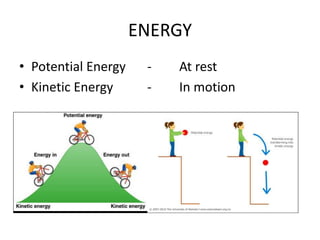
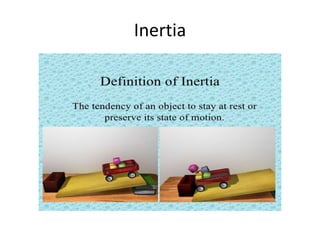
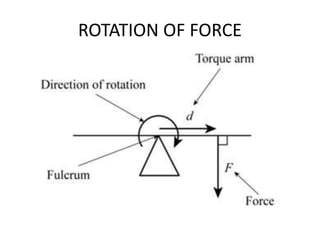
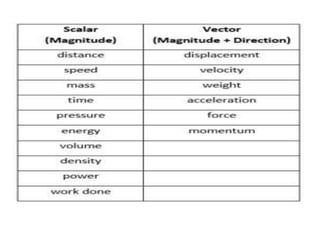
This document provides an overview of key concepts in physical science including:
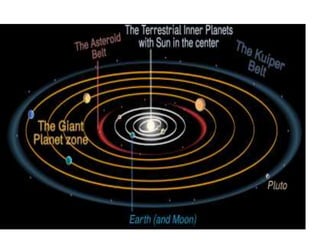
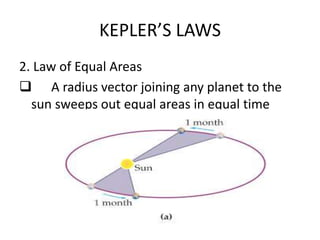
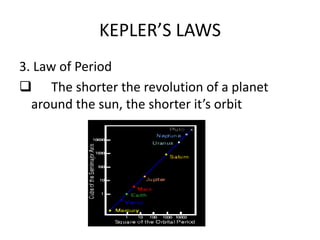
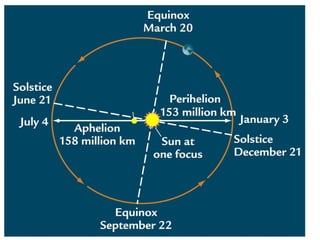
1) Kepler's laws of planetary motion which describe how planets move around the sun in elliptical orbits with the sun at one focus.
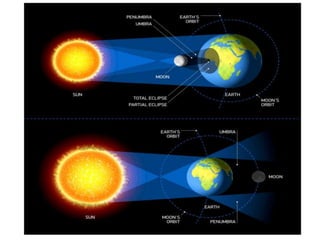
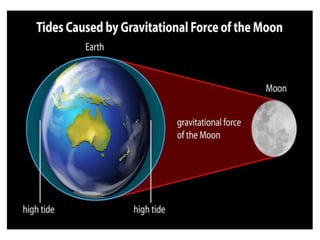
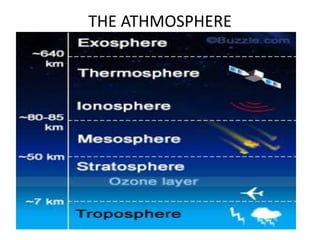
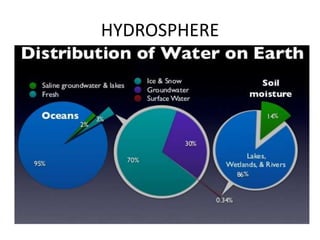
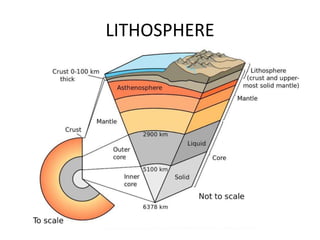
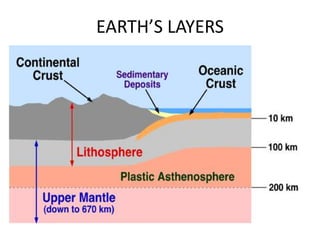
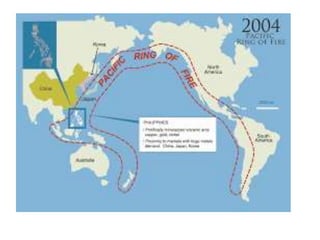
2) The structure of the Earth which is composed of layers including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and inner and outer cores.
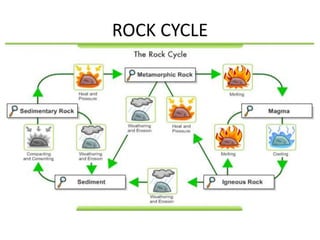
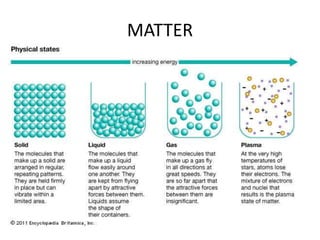
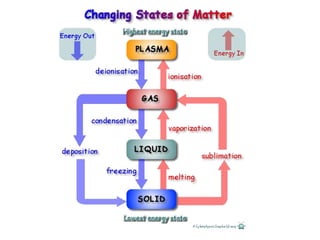
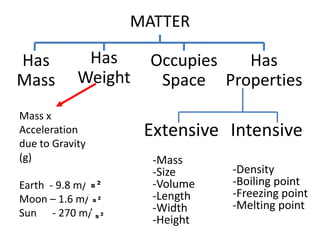
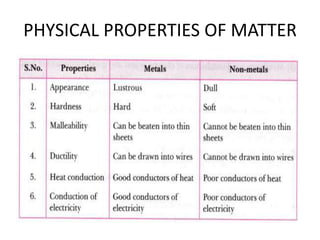
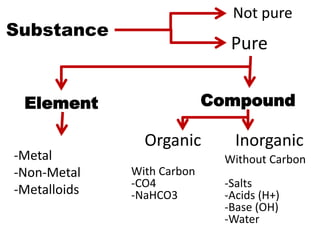
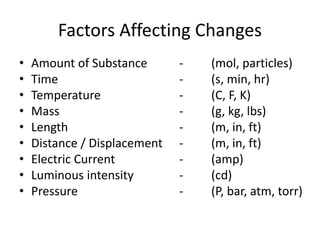
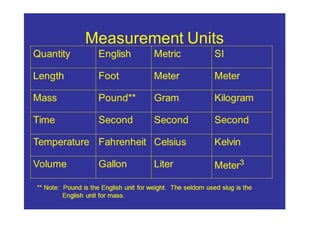
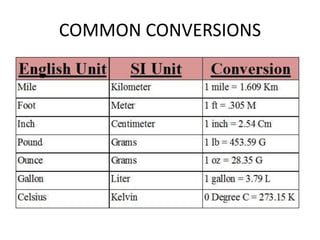
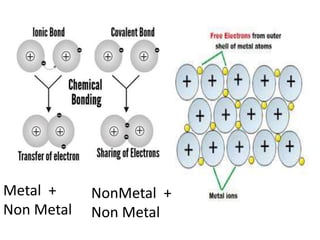
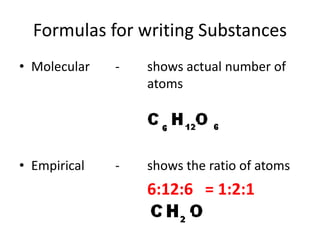
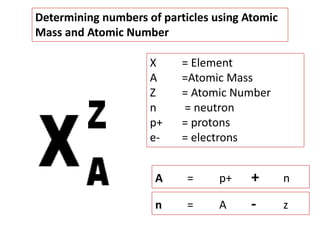
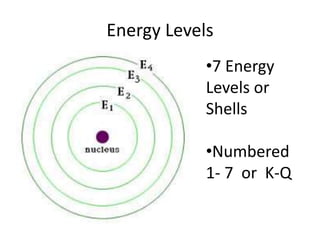
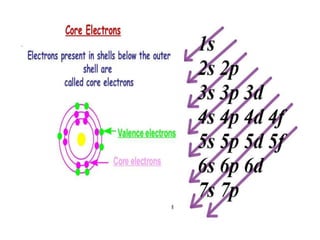
3) The composition of matter including its physical and chemical properties as well as changes in state that can occur.
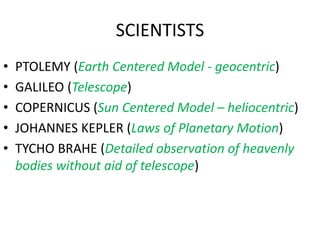
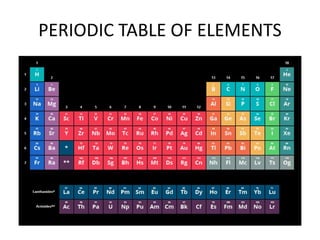
4) Important scientists such as Ptolemy, Copernicus, Galileo, Kepler, Tycho Brahe, Avogadro, Lavoisier, and others who contributed to our understanding of astronomy, chemistry and physics.