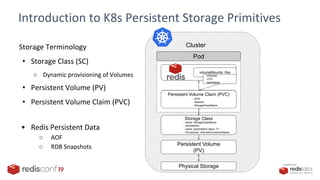
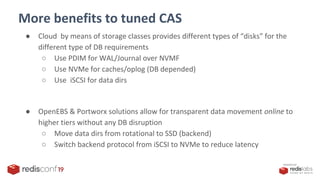
The document discusses container attached storage solutions for Redis within the context of Kubernetes, outlining challenges and benefits associated with storage management in cloud-native environments. It emphasizes the need for scaling, data portability, and seamless integration, highlighting how cloud native storage enhances stateful applications through observability and efficient backup strategies. Additionally, it compares traditional databases and storage, advocating for container attached storage that offers cost savings and operational simplicity.