Embed presentation


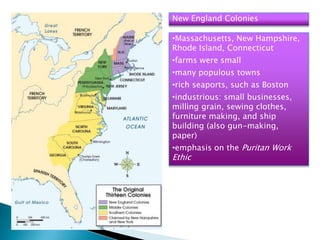
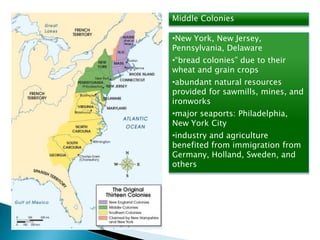
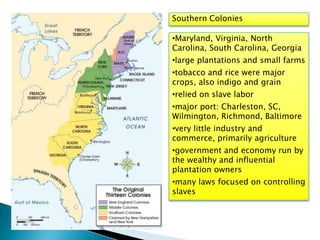

The 13 original British colonies in North America had diverse economies and cultures. The New England colonies focused on small farms, towns, seaports, and industries like shipbuilding. The Middle colonies grew wheat and other grains and had natural resources that supported mills, mines, and ironworks. The Southern colonies centered around large plantations and farms that grew cash crops like tobacco and rice using slave labor, with port cities and economies dominated by wealthy plantation owners.




