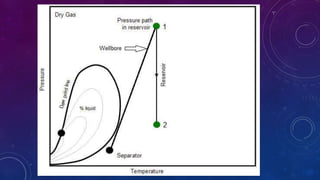
This document classifies and describes five types of reservoir fluids: black oils, volatile oils, condensate (retrograde gas), wet gas (rich gas), and dry gas. Black oils contain heavy hydrocarbons and have low gas-oil ratios. Volatile oils contain lighter molecules and higher gas-oil ratios than black oils. Condensate gas resembles volatile oil but exists as a gas in the reservoir. Wet gas contains significant heavy gas hydrocarbons. Dry gas is primarily methane with no condensate.