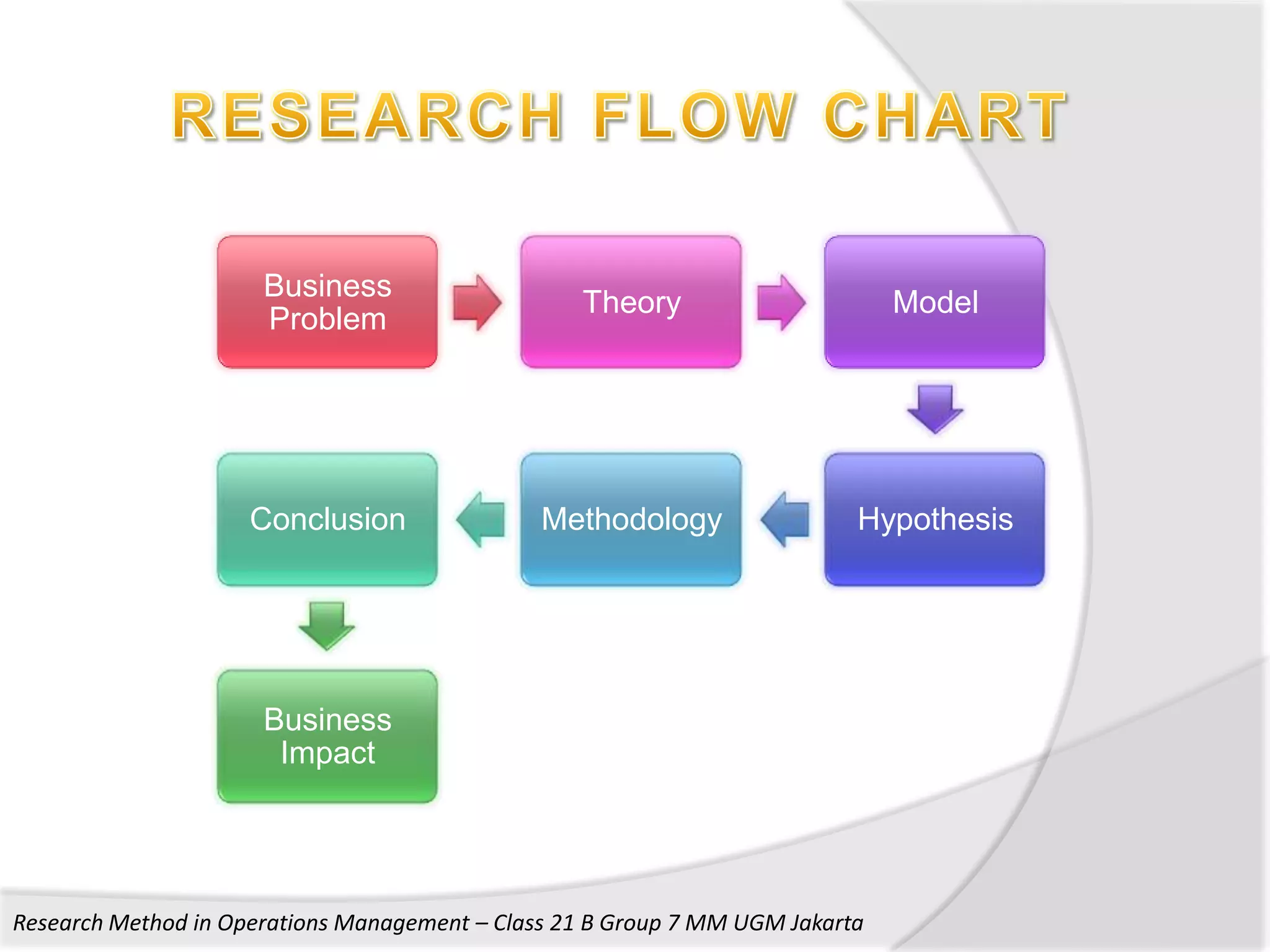
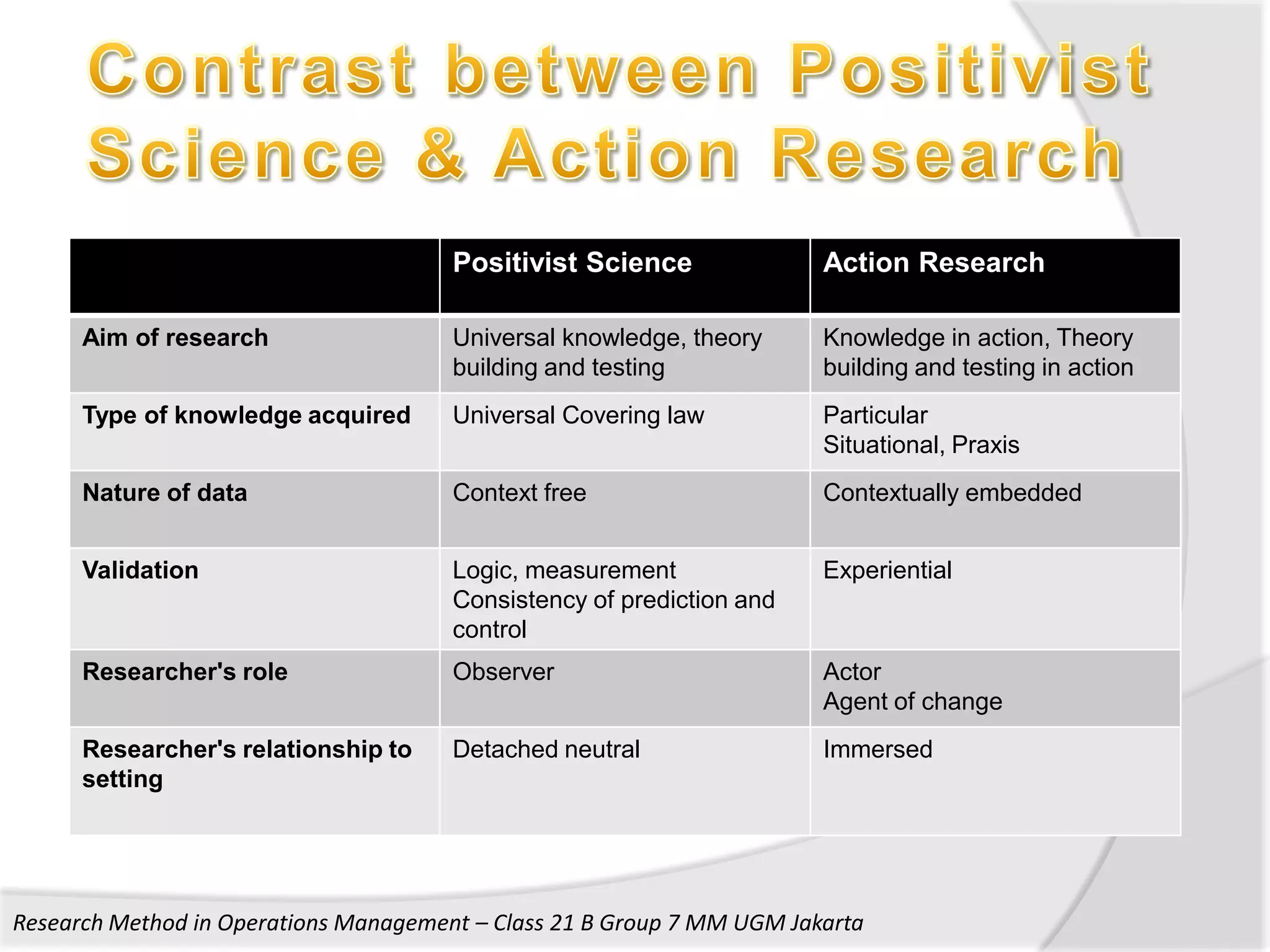
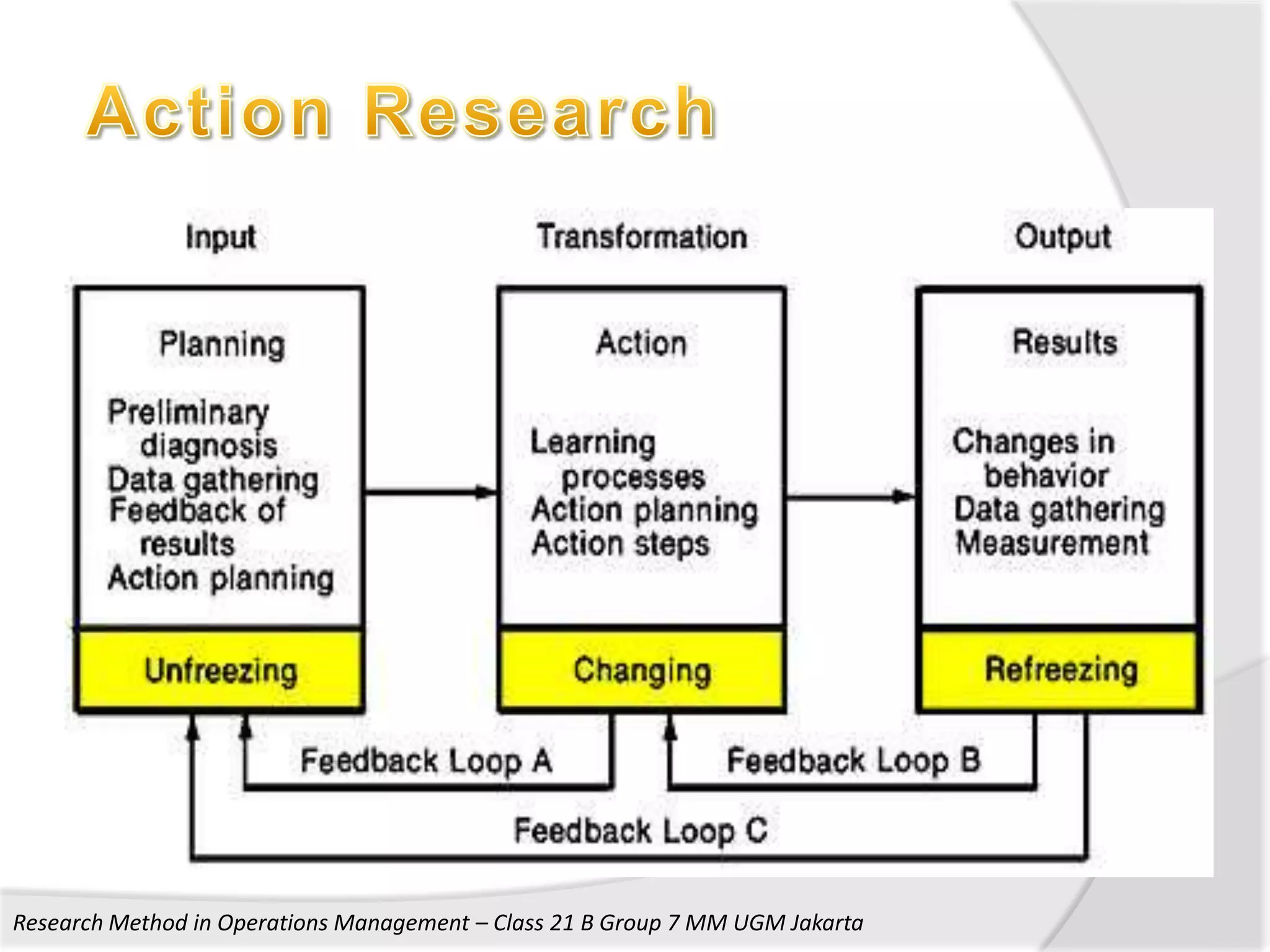
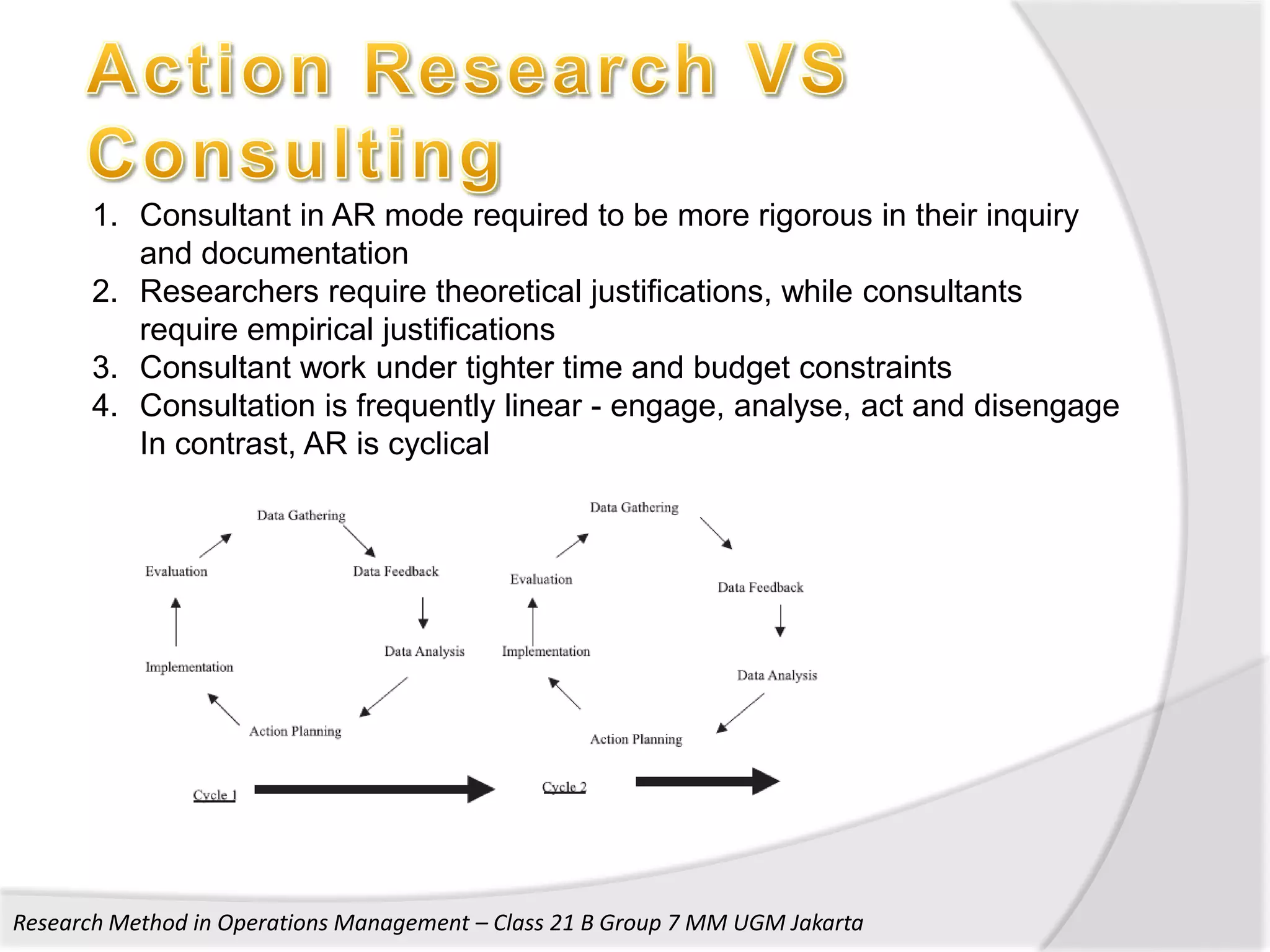
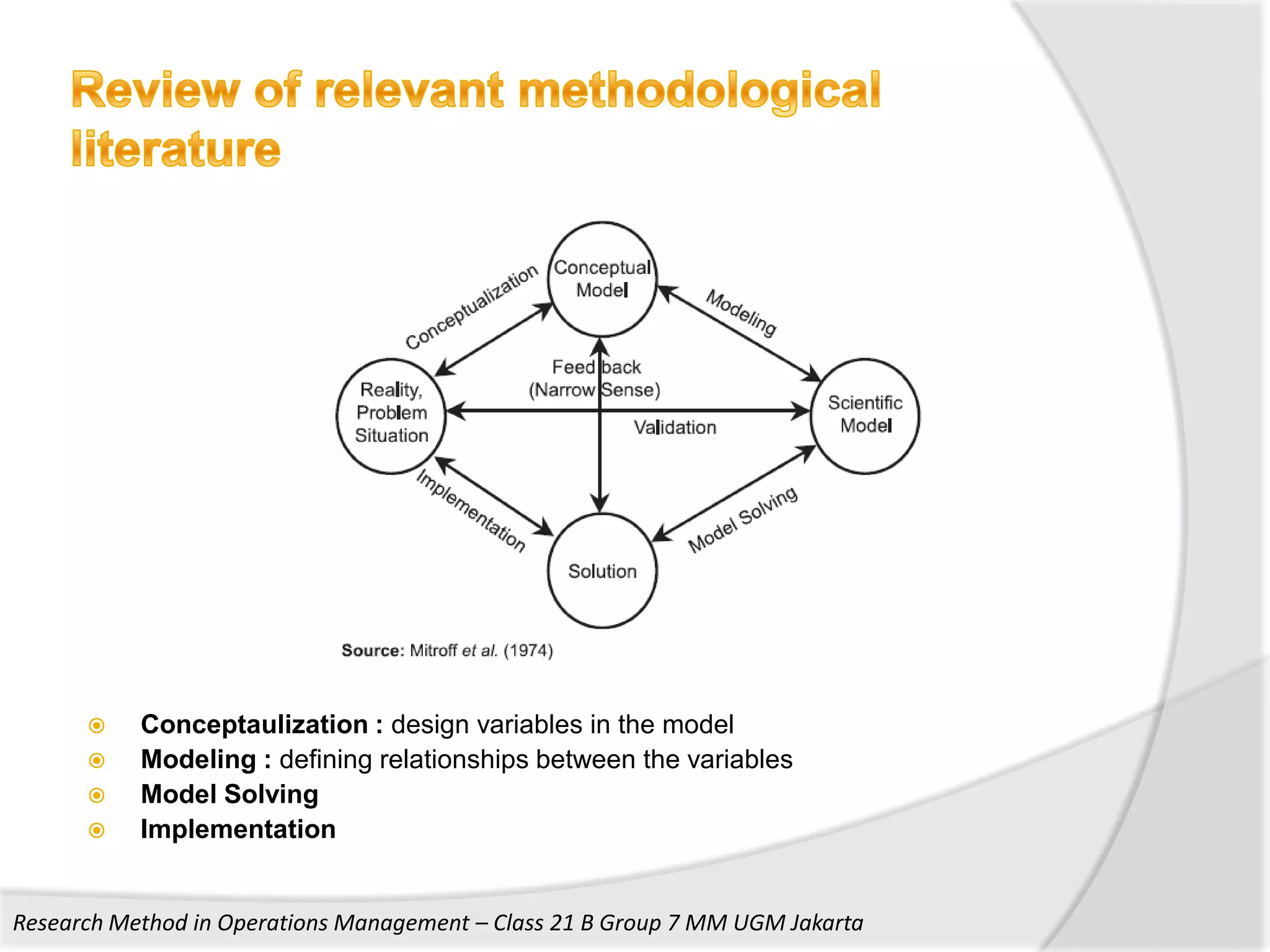
1. The document discusses research methods used in operations management, including survey research, case study research, and action research.
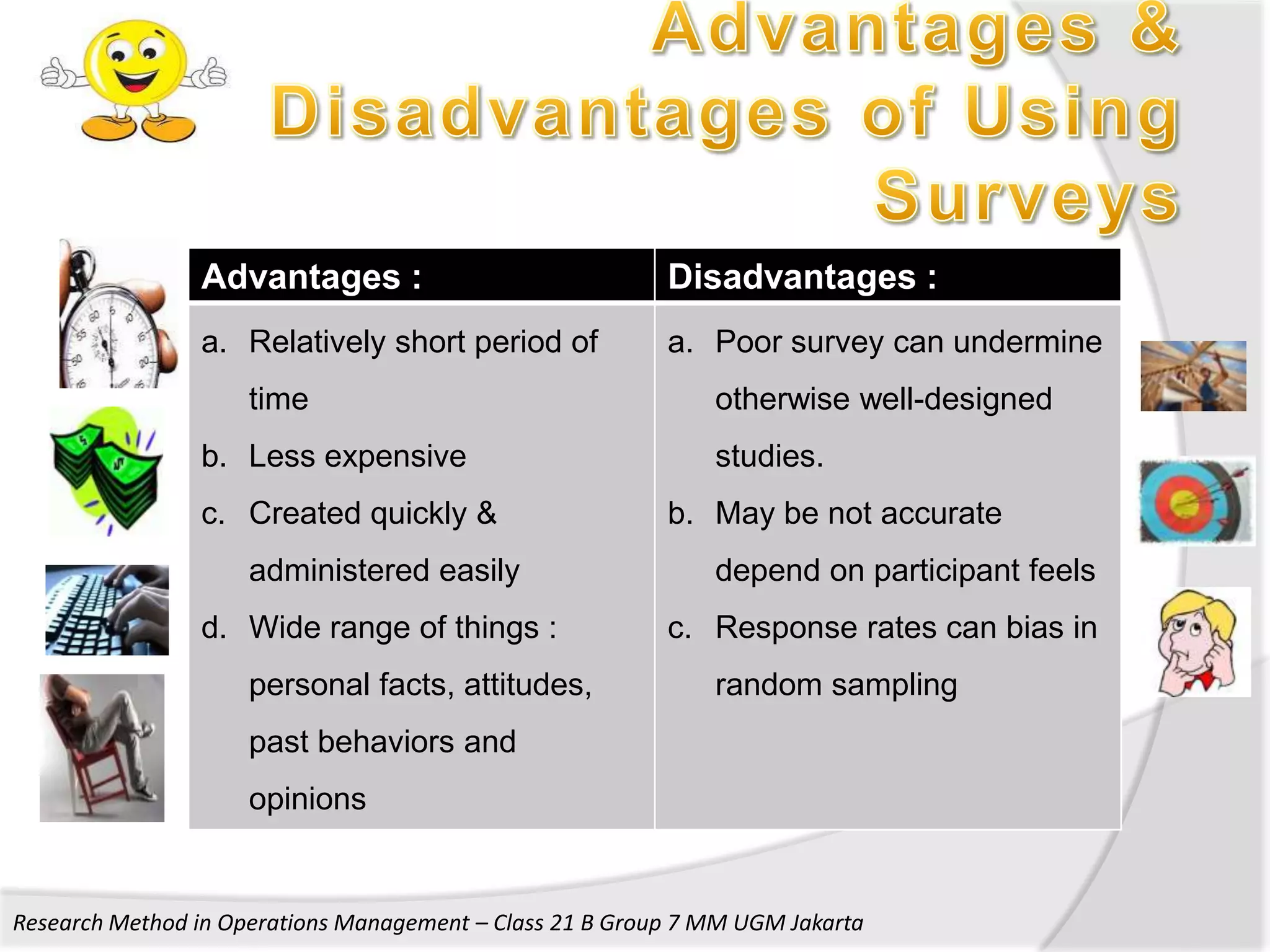
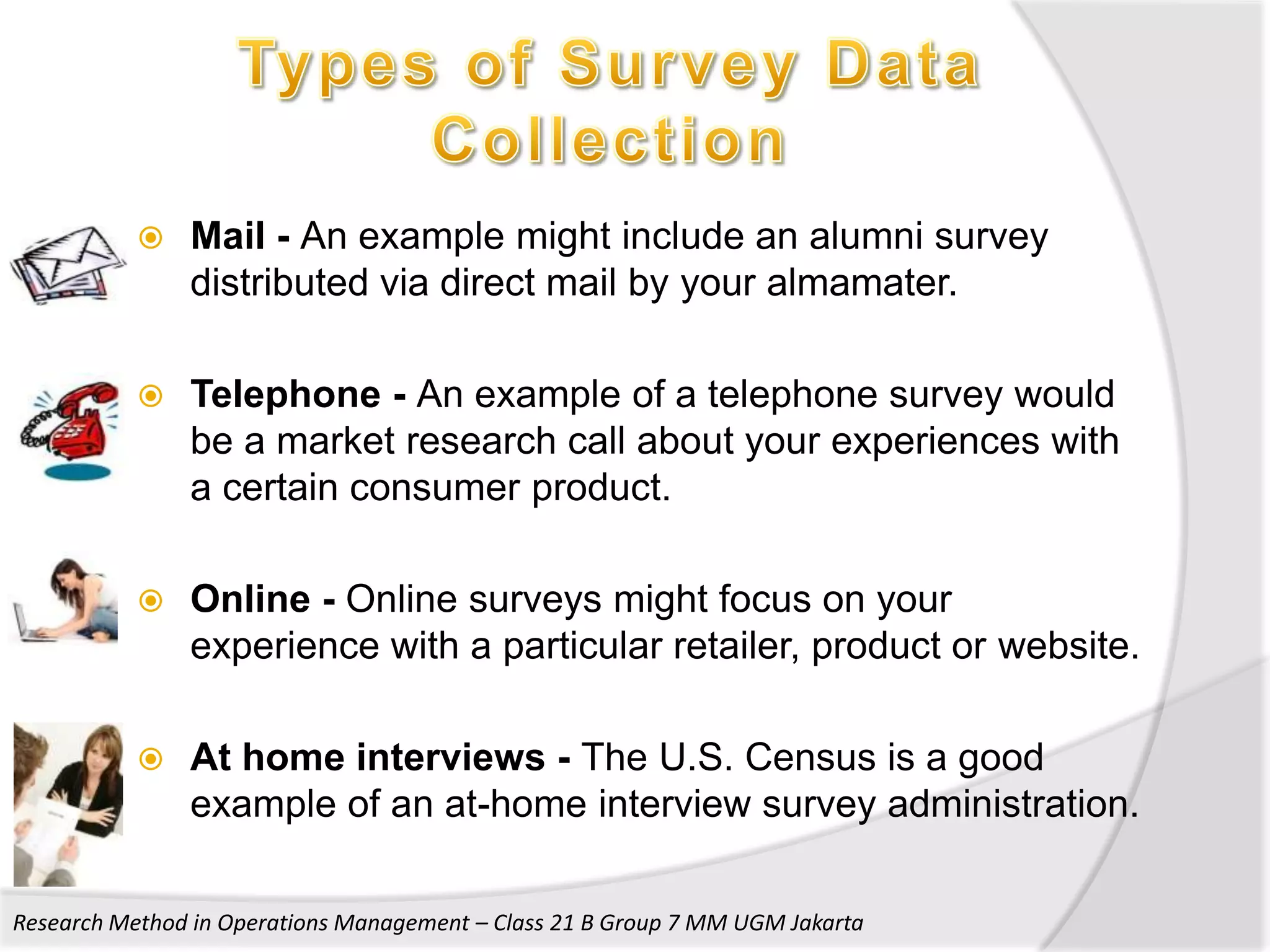
2. It provides details on the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of survey, case study, and action research methods.
3. The document also discusses key aspects of conducting research using these methods such as developing frameworks, collecting and analyzing data, and ensuring validity and reliability.