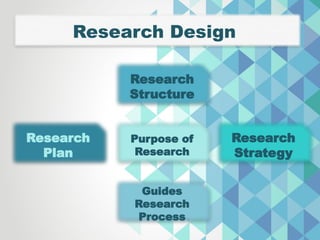
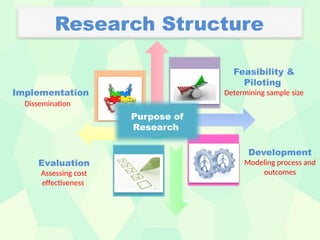
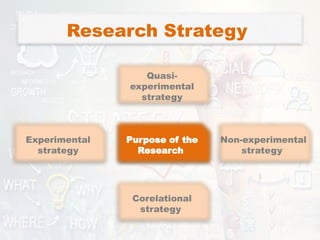
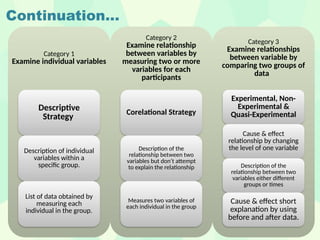
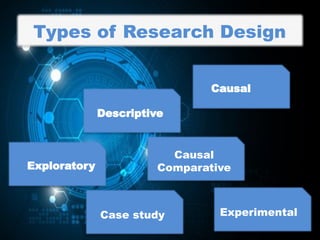
The document presents a comprehensive overview of various research designs and strategies, focusing on their purposes, types, and methodologies. It discusses exploratory, descriptive, comparative, and experimental research designs, including the distinction between causal-comparative types and highlights the importance of research design in achieving accurate and reliable results. The structure includes planning, designing, operational stages, and evaluation processes to guide effective research implementation.