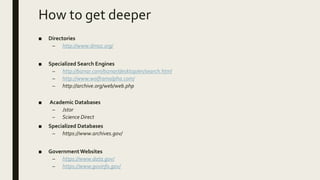
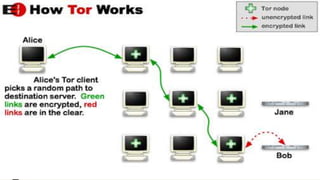
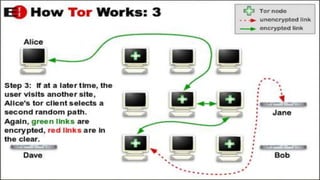
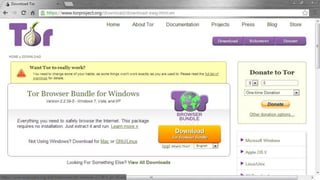
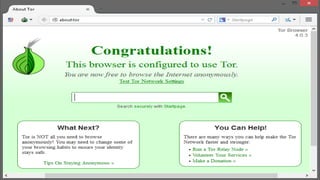
The document discusses the deep web and dark web. The deep web includes privately hosted websites and databases that are not indexed by search engines. The dark web is intentionally hidden and can only be accessed using software like Tor, which encrypts internet traffic to maintain anonymity. While the dark web can enable privacy and whistleblowing, it is also used for illegal activities due illegal goods and services due to its anonymity. Tor works by bouncing communications through a network of volunteers servers around the world to hide a user's location and usage.