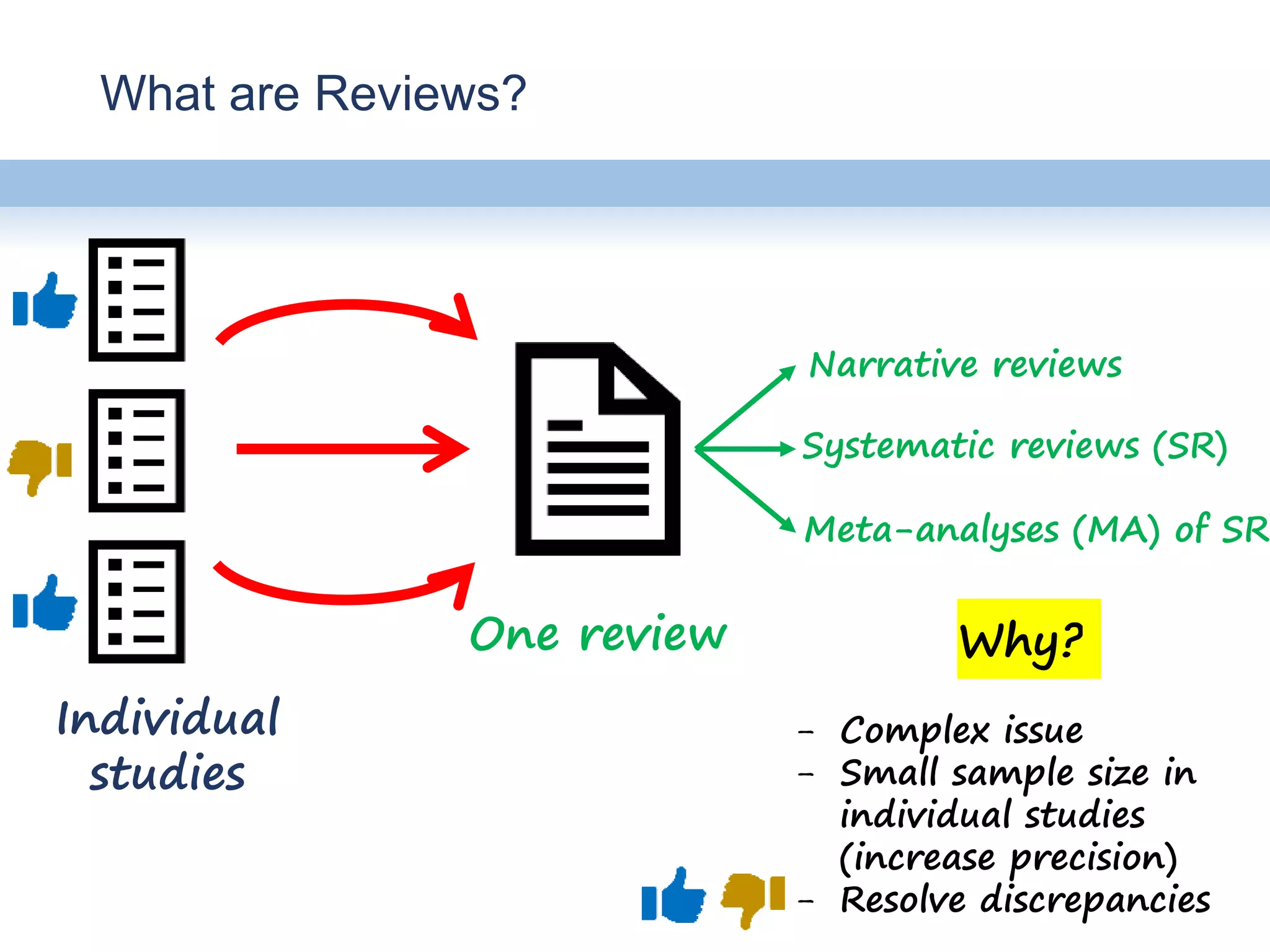
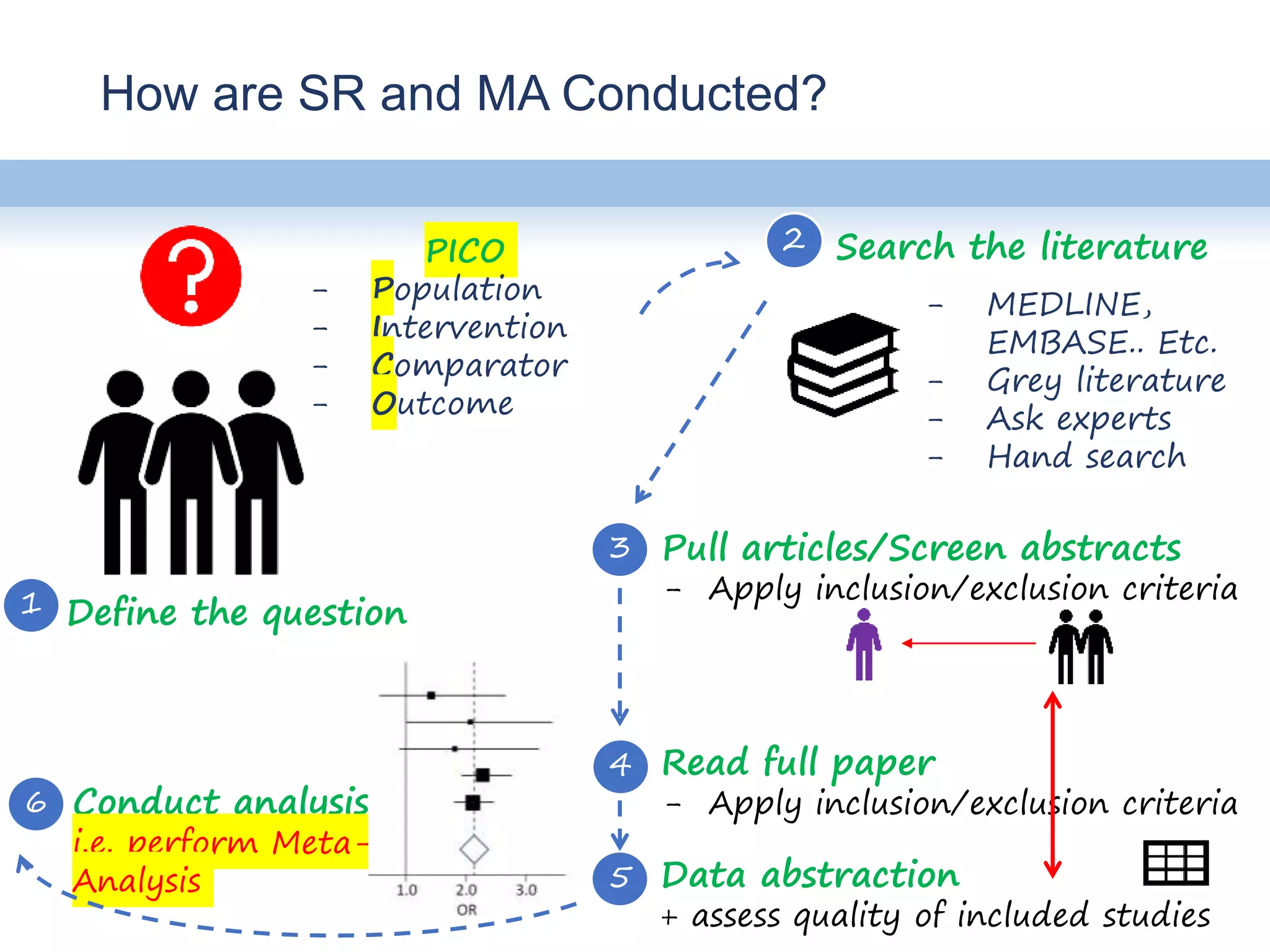
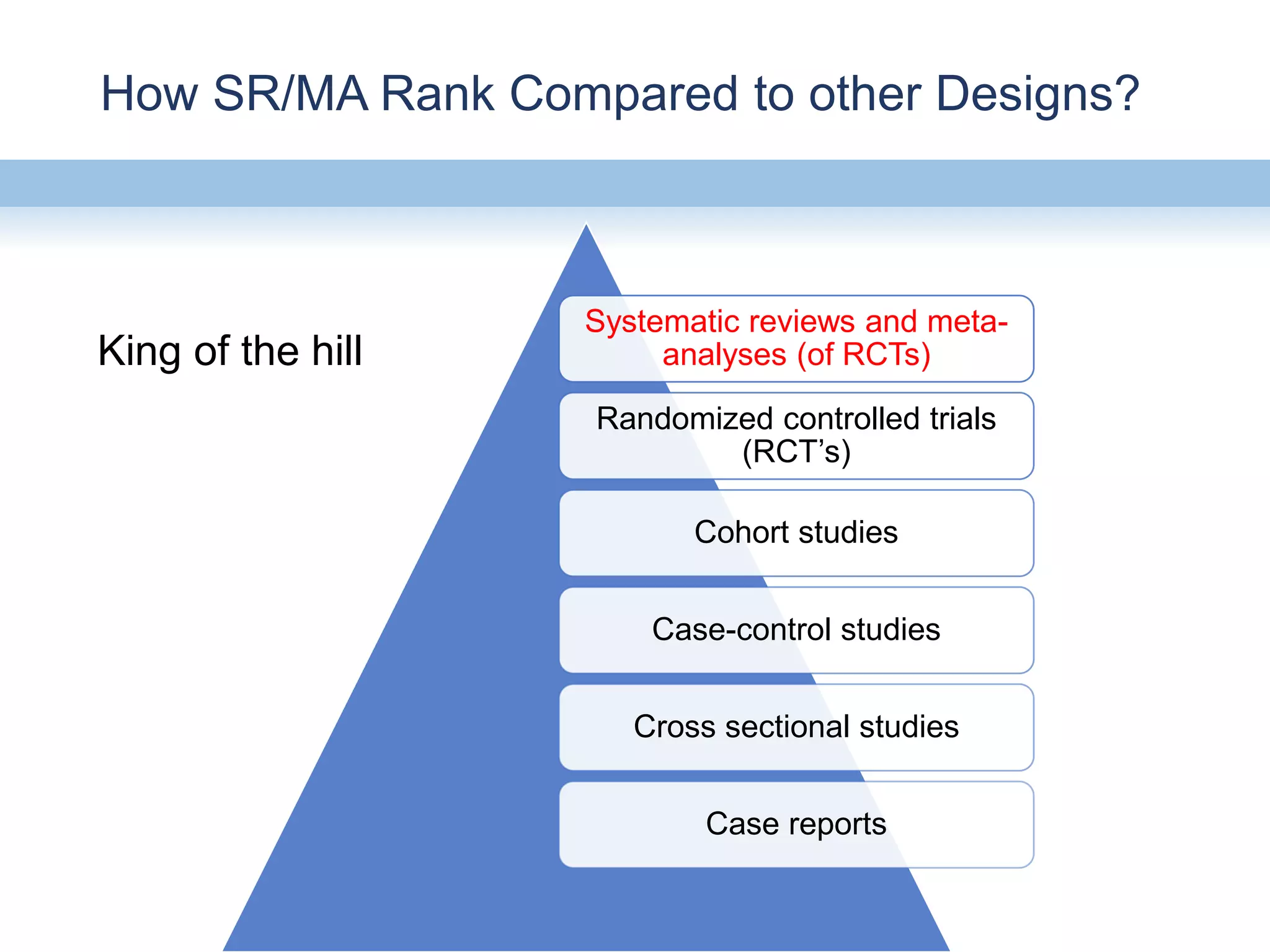
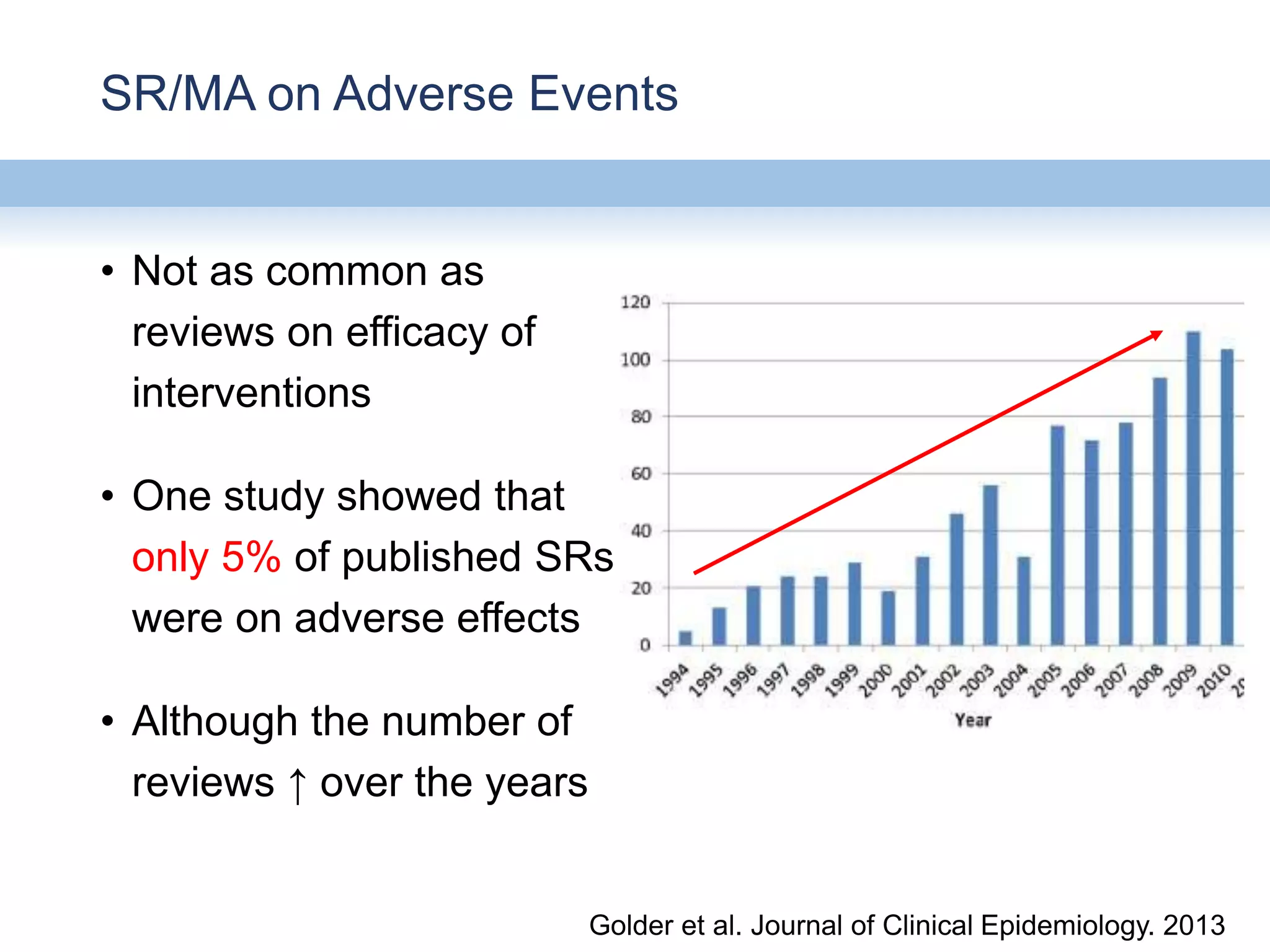
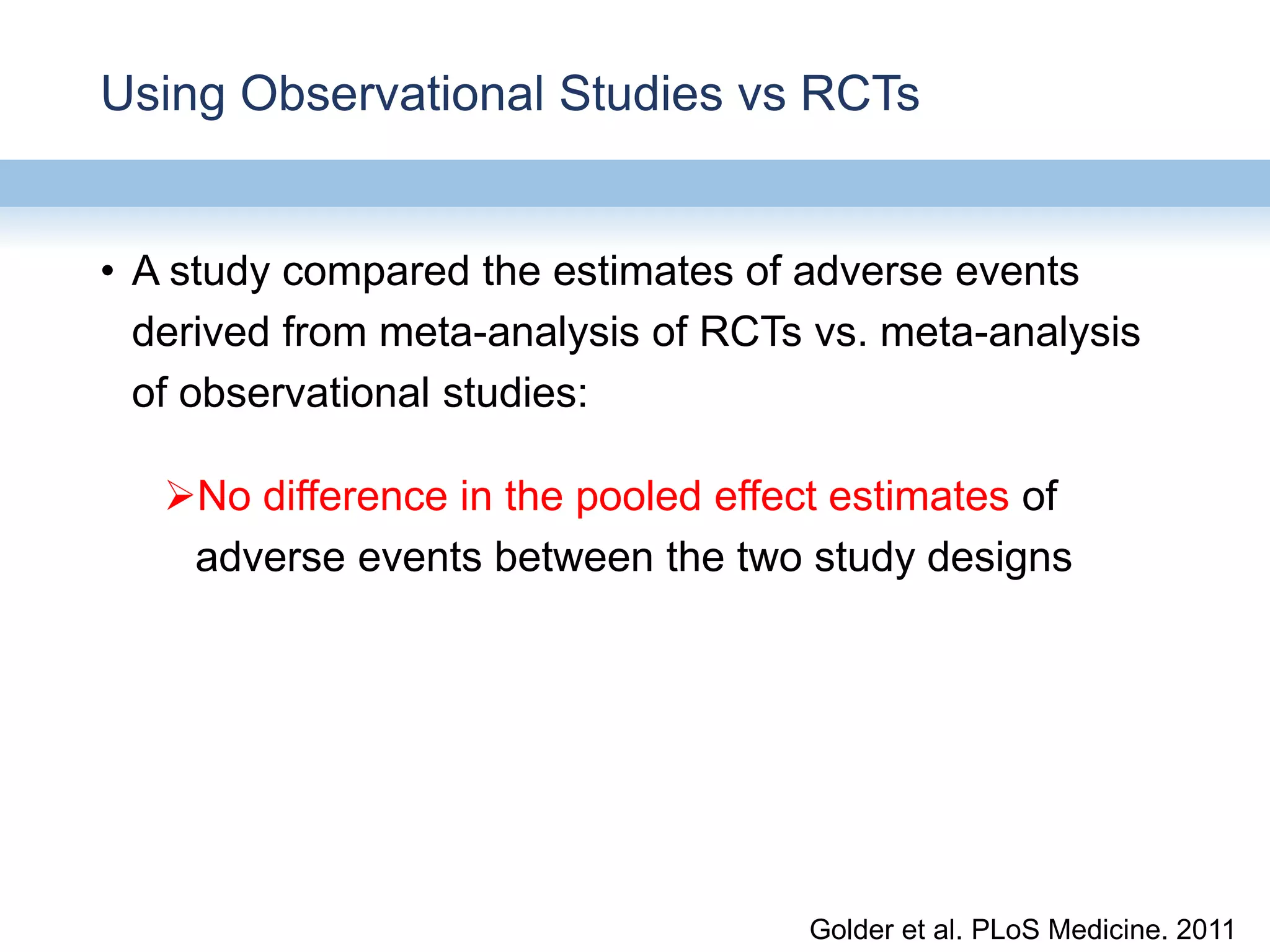
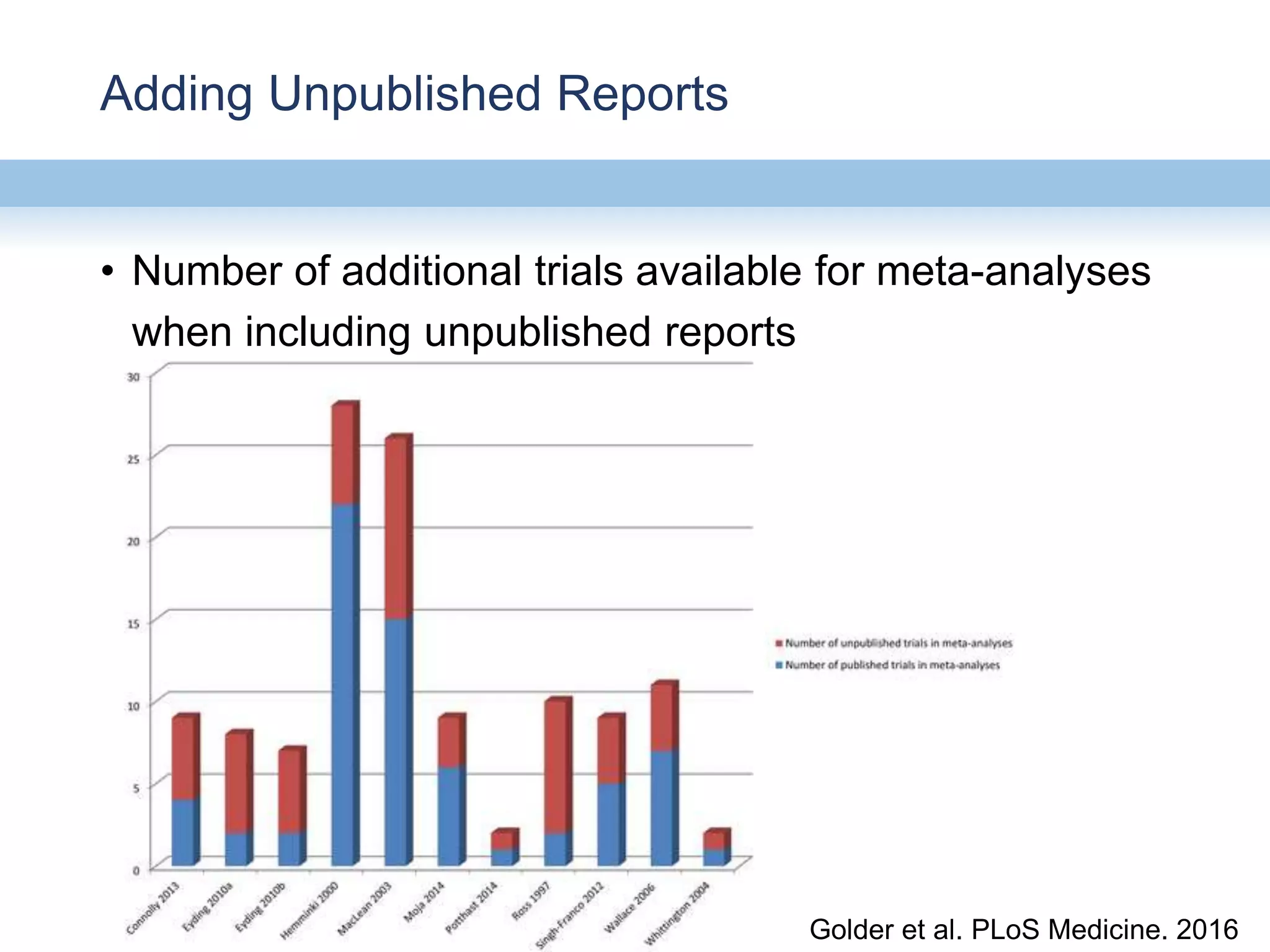
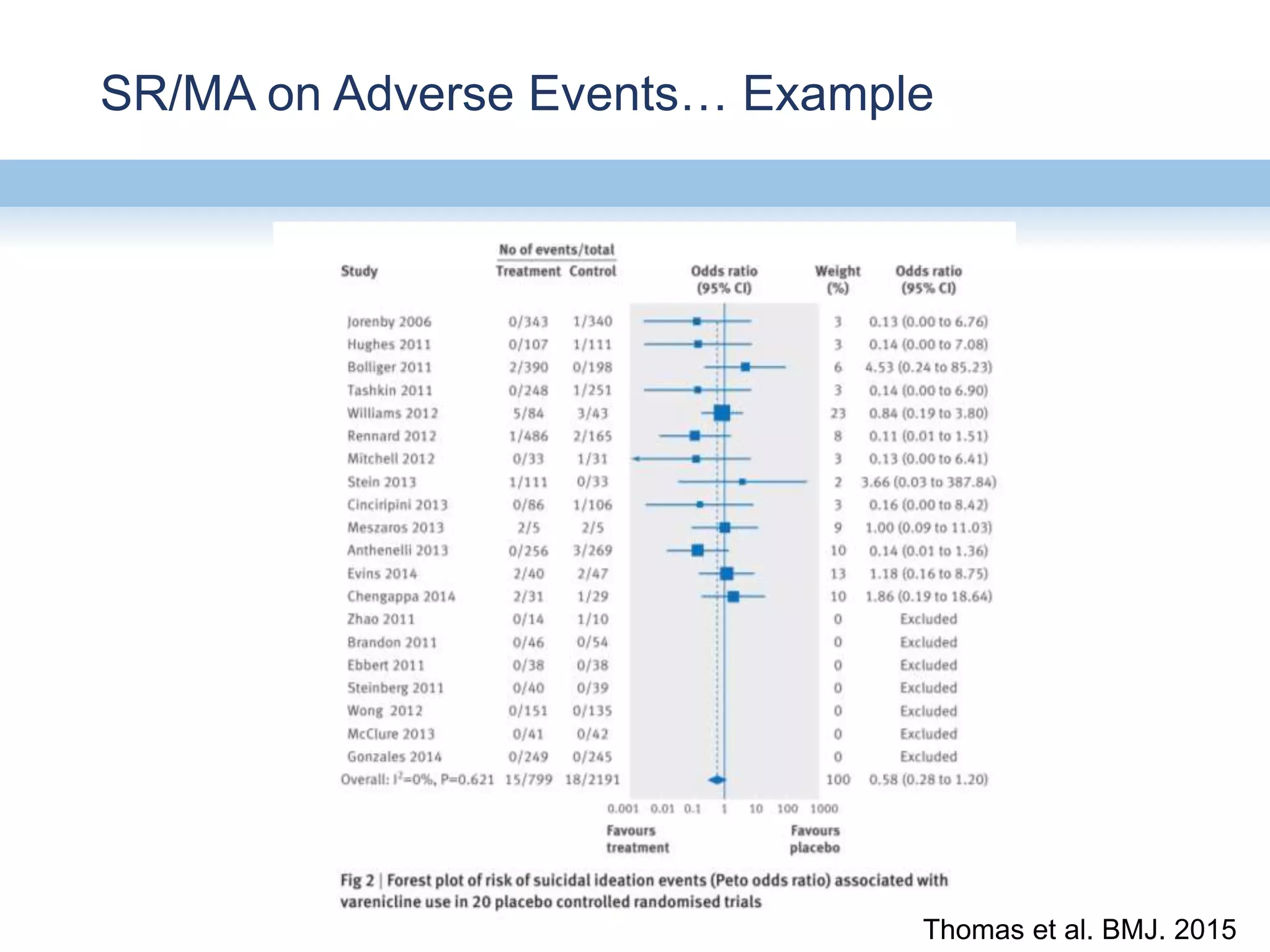
This document provides an overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses, their application to medication safety data, and how to conduct such reviews. It defines systematic reviews and meta-analyses and explains how they are conducted more rigorously than traditional narratives. Reviews of safety data can help resolve inconsistencies across studies and increase precision through pooling of data. While less common than efficacy reviews, meta-analyses of both randomized trials and observational studies are valuable for understanding adverse events. It is important to search unpublished literature and include various study designs when reviewing safety. Quality assessment and reproducible search methods are also important aspects of conducting a rigorous systematic review or meta-analysis of medication safety data.