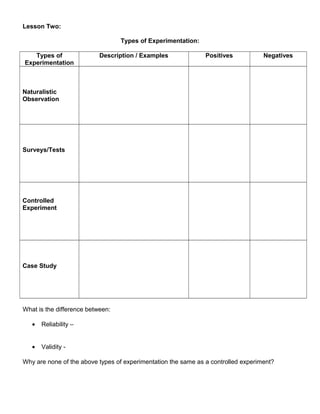
This document summarizes key concepts in research methods and psychology. It discusses the importance of replication, controlling for confounding variables, and ethical guidelines. It also outlines different types of studies and variables, statistical analysis techniques like measures of central tendency, and the differences between quantitative and qualitative research. The goal is to understand fundamental aspects of designing, conducting, analyzing, and interpreting psychological research studies.