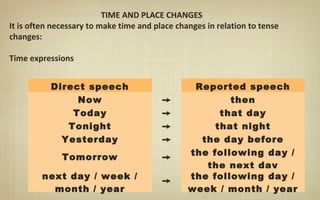
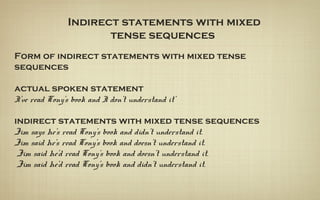
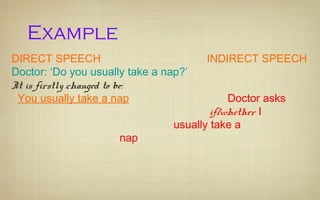
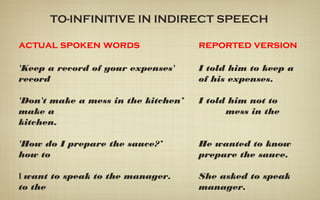
When reporting speech, verb tenses are usually changed to be in the past. This is because reported speech refers to something that was said in the past. Verb tenses are moved back, or "backshifted", following specific rules. For example, the present simple becomes the past simple. Pronouns and expressions of time and place are also typically changed in reported speech.