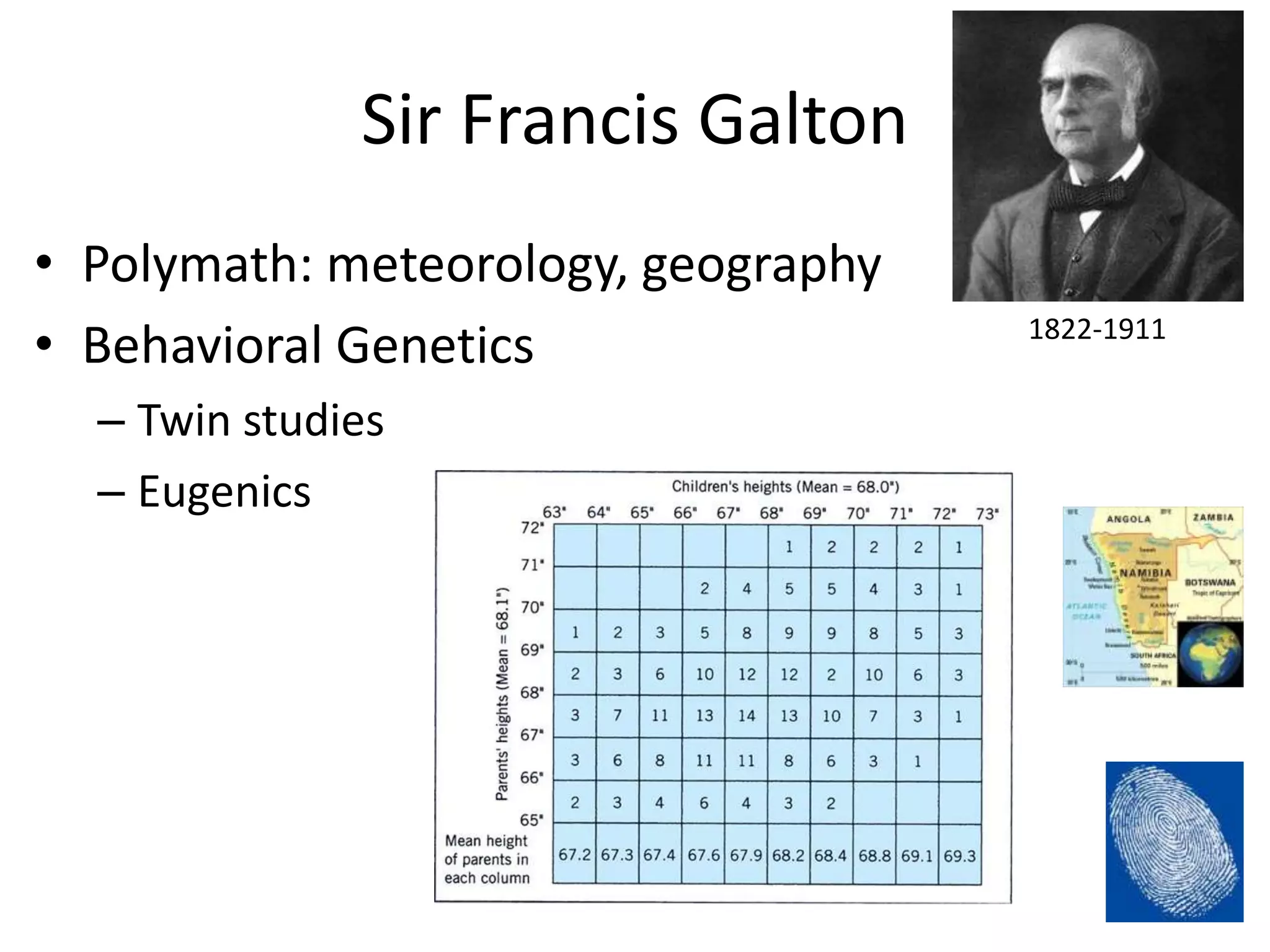
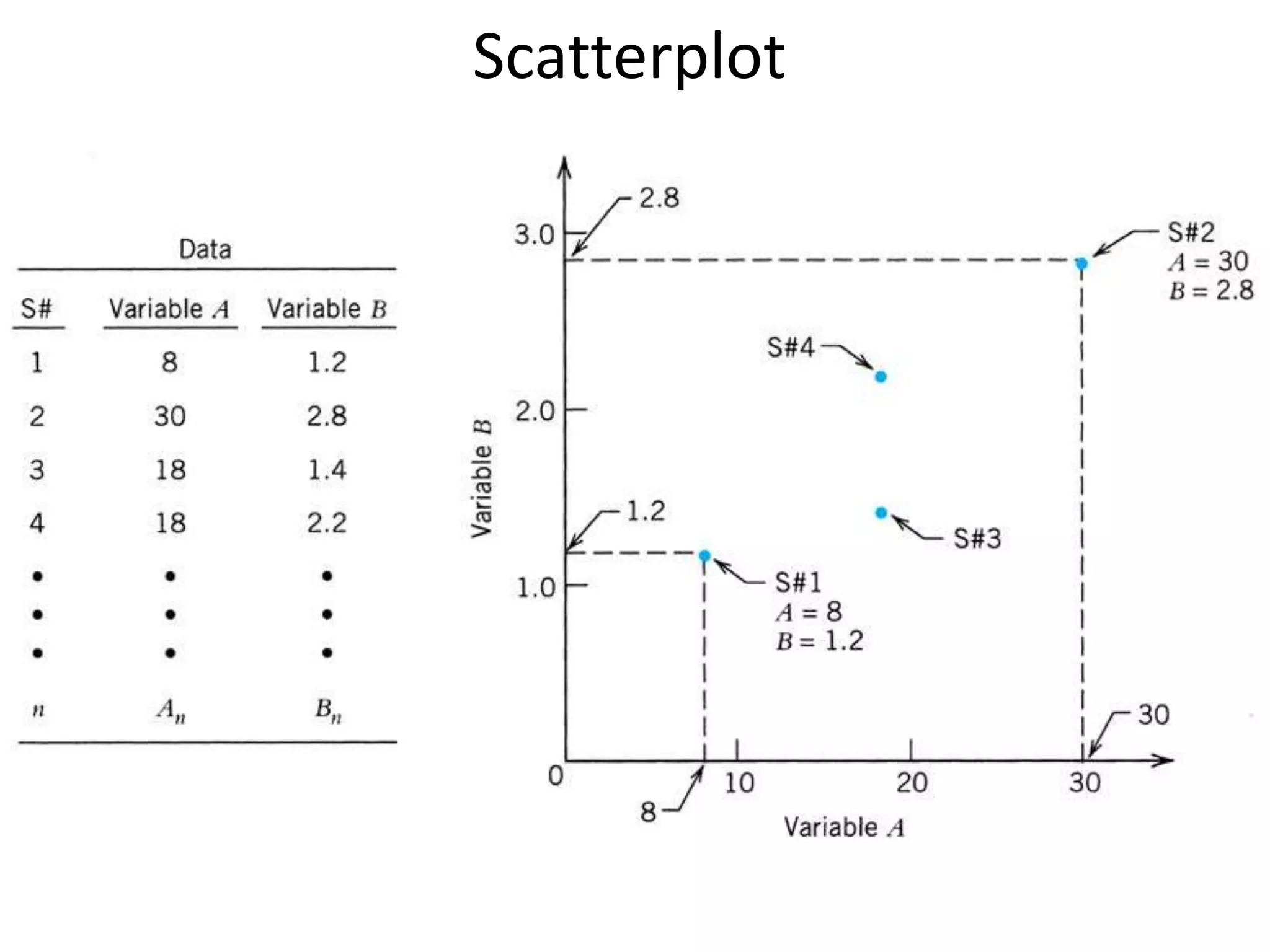
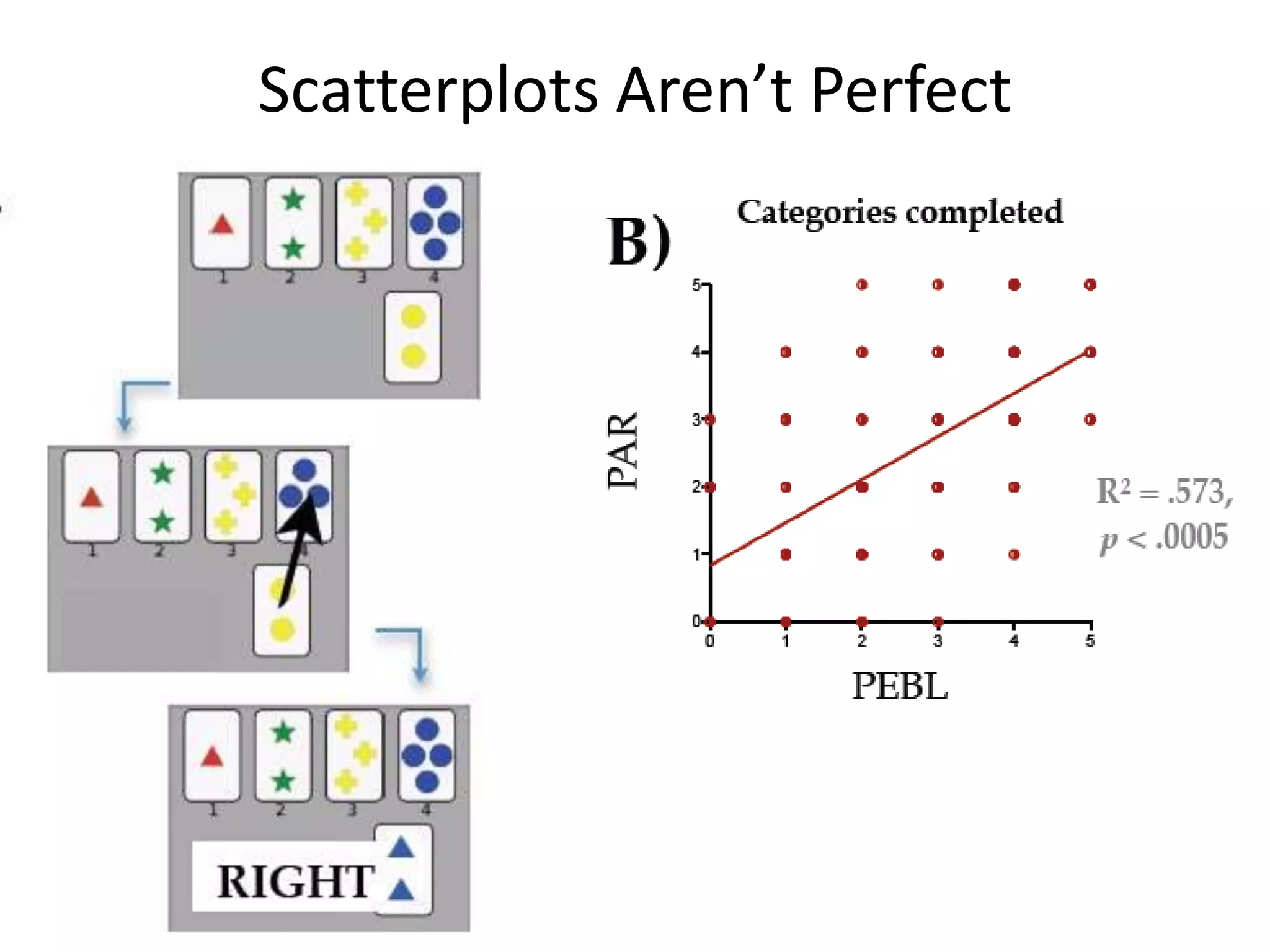
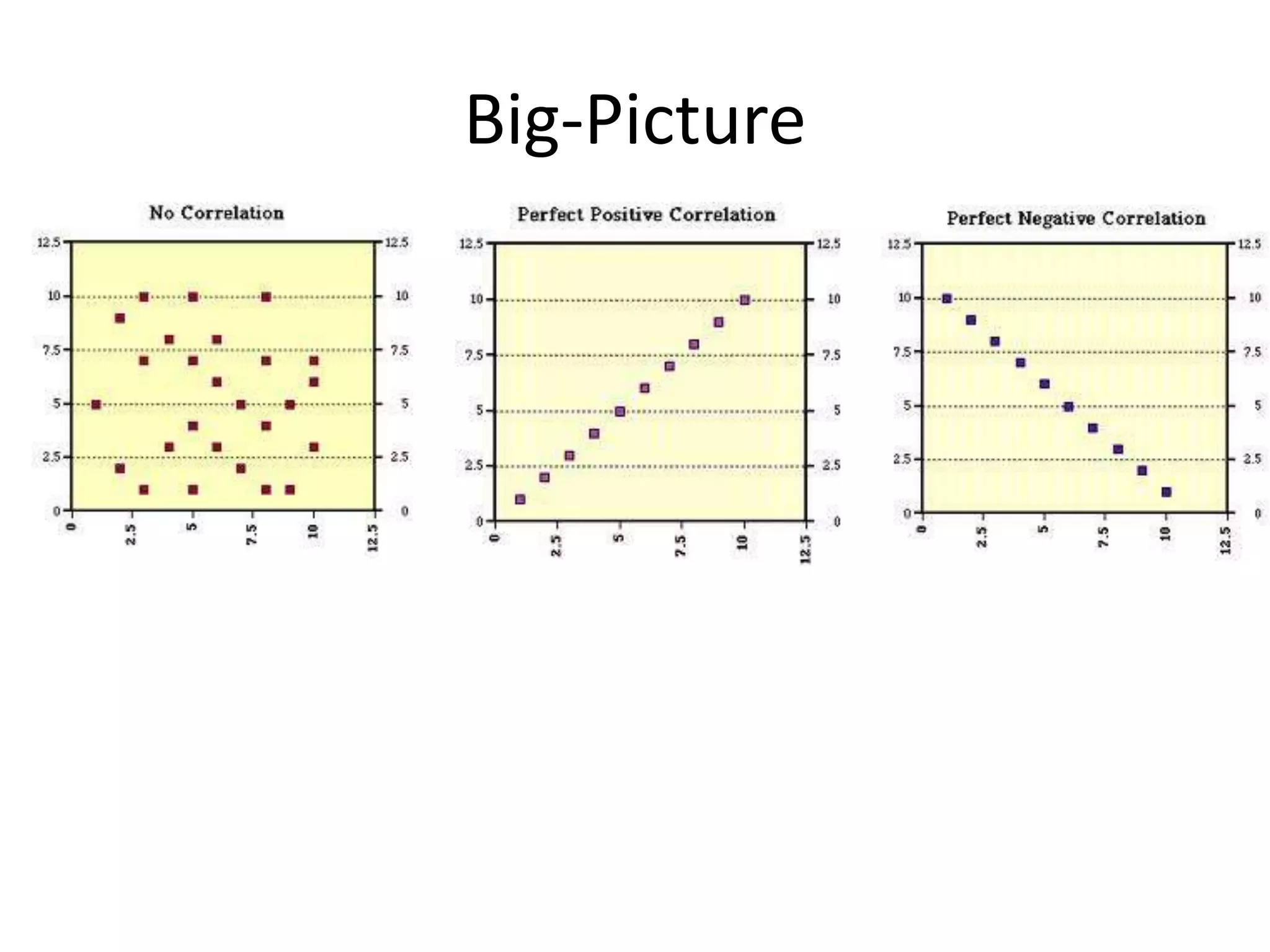
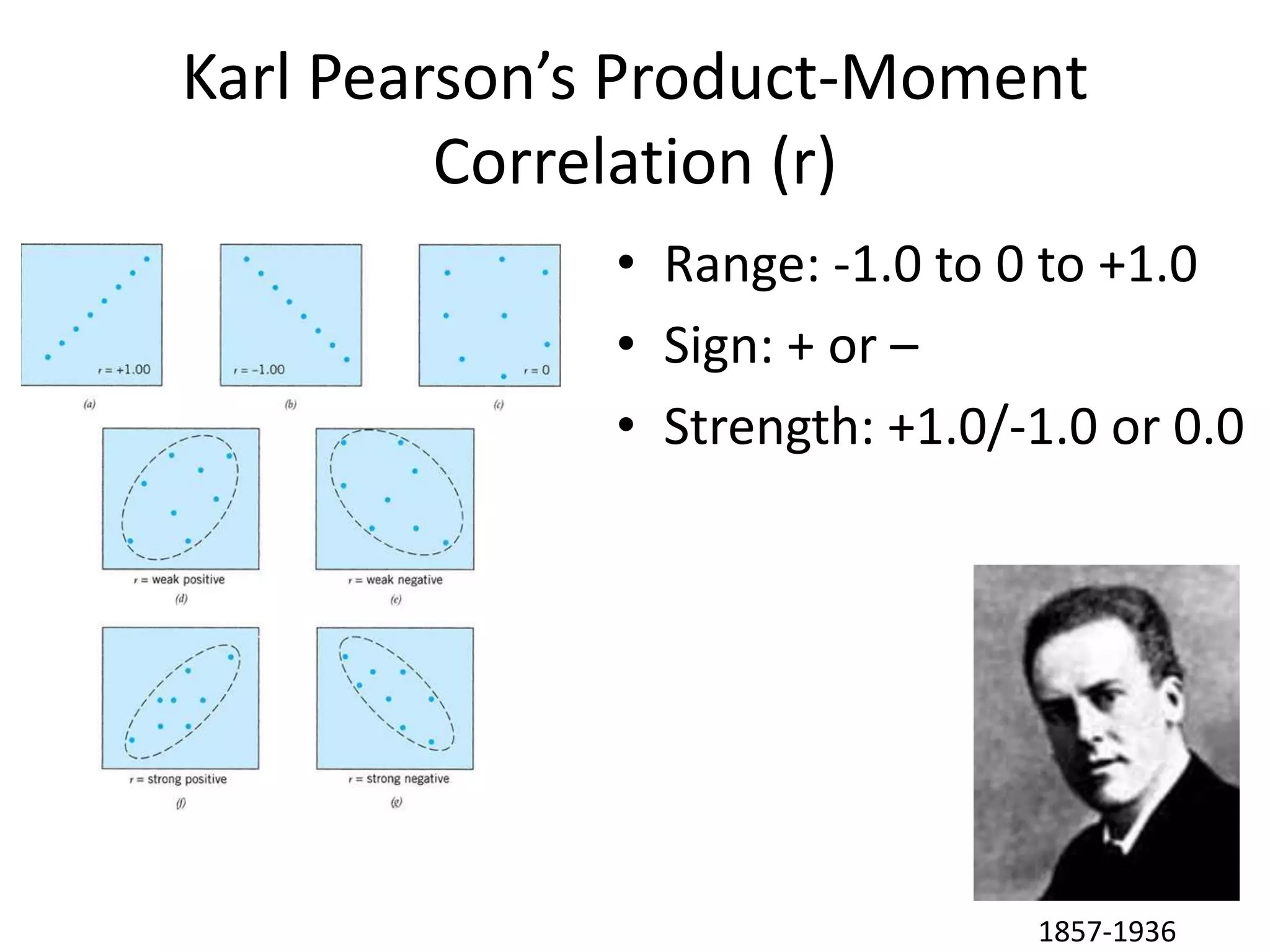
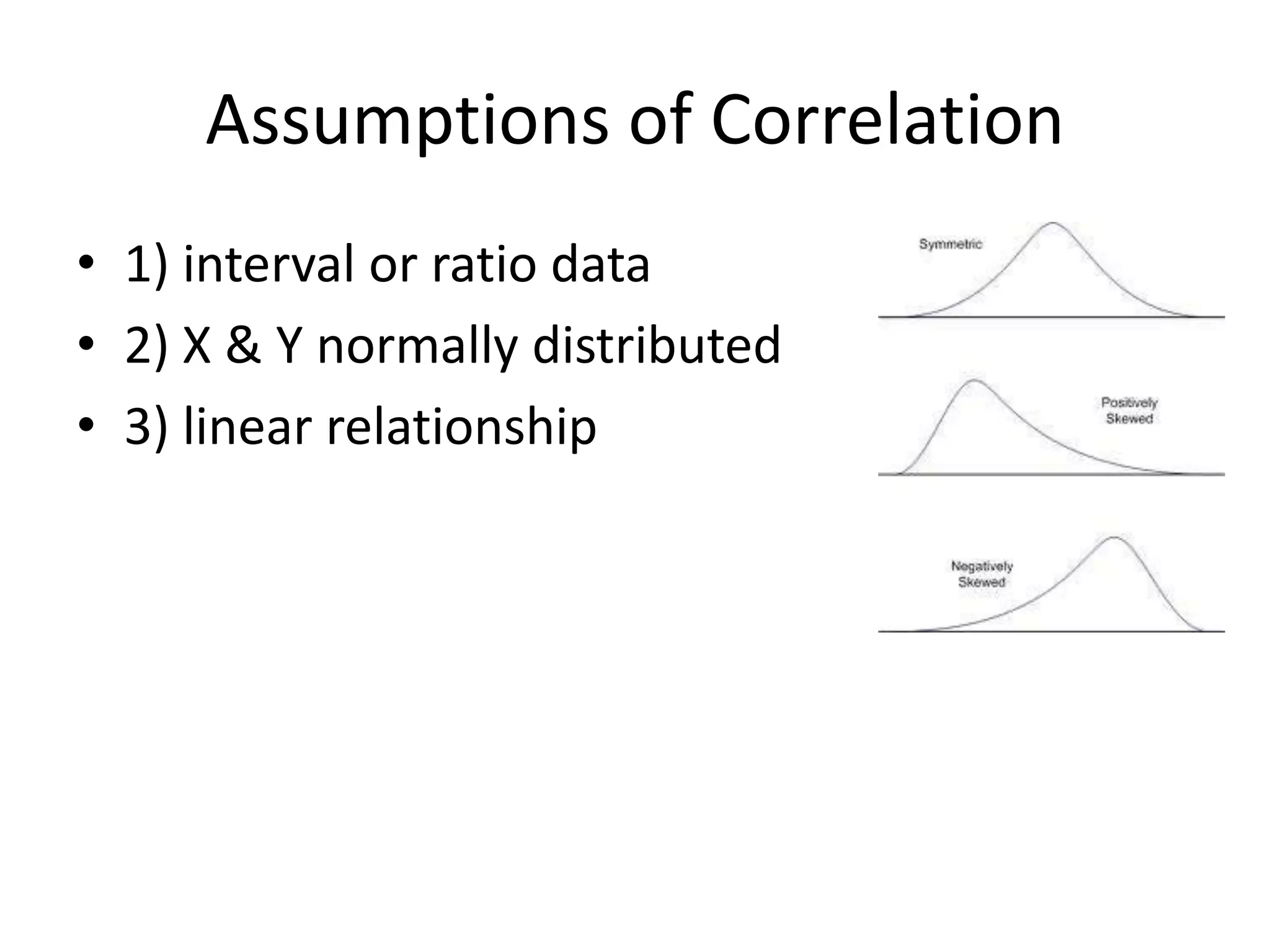
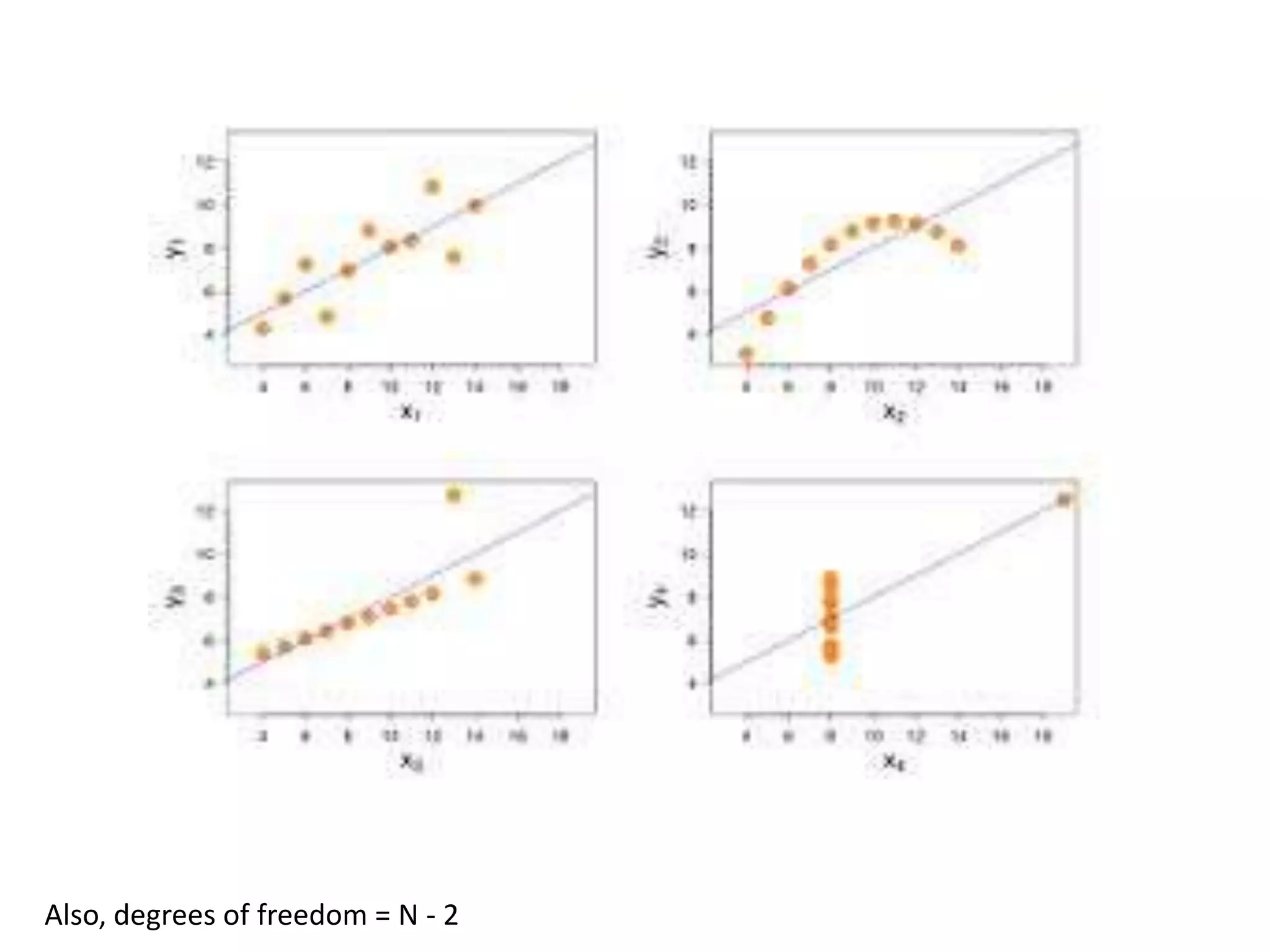
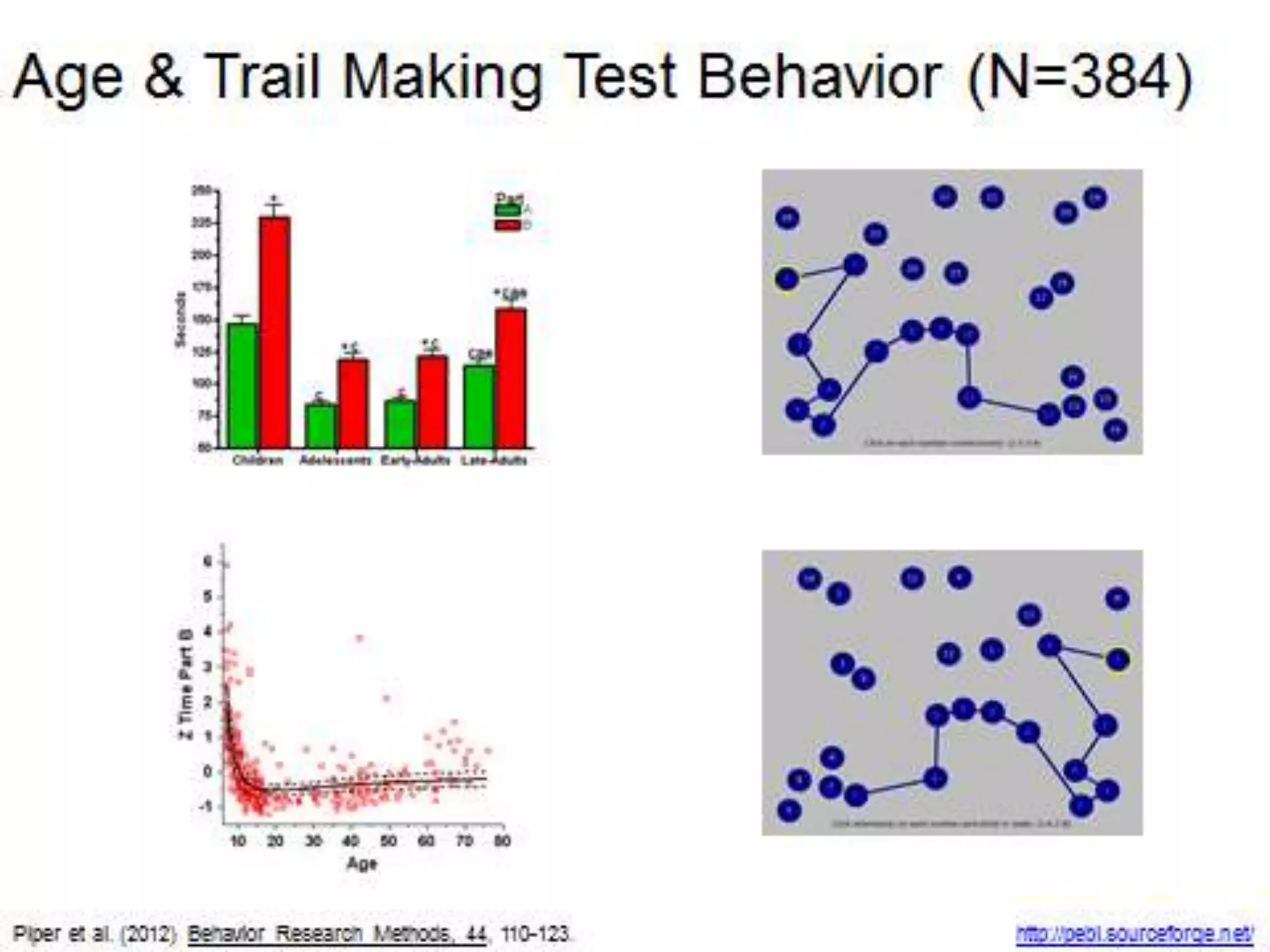
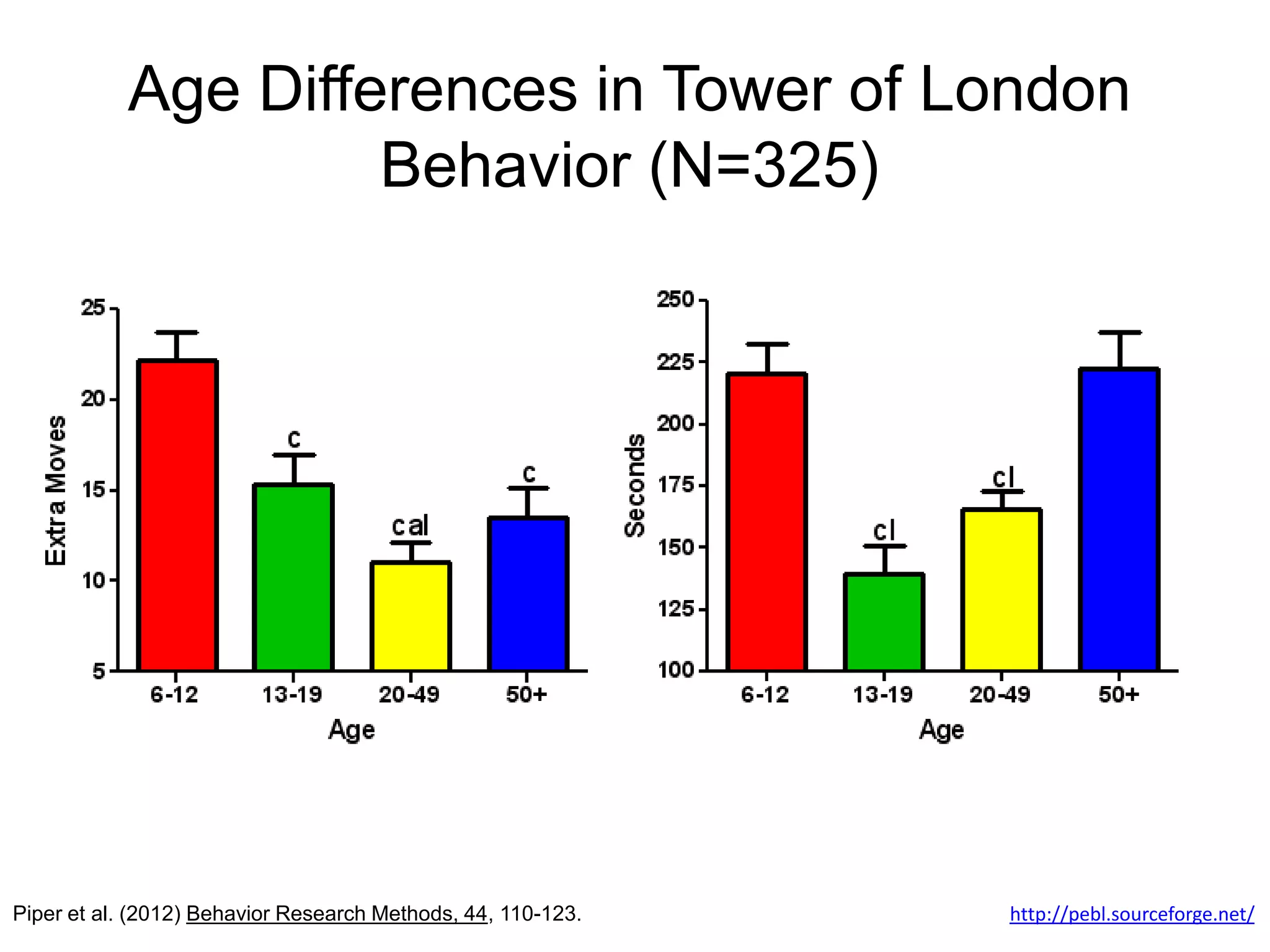
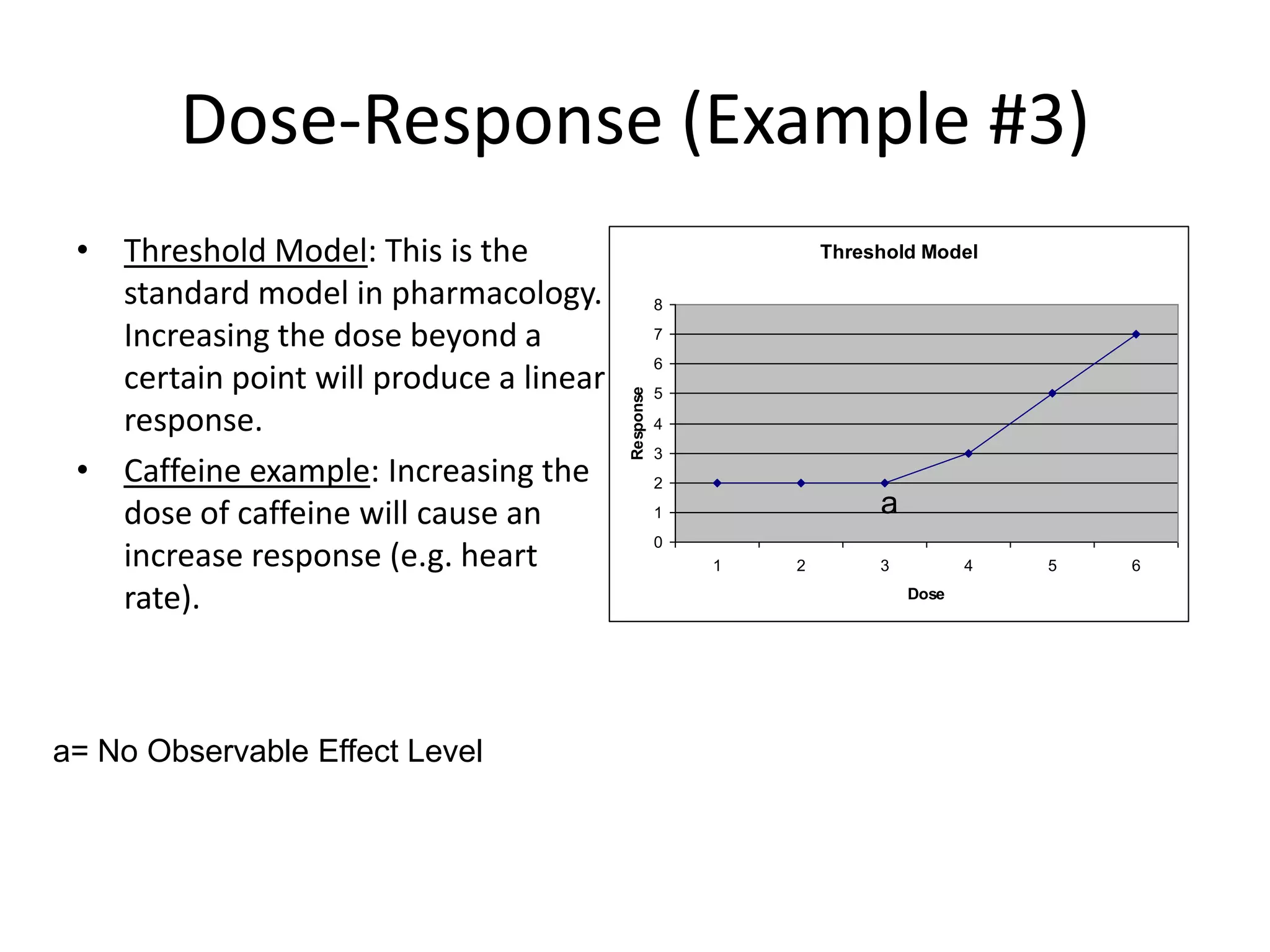
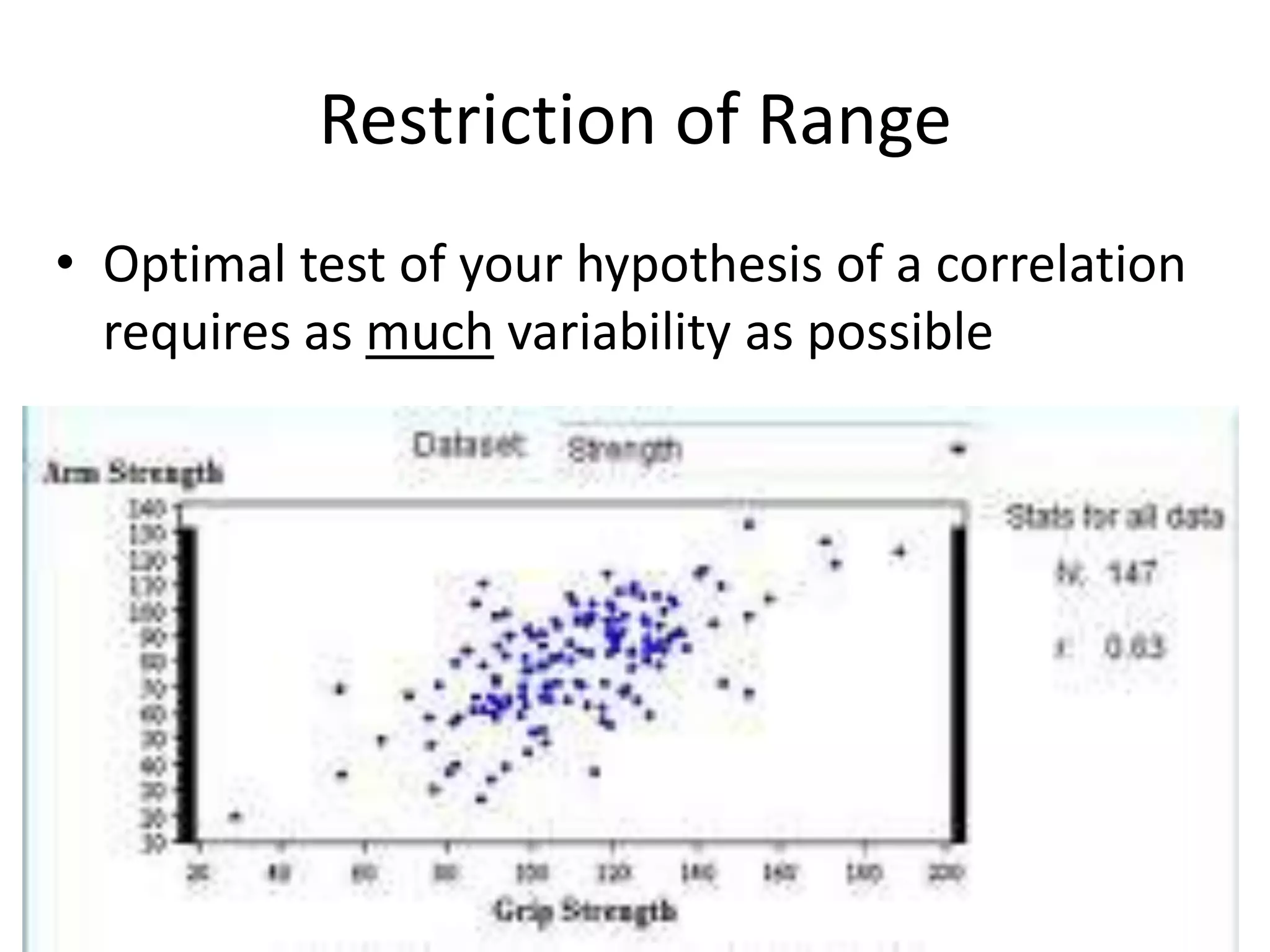
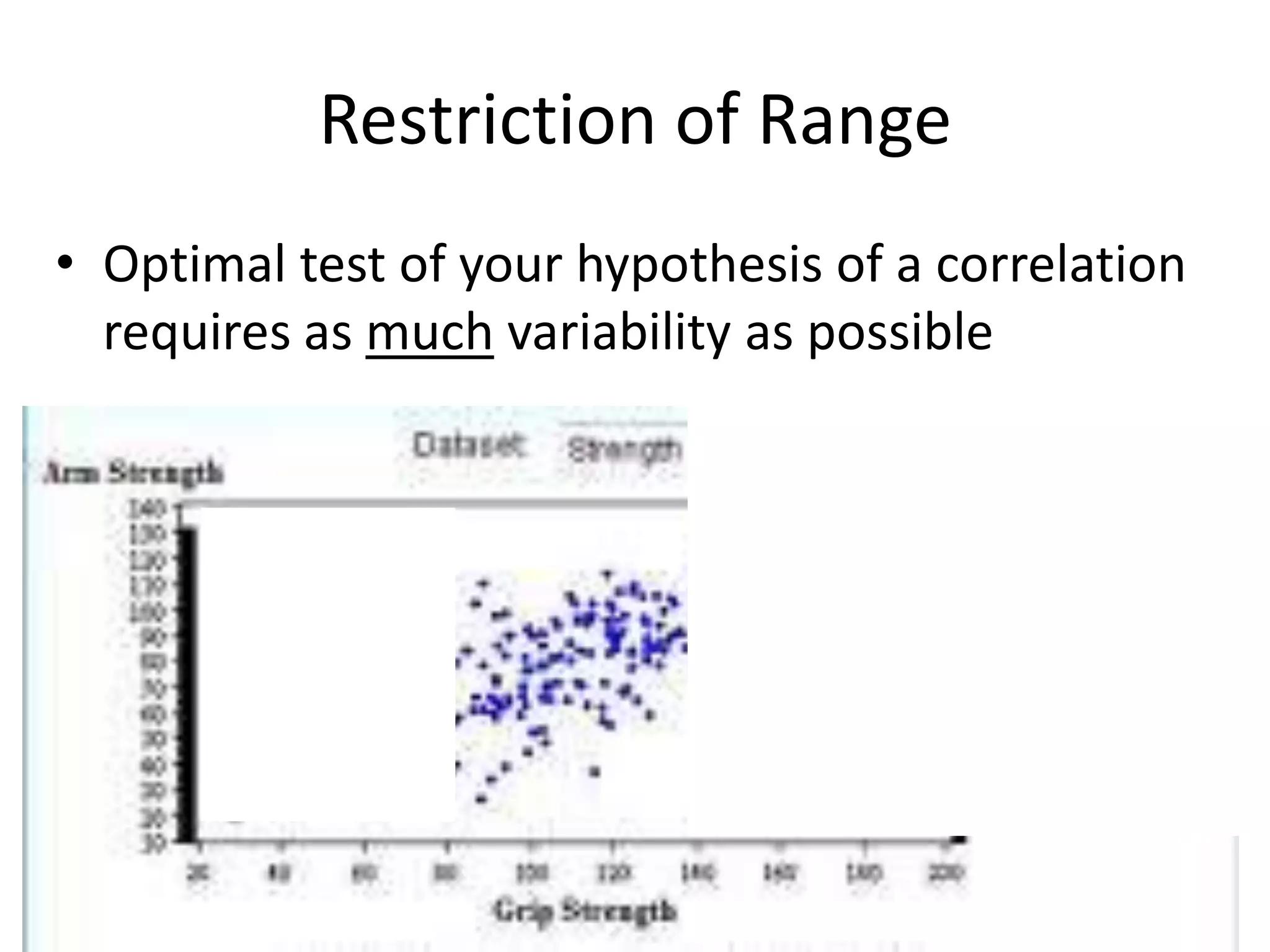
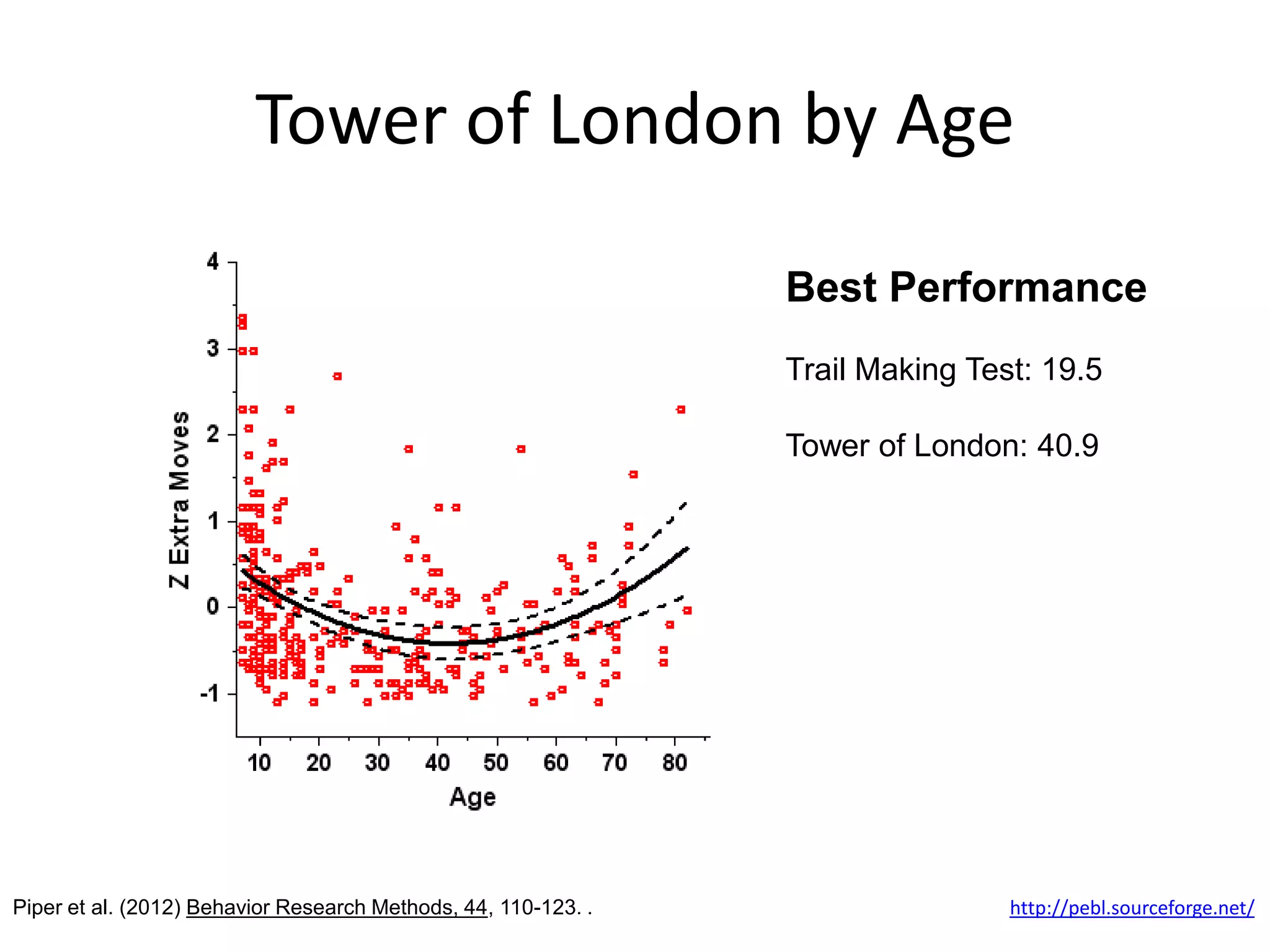
The document discusses correlation and regression, emphasizing the work of Sir Francis Galton and Karl Pearson, and outlines the assumptions necessary for correlation analysis. It includes examples like the Tower of London task and explores concepts like dose-response relationships and the coefficient of determination (r²). The document also highlights the importance of variability for accurate hypothesis testing in correlation studies.