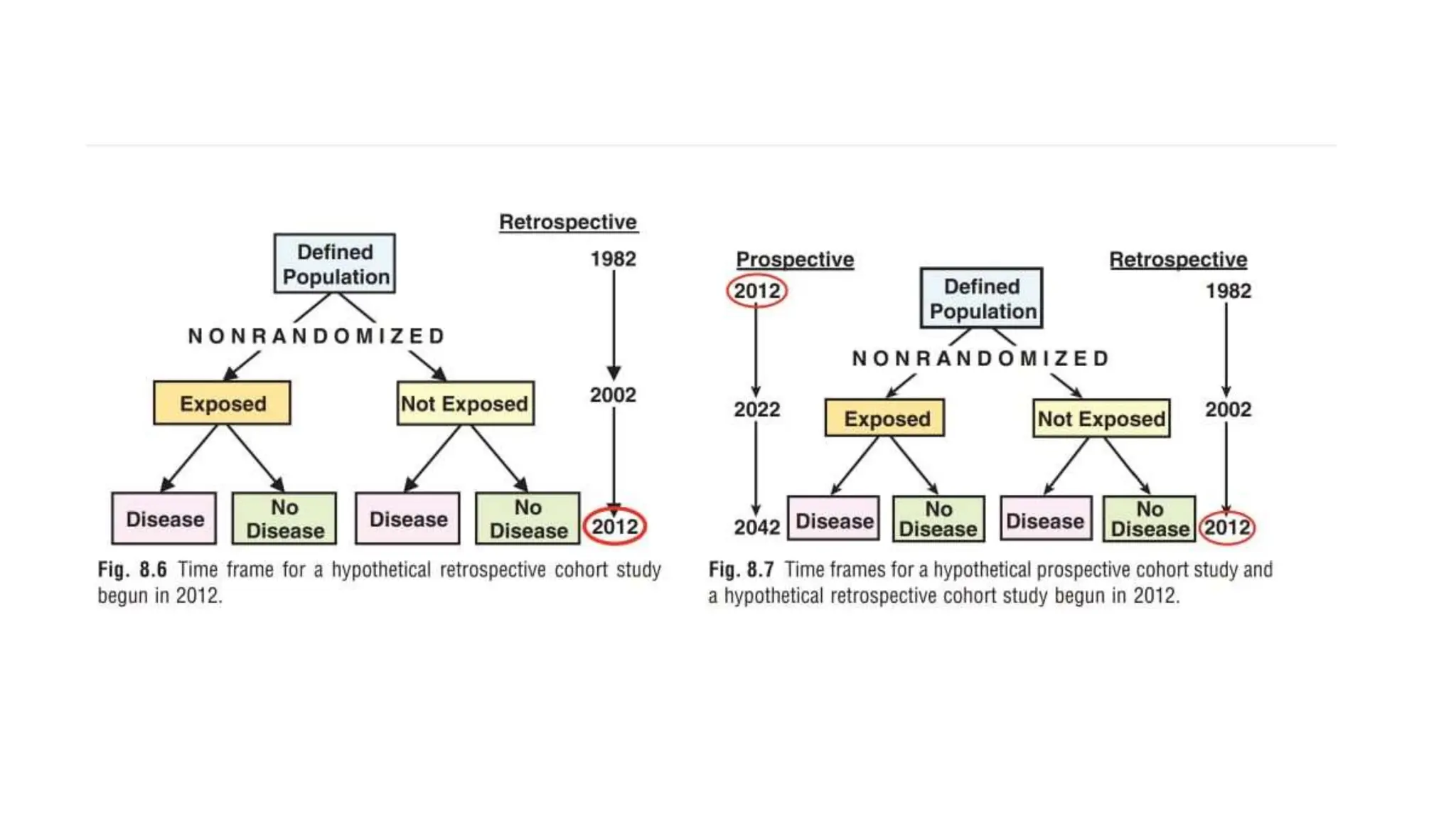
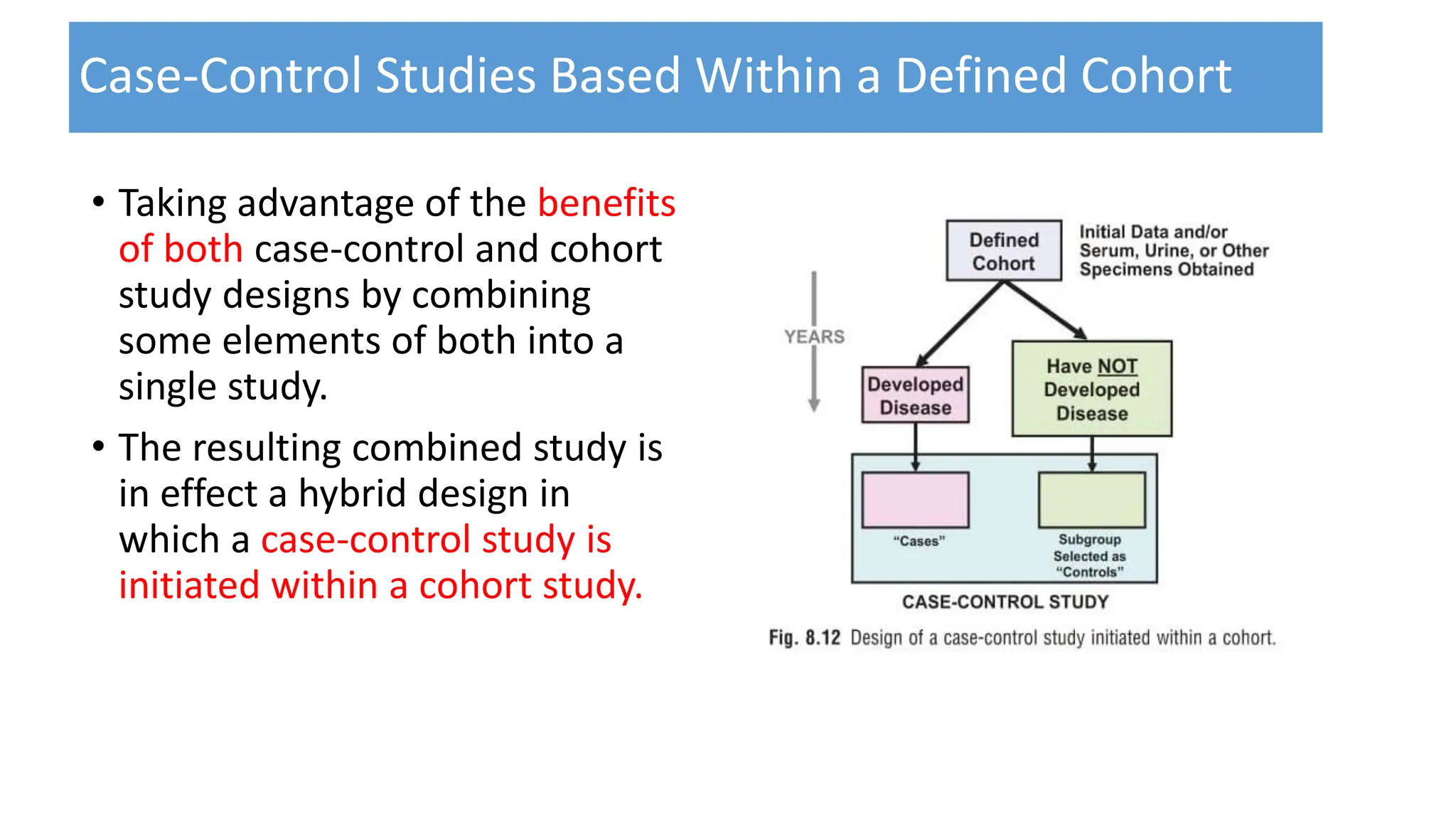
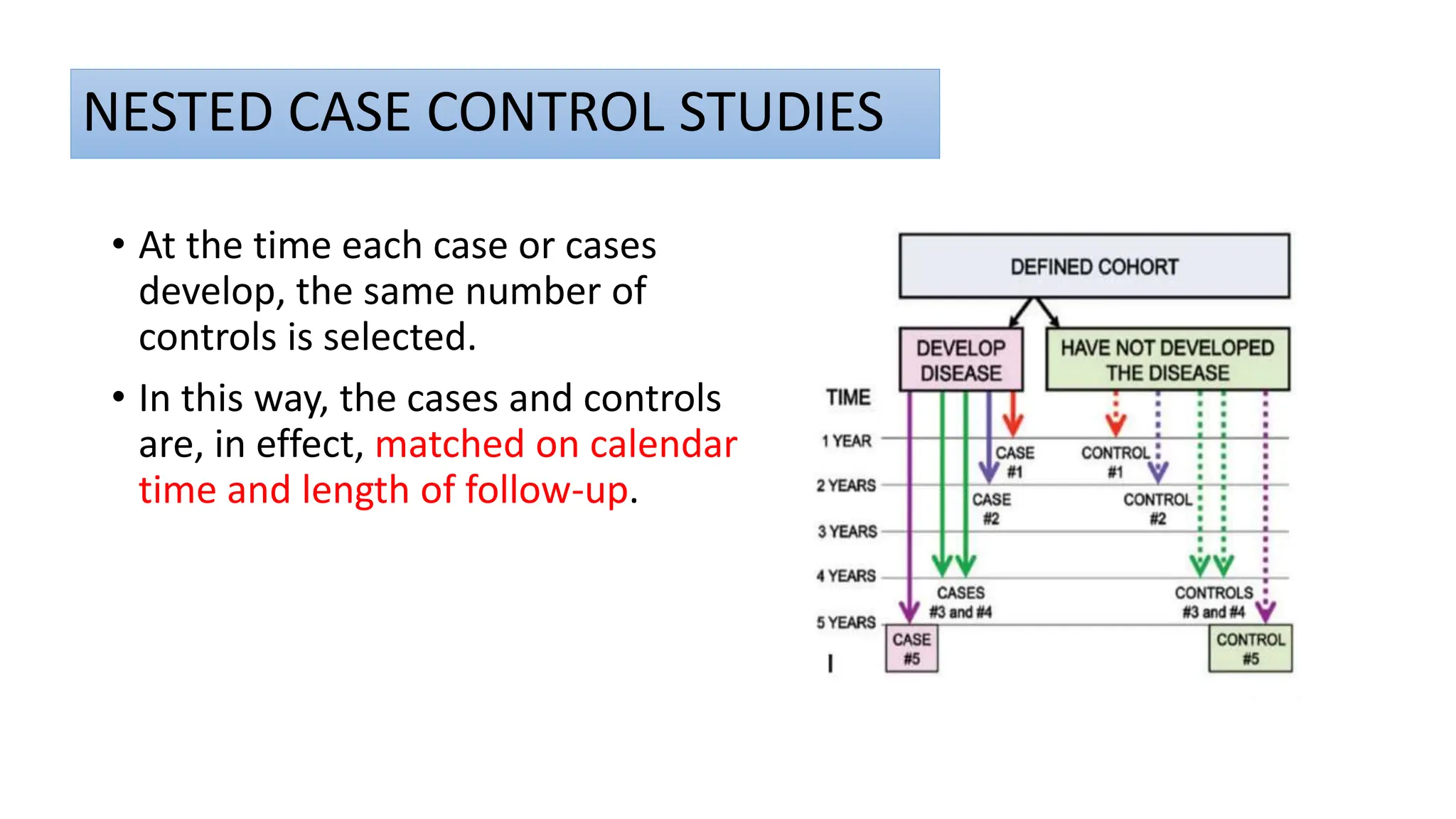
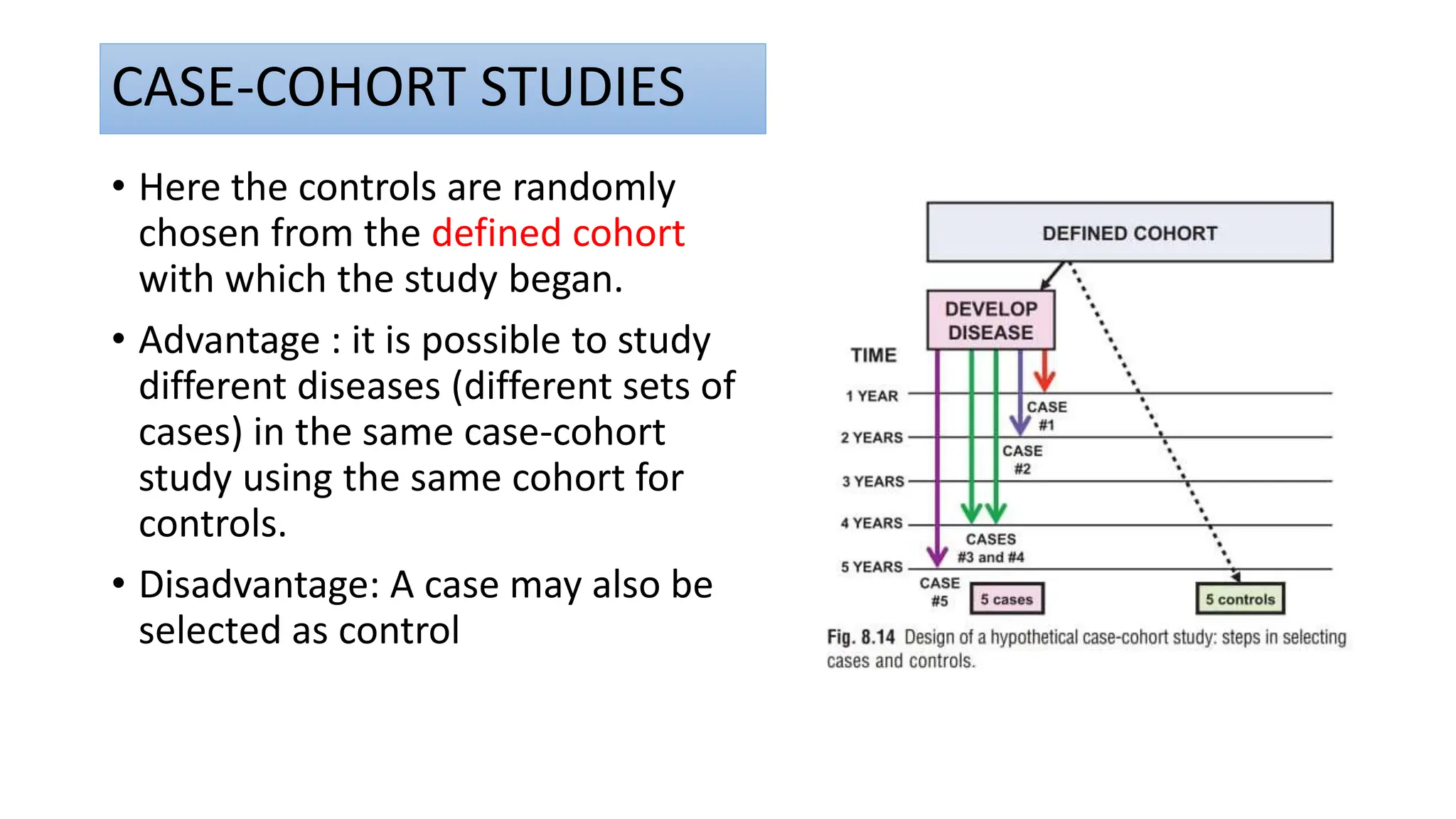
This document outlines the design and conduct of cohort studies. It defines a cohort study as selecting exposed and unexposed groups and following them over time to compare disease incidence. Key points include: cohort studies can establish temporal relationships between exposures and outcomes; they calculate relative risk to measure effects; and they can be prospective, retrospective, or combine features of both. Biases, reporting, and critical appraisal of cohort studies are also discussed.