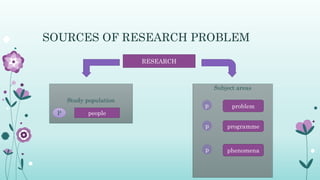
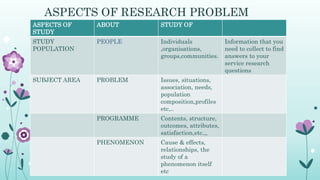
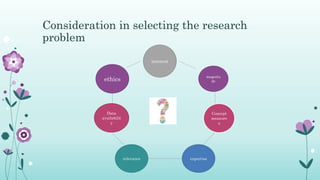
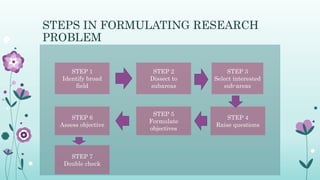
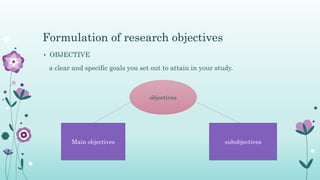
This document discusses the importance of formulating a research problem and outlines the steps to do so. It states that formulating the research problem is the first and most critical step of the research process. Some key points discussed include identifying the broad field of study, narrowing it down to subareas of interest, considering factors like relevance and feasibility when selecting a problem, and formulating clear objectives to focus the study. The document provides guidance on sources of research problems, aspects to consider, and a 7-step approach to properly formulating the research problem.