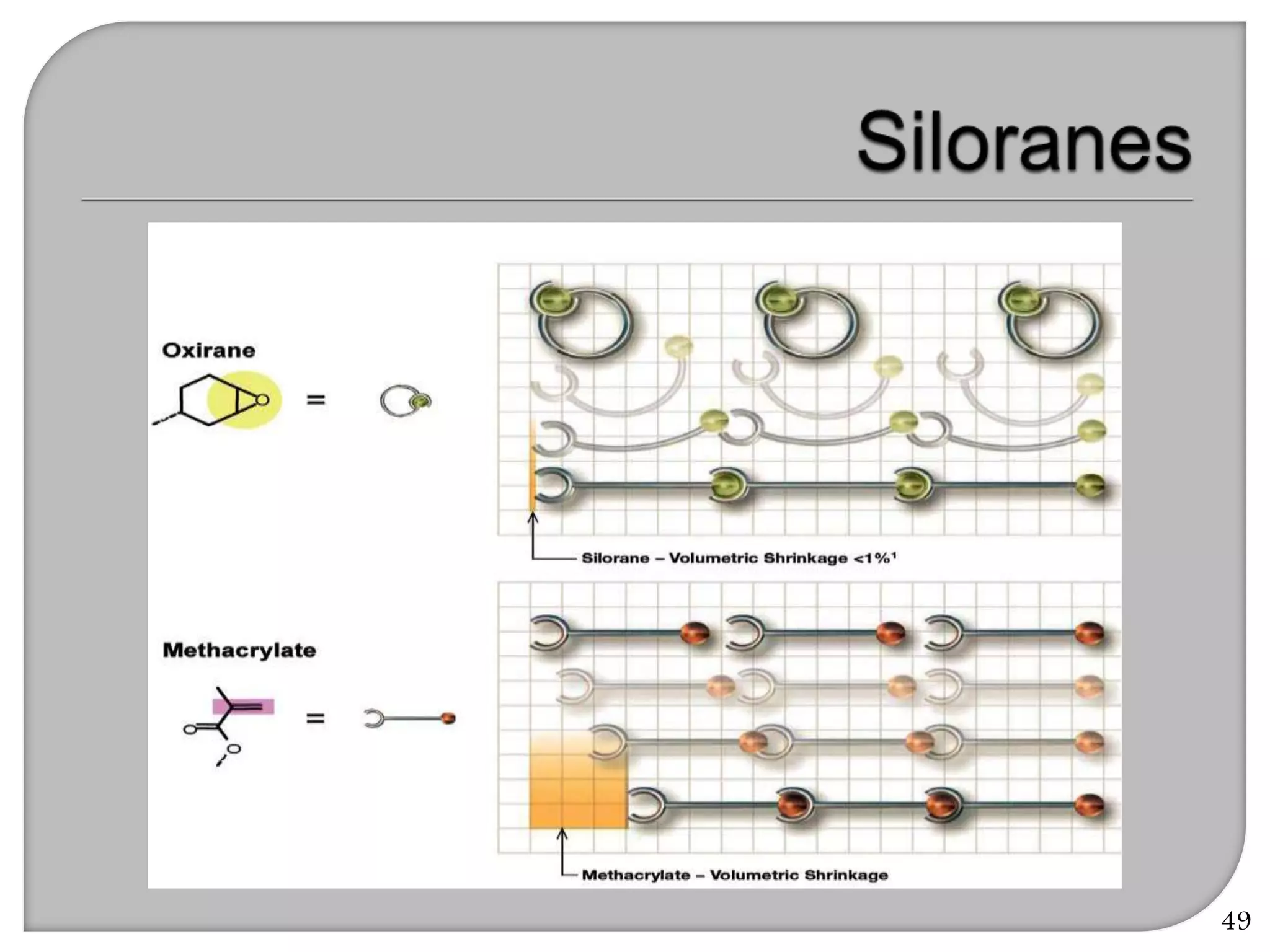
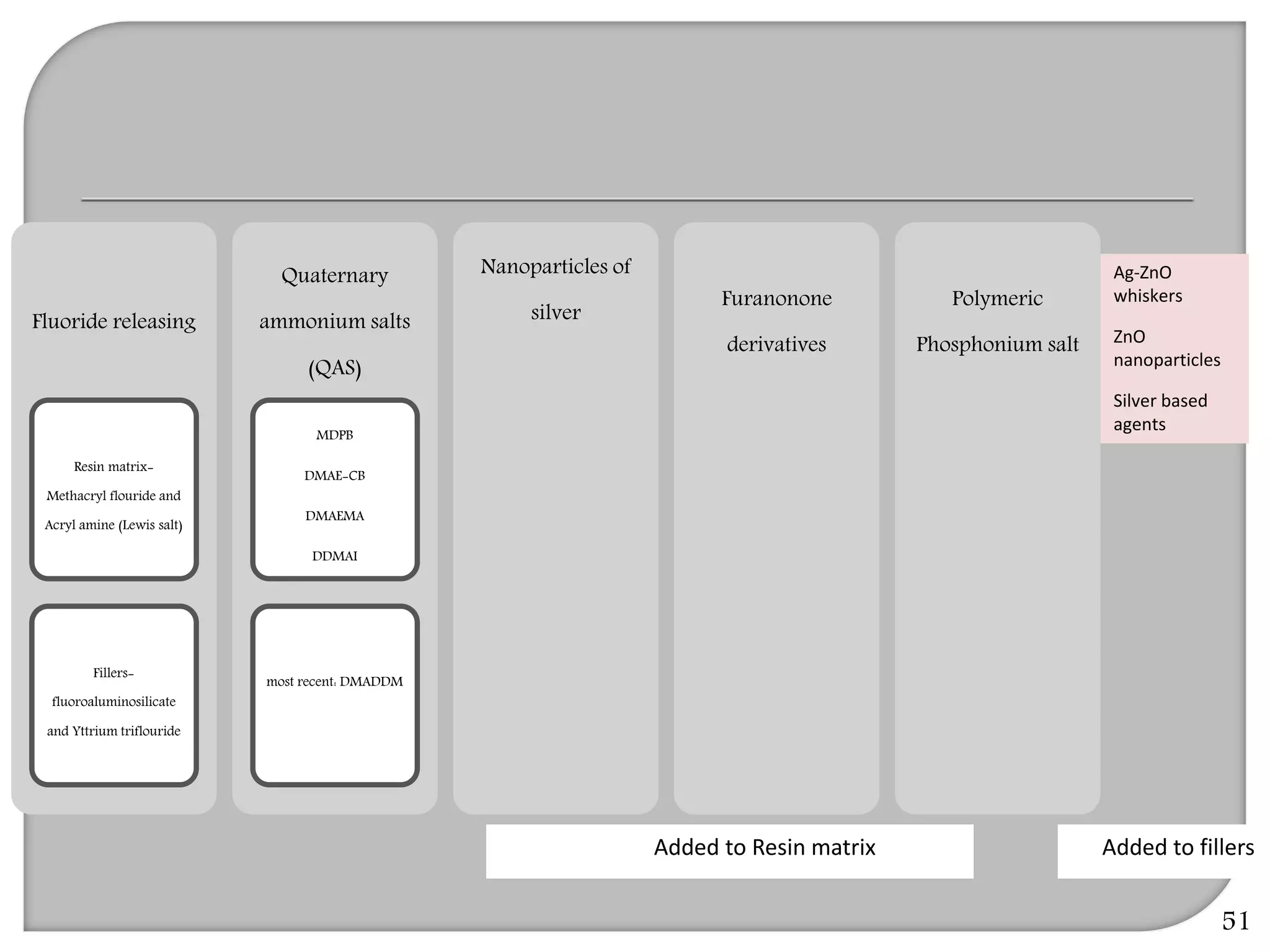
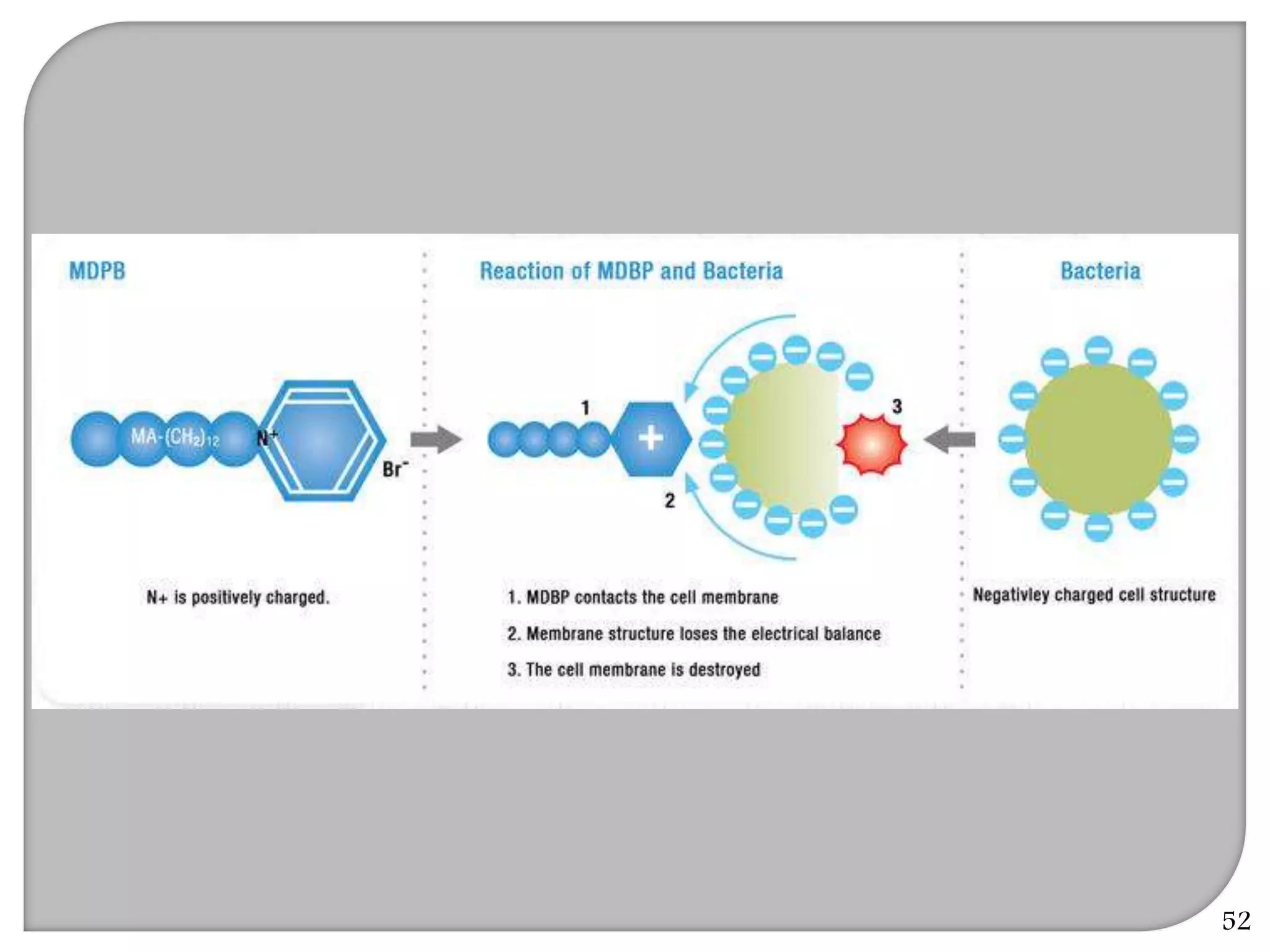
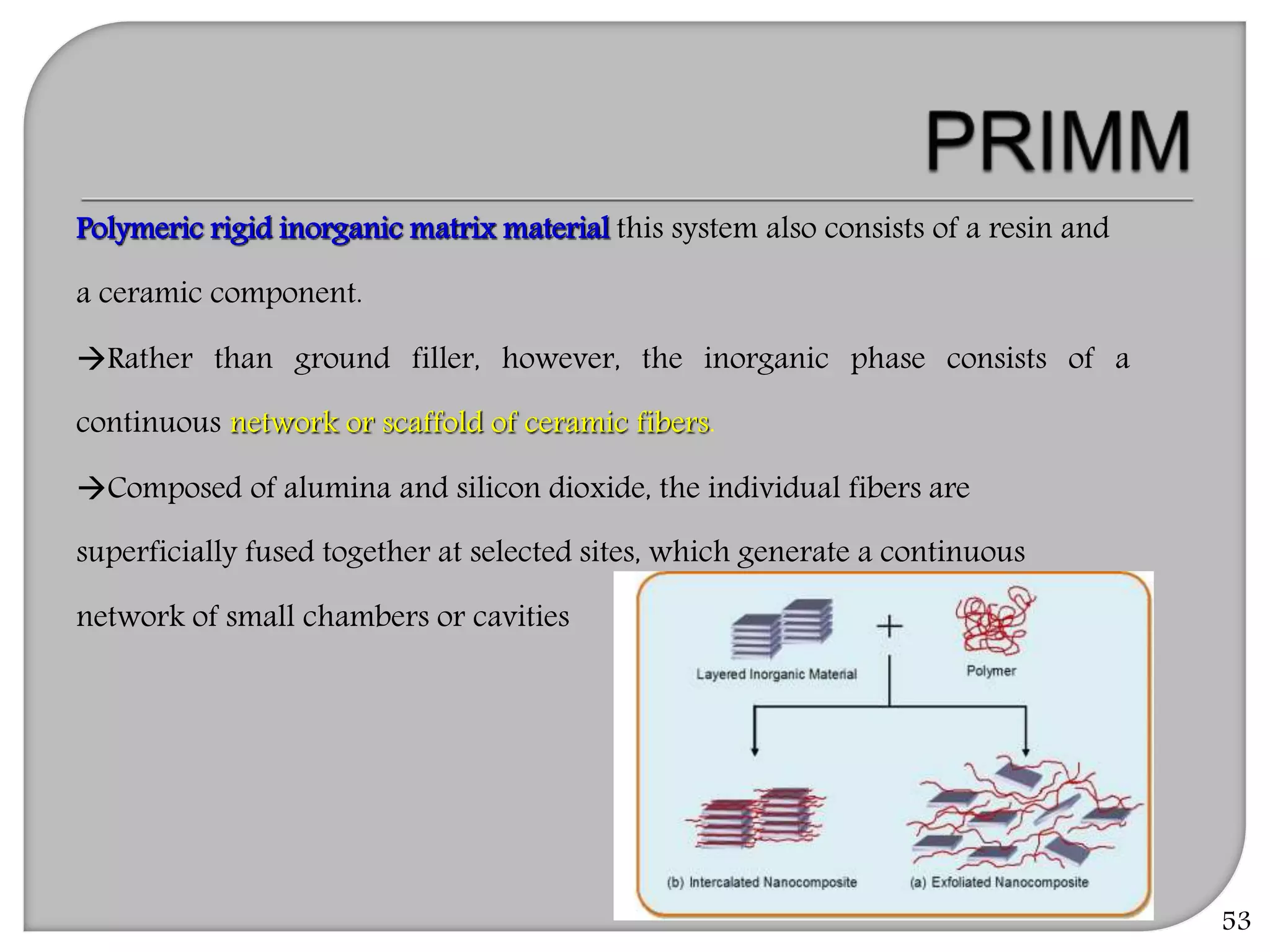
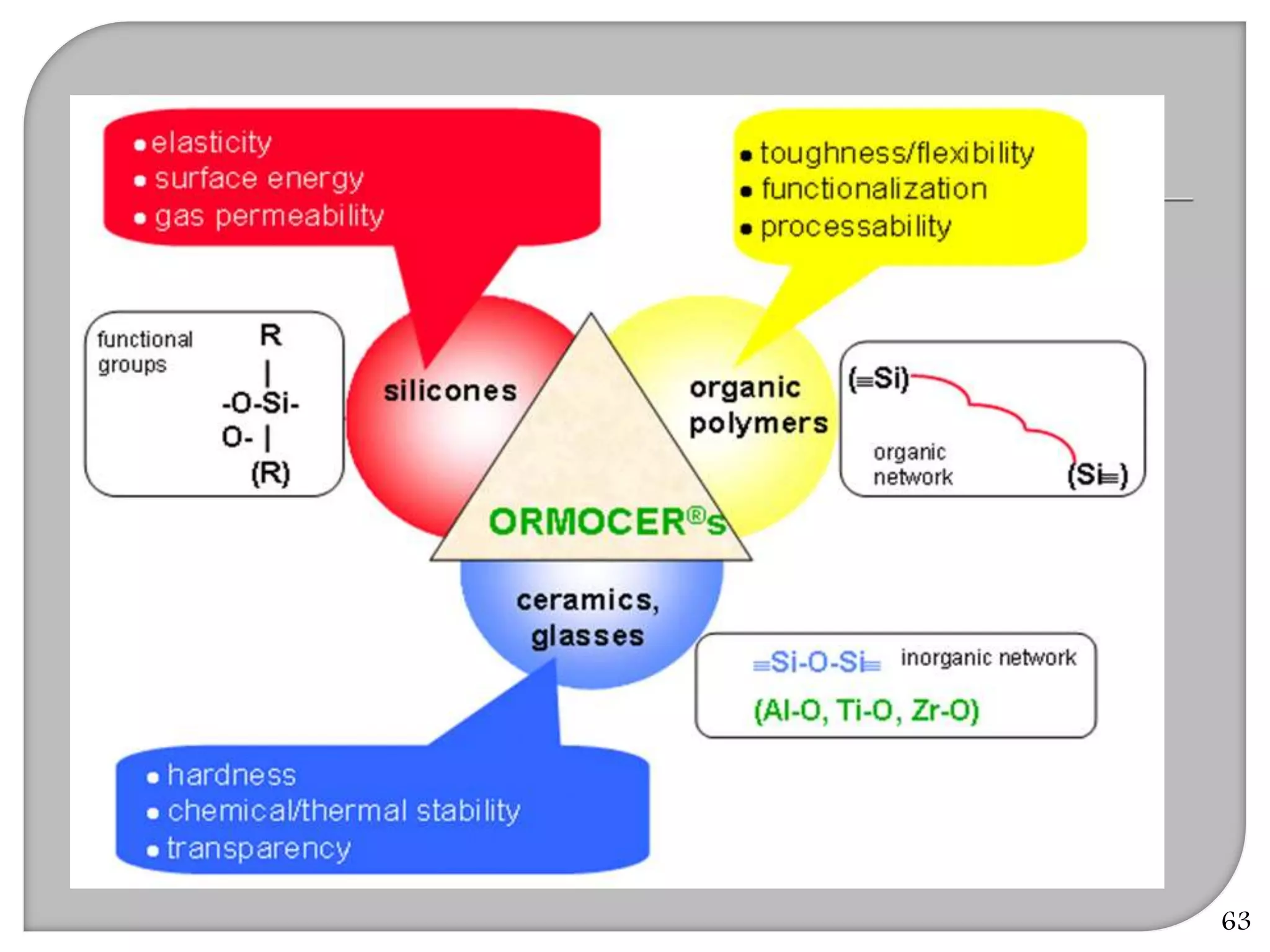
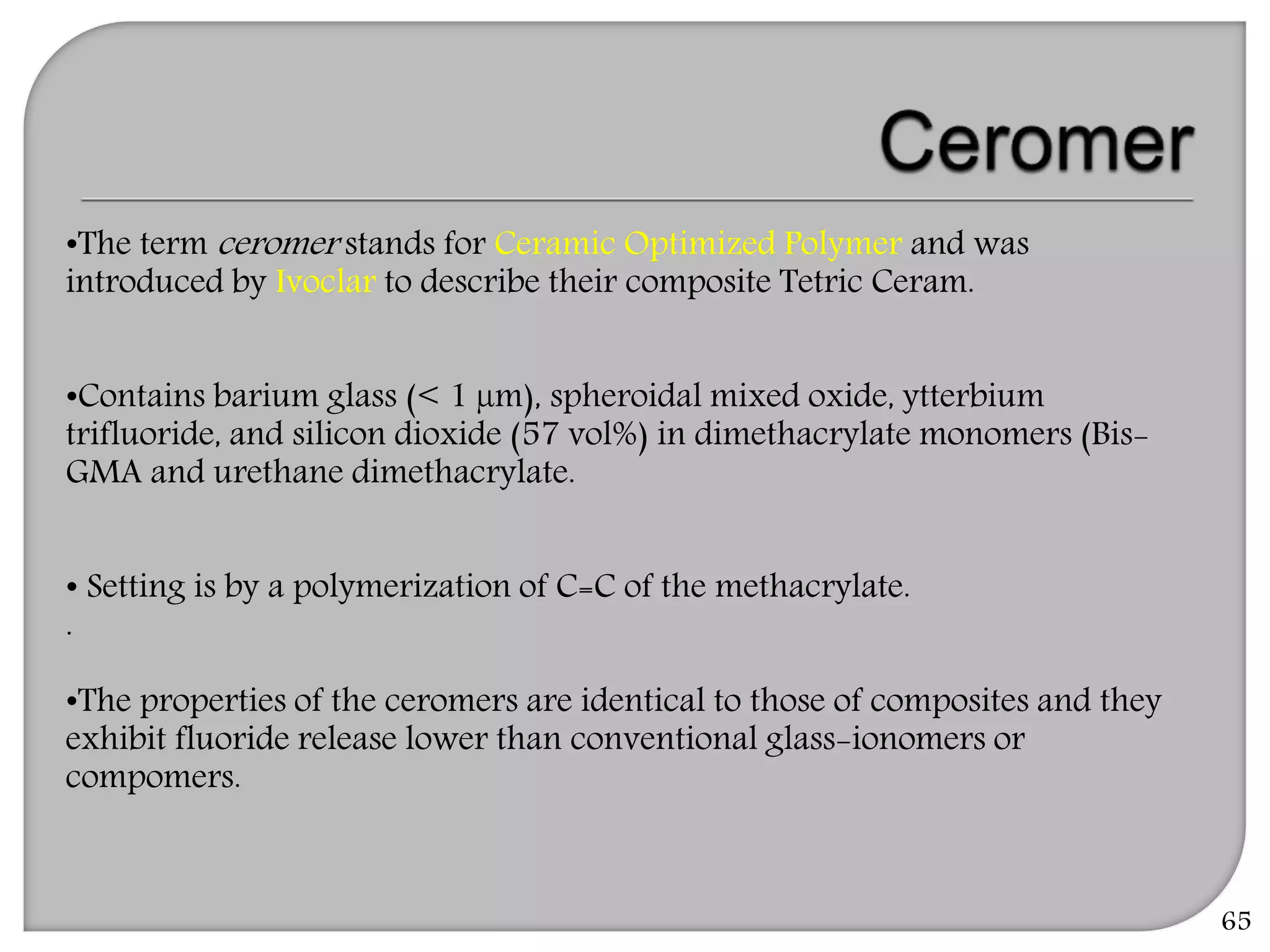
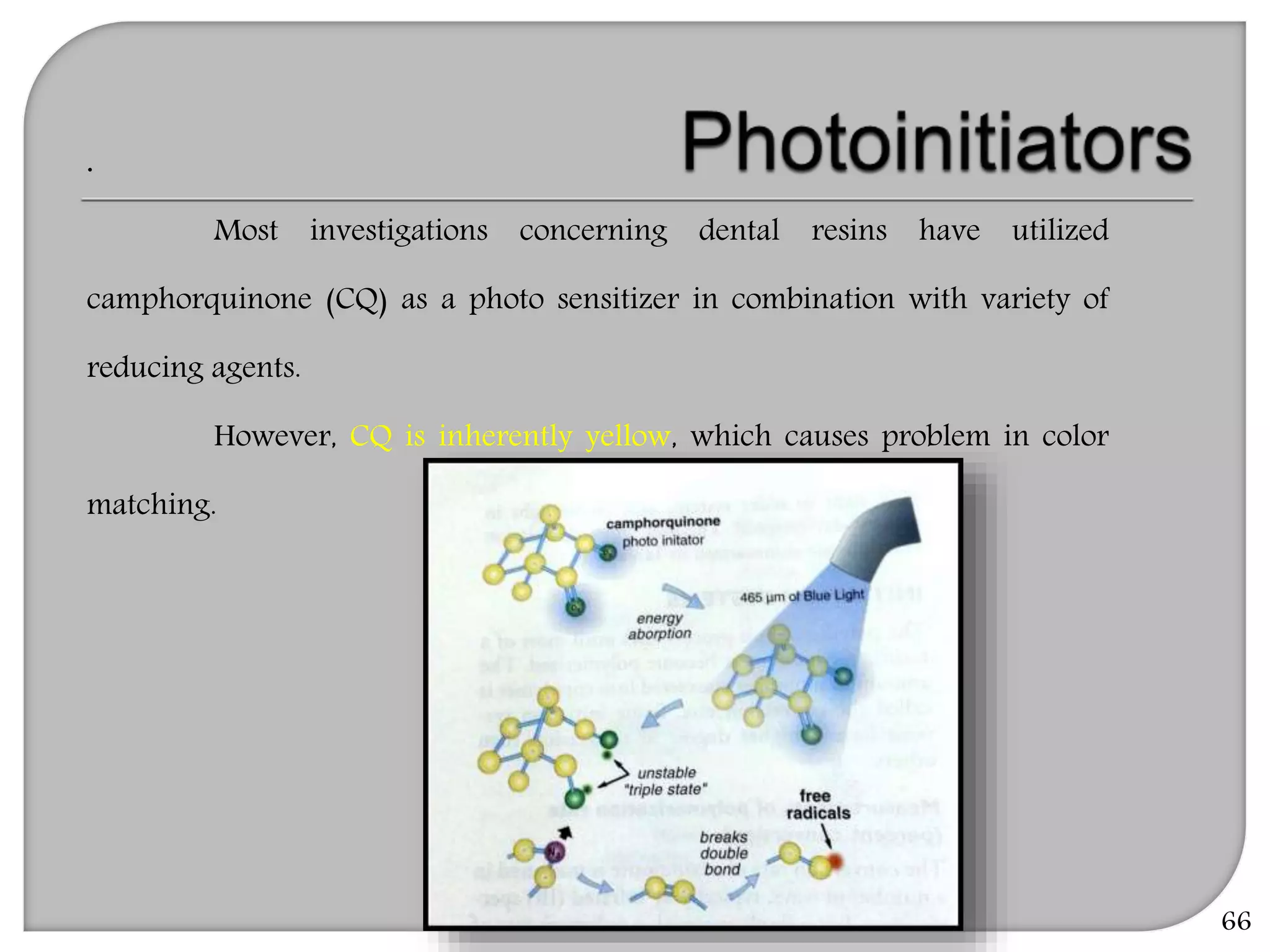
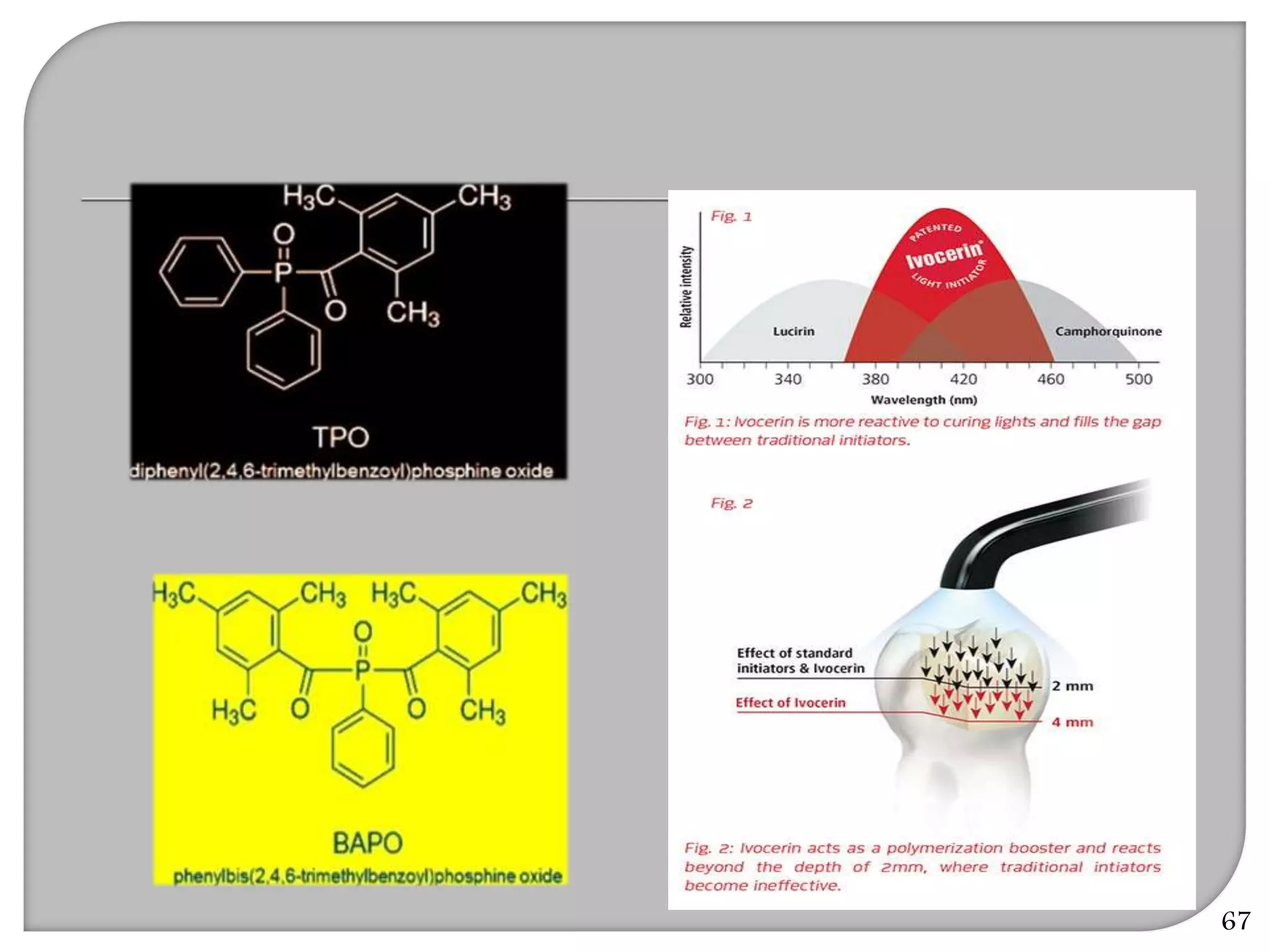
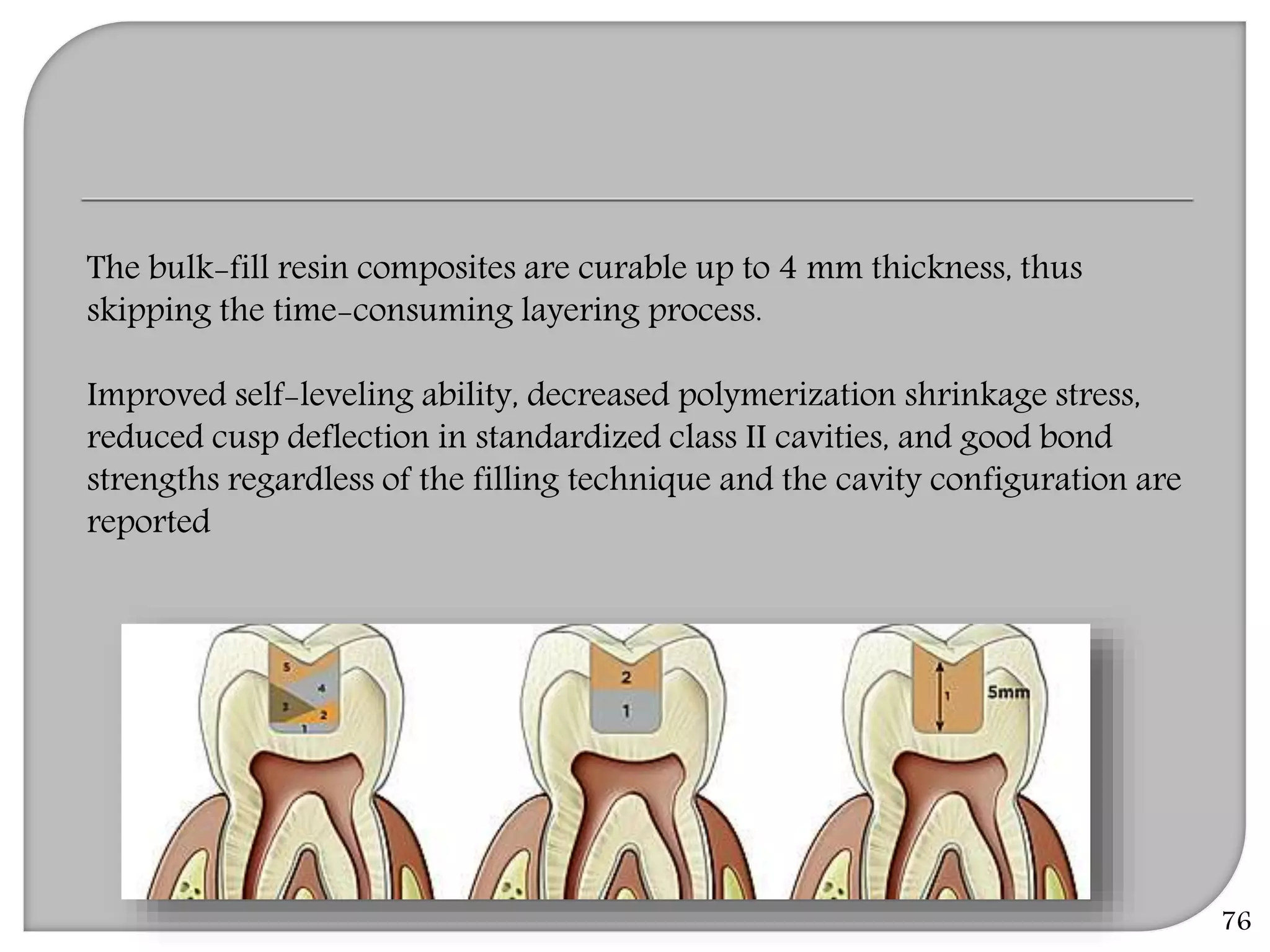
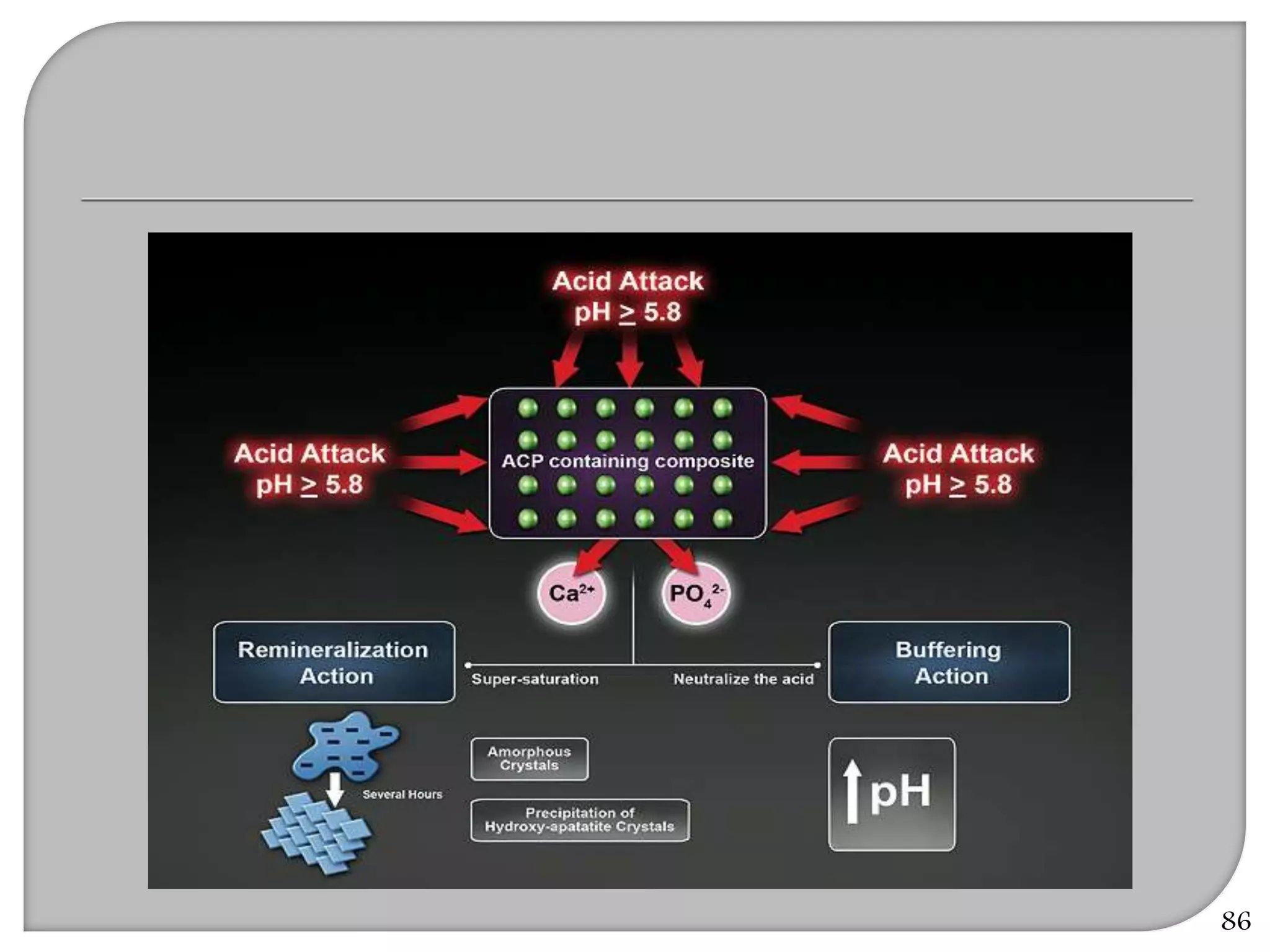
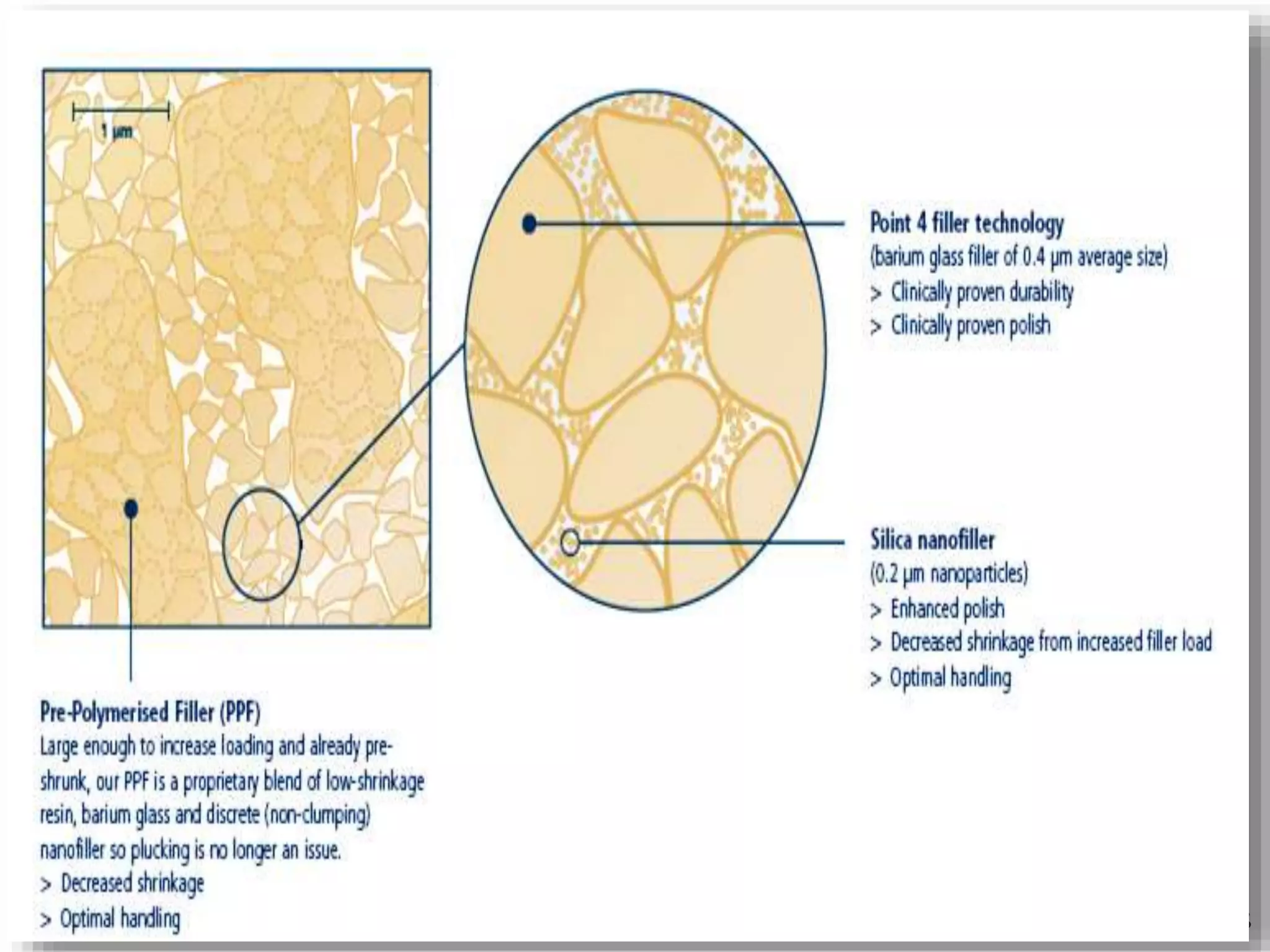
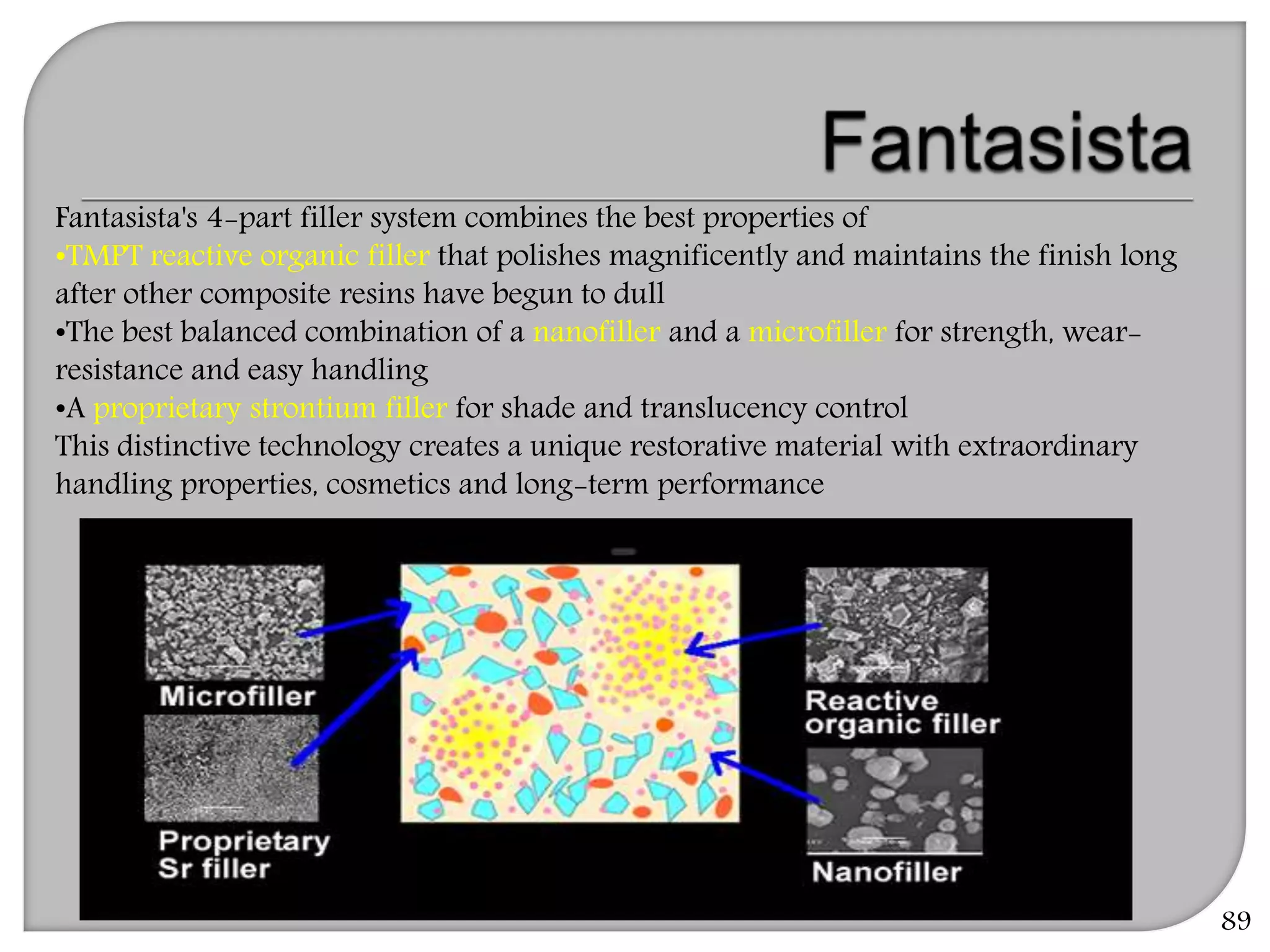
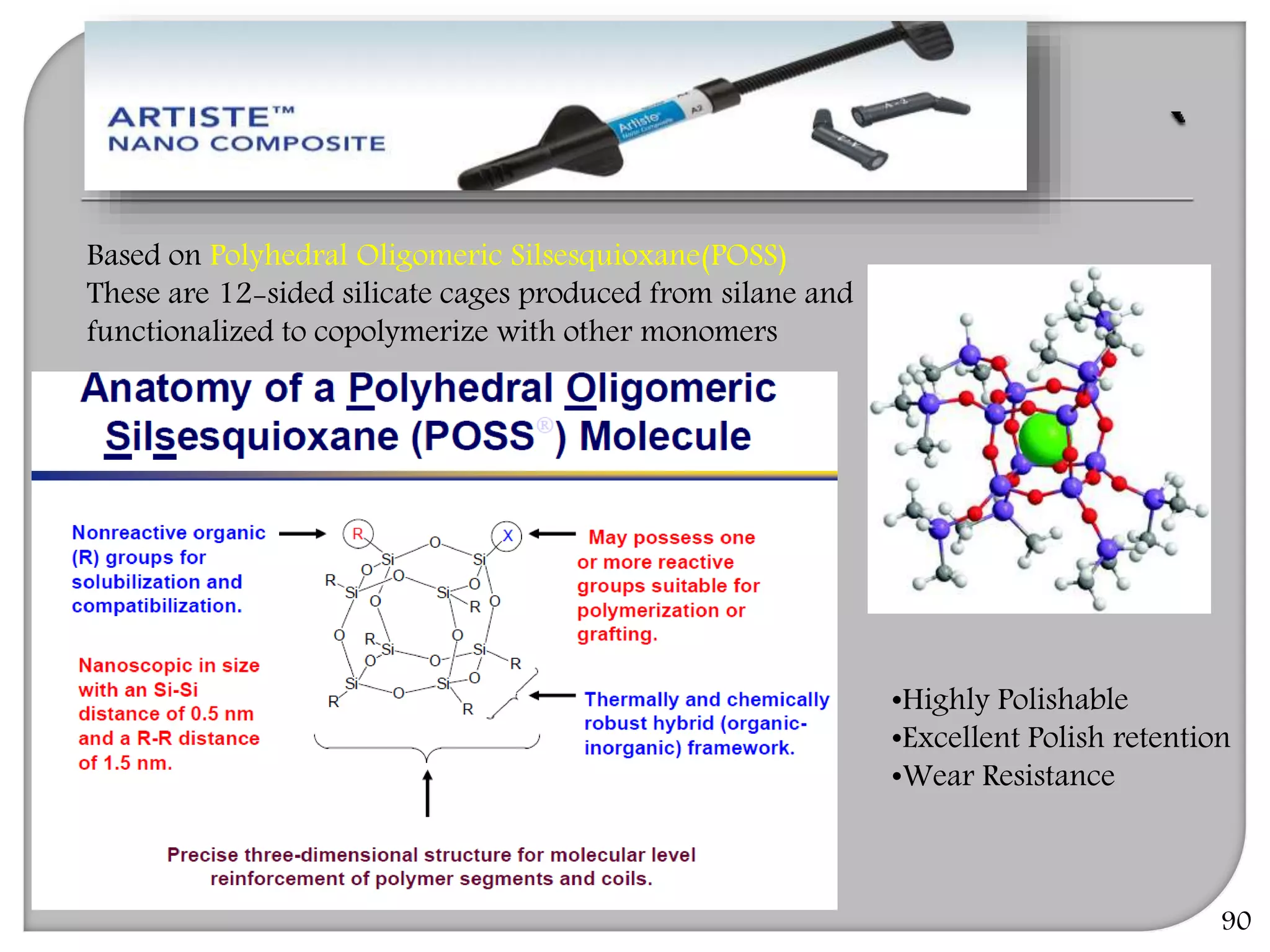
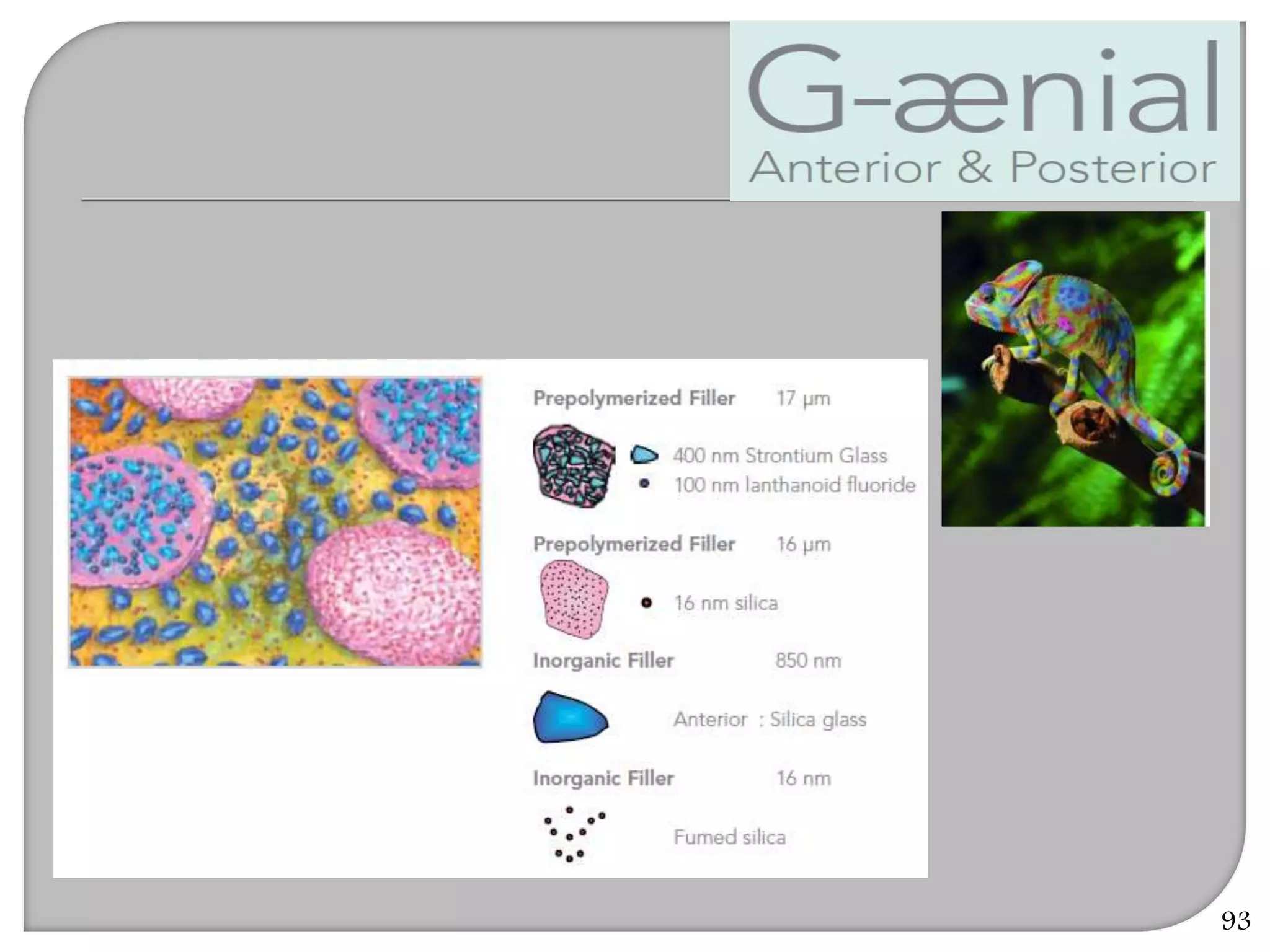
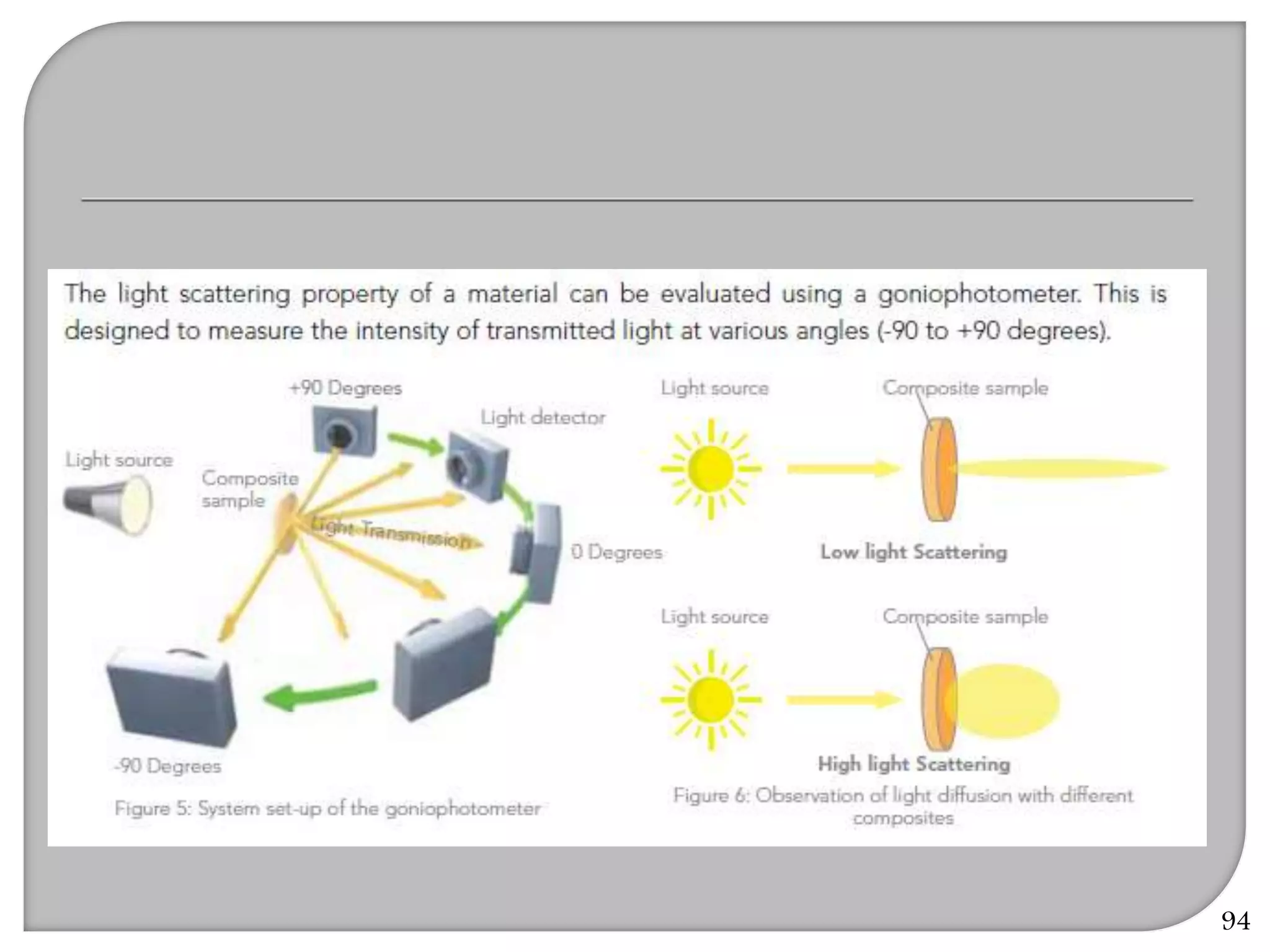
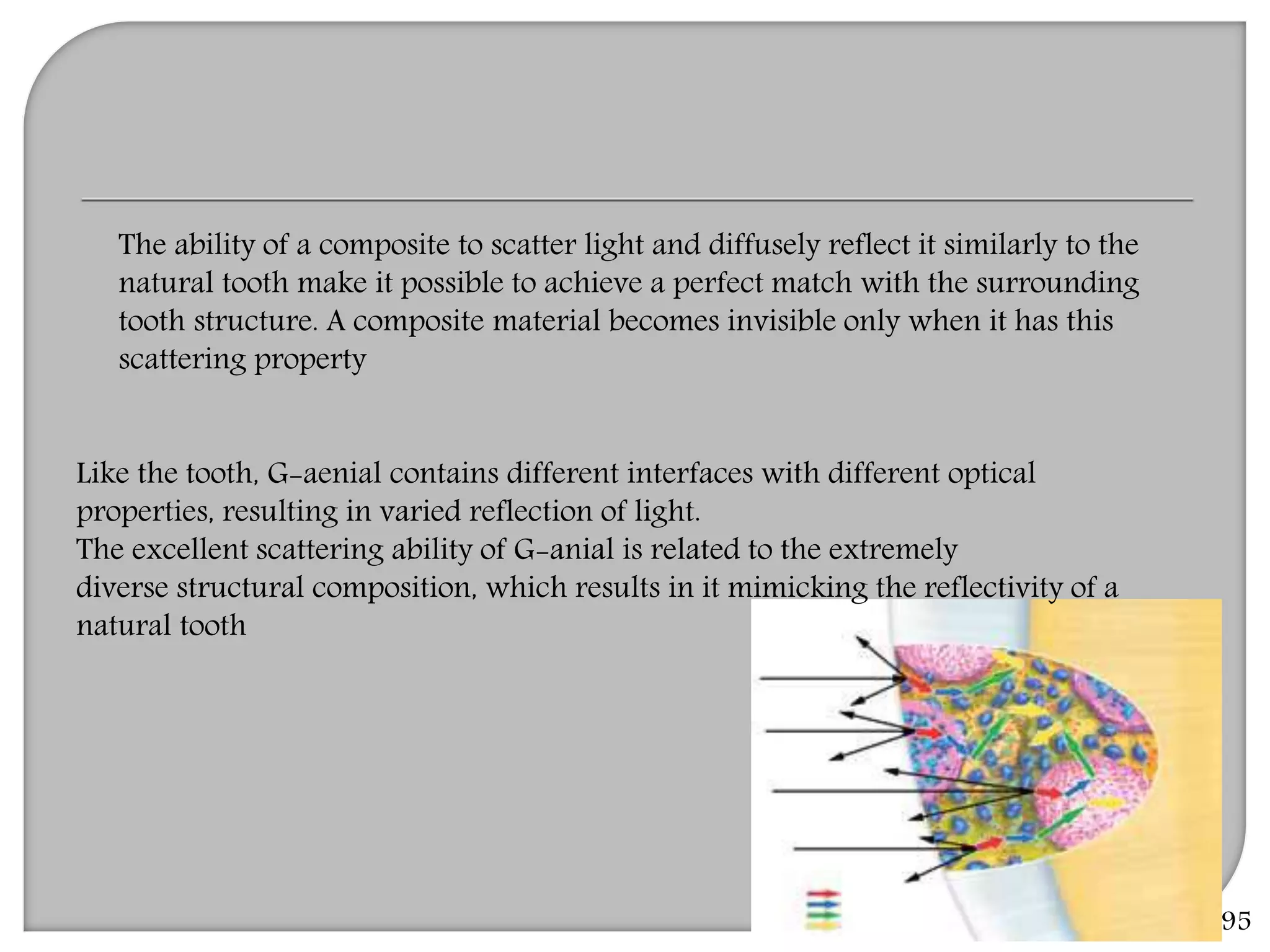
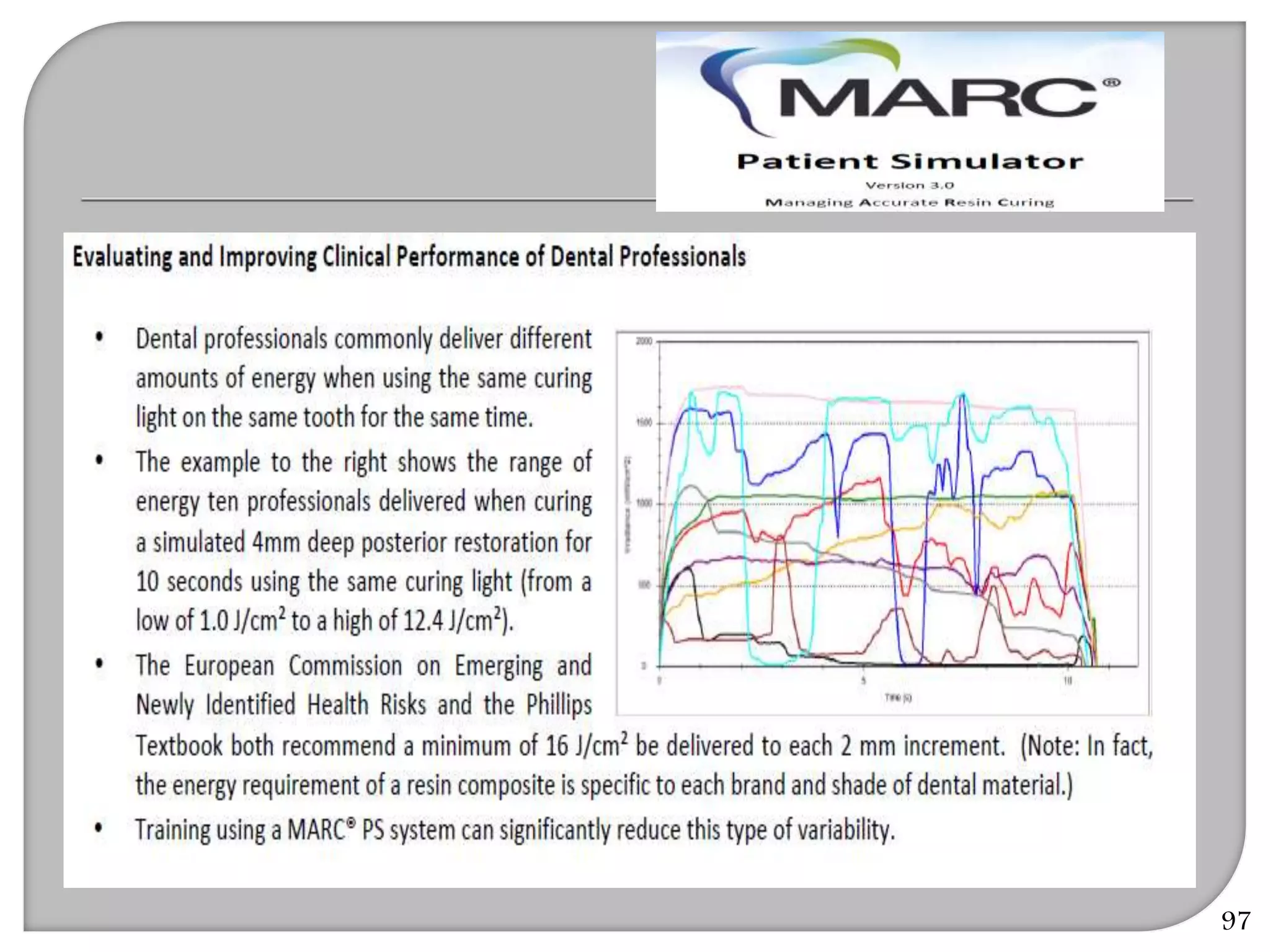
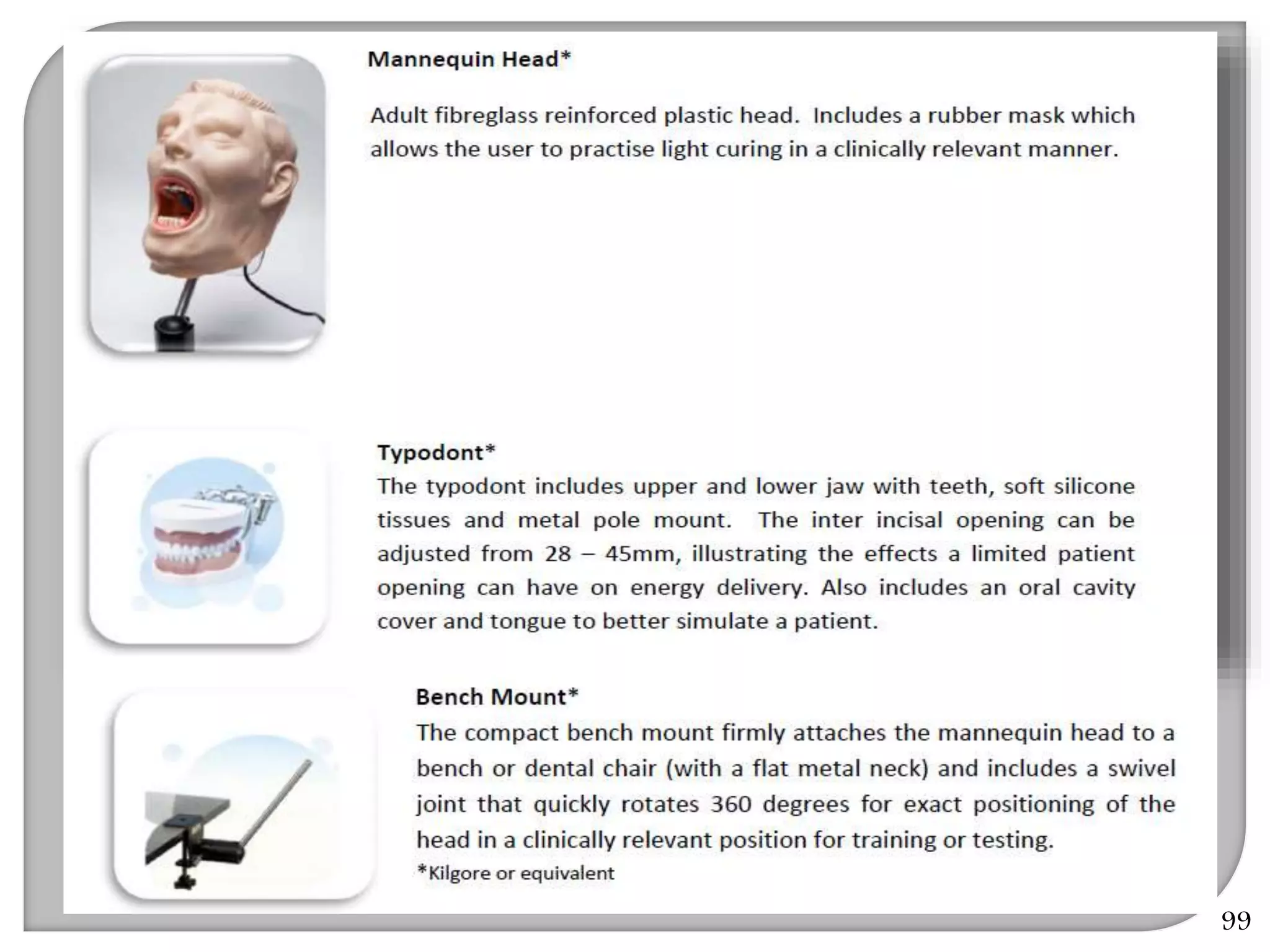
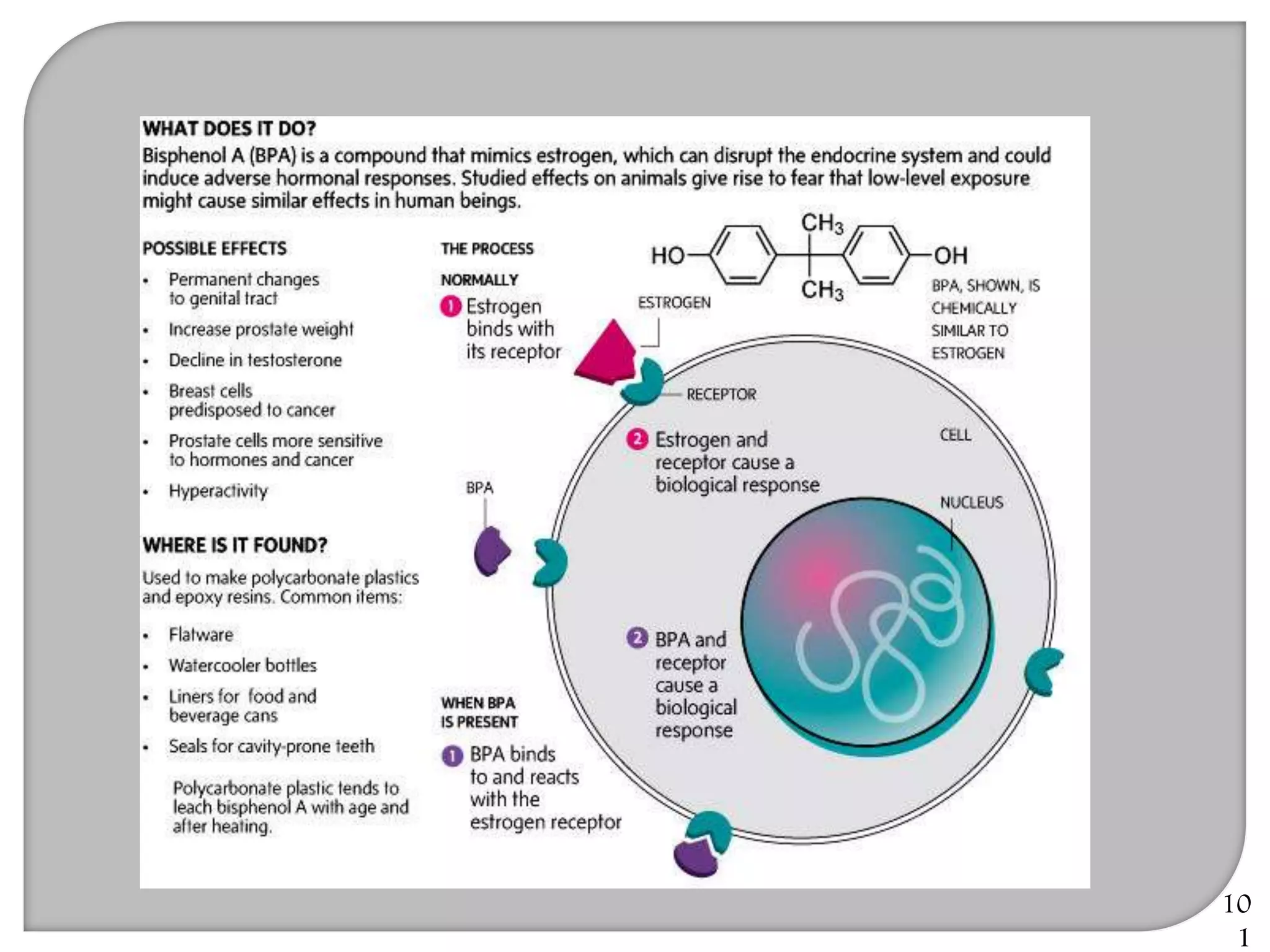
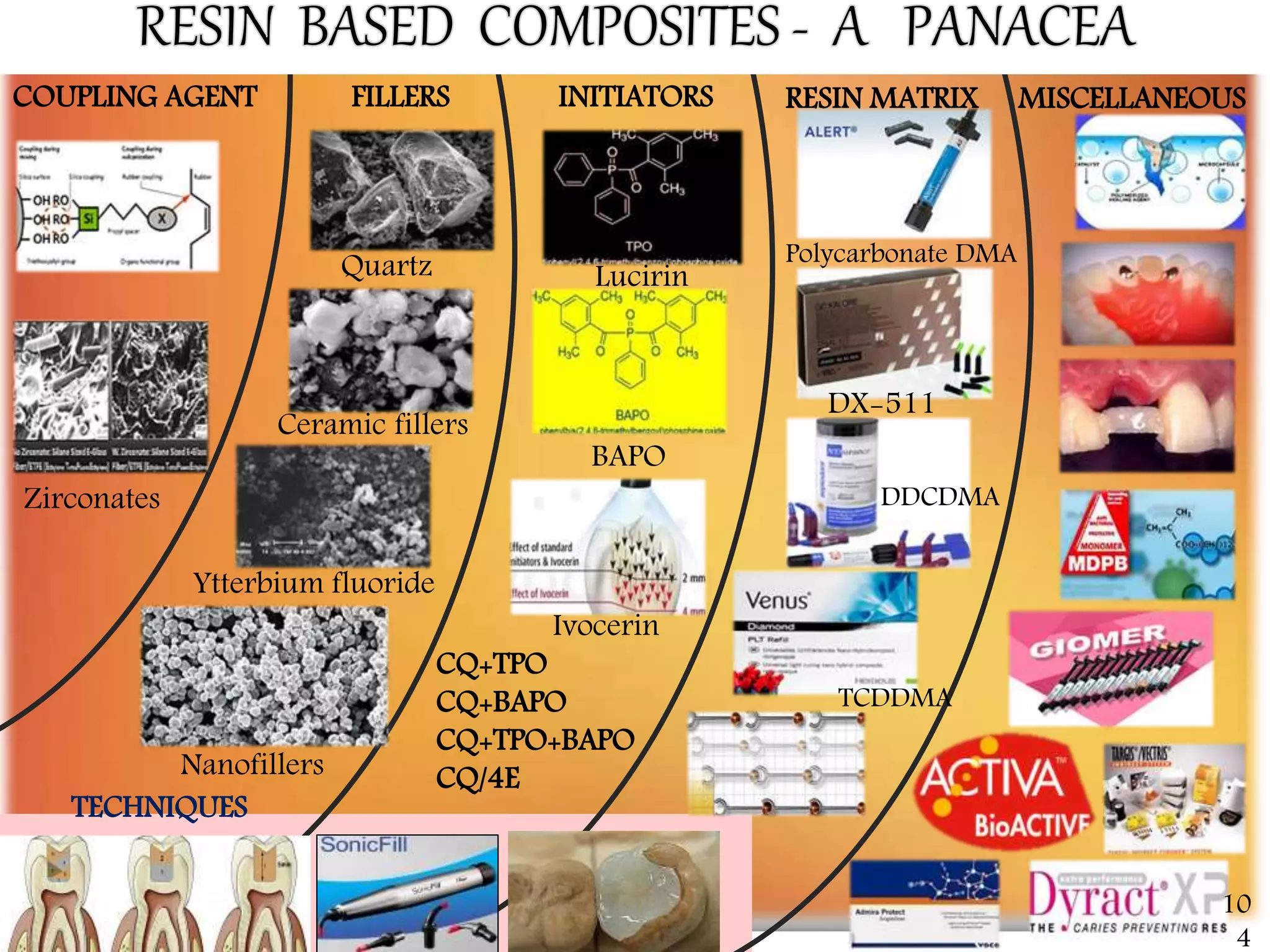
This document provides an overview of dental composites, including their history, classification, composition, properties, and recent developments. It discusses the key components of composites such as the resin matrix, fillers, coupling agents, and photoinitiators. It also summarizes the different types of composites based on particle size, polymerization method, and other characteristics. Recent innovations in composites include antibacterial, flowable, packable, compomers, and fiber-reinforced formulations.