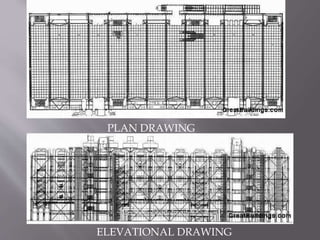
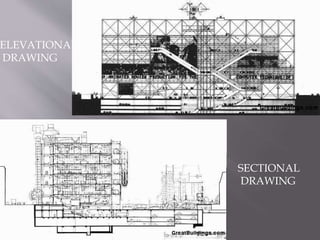
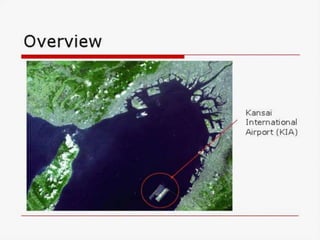
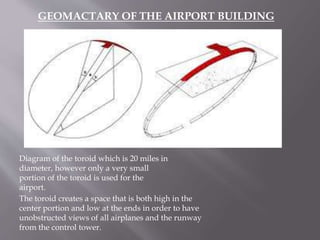
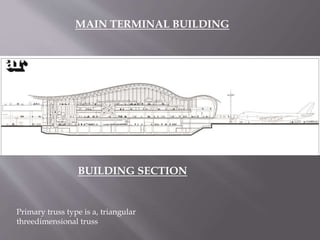
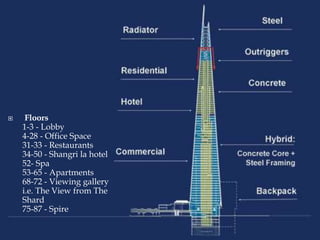
Renzo Piano is an Italian architect known for his high-tech modern designs that showcase technological shapes and materials. Some of his most famous works include the Centre Pompidou in Paris, Kansai International Airport Terminal in Osaka, and the New York Times Building. Piano's buildings are characterized by their use of steel, aluminum, and glass, with functional elements like ducts and pipes displayed on the exterior. He is considered a pioneer of high-tech architecture focused on maximizing interior space through exposed structural elements.