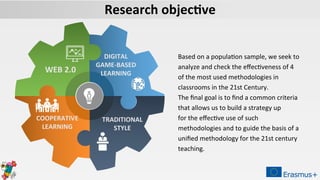
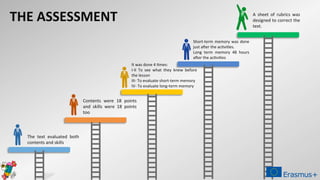
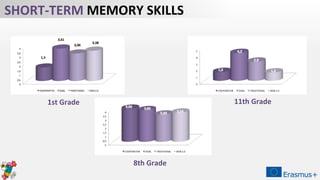
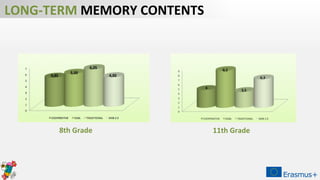
The document discusses a project aimed at evaluating the effectiveness of four teaching methodologies—cooperative learning, digital game-based learning, traditional style, and Web 2.0 tools—on student learning in various subjects. The study reveals that active methodologies, particularly digital game-based learning, significantly enhance both short-term and long-term memory retention compared to traditional methods. However, some issues within cooperative learning practices are noted, highlighting variability in student outcomes.