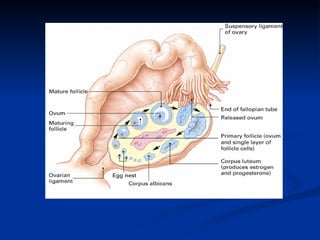
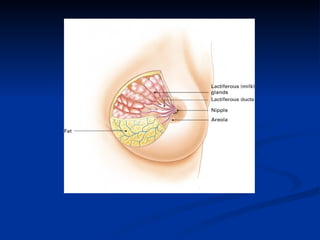
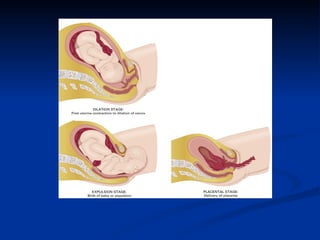
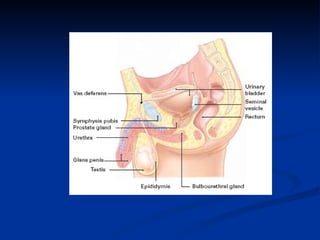
The document summarizes the key organs of the male and female reproductive systems. For females, it describes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, vulva, and breasts. It notes the functions of producing eggs and hormones for the ovaries, transporting eggs for the fallopian tubes, preparing to receive fertilized eggs for the uterus, receiving the penis during intercourse for the vagina, and producing milk for breasts. For males, it lists the testes, epididymis, penis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands as the key organs.