1. Leonardo da Vinci was an Italian polymath during the Renaissance who perfected techniques like sfumato, aerial perspective, and linear perspective. However, he often did not finish projects and few of his works remain.
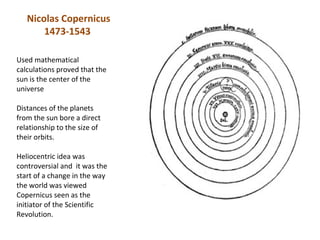
2. Scientific Revolution thinkers like Copernicus, Galileo, Newton, and Leeuwenhoek used careful observation and experimentation to develop scientific theories that challenged accepted beliefs and expanded knowledge of the natural world.
3. Enlightenment philosophers such as Descartes, Locke, Montesquieu, and Rousseau influenced political and social thought by advocating rational thinking and limiting governmental power through concepts like separation of powers and popular sovereignty.